Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by erosive arthritis and pathologically based on synovitis [1]. It is often accompanied by systemic damage, including subcutaneous tissue, blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, nervous system and blood system, resulting in complex and diverse extraarticular lesions. The clinical manifestations of RA often include joint morning stiffness, swelling, pain and so on, which can eventually develop into joint deformities and loss of the normal function of joints, affecting the quality of life of patients [1–3]. According to statistics [4–6], the average incidence of RA in the world is about 1%, and the prevalence rate of RA in China is 0.32–0.36%. The disease is one of the main causes of human labor loss and disability. If it is not diagnosed and treated in time, 70% of the patients will be disabled after 2 years, and the average life expectancy will be shortened by 10–15 years [7, 8]. Therefore, the treatment and nursing care of RA is the current focus of medical scientists.
Studies [9, 10] have shown that the incidence of RA is increasing, and the incidence of RA complicated with anemia is also increasing year by year. As one of the common manifestations of RA, the incidence of anemia in RA patients is high – it can be as high as 75.28% [11]. It will also have a certain adverse effect on the prognosis of RA patients. At present, the related factors of anemia in patients with RA are not clear. Therefore, this study analyzed the clinical data of elderly patients with RA complicated with anemia, aiming to evaluate the status quo of anemia in RA patients, to provide evidence for the clinical treatment and care of anemia in RA patients.
Material and methods
This study obtained the approval of the medical ethics committee of Lianyungang First People’s Hospital (approval number: KY-20221102001-01). All patients signed the informed consent and agreed to participate in this study voluntarily.
In this study, elderly patients with RA who were treated in our hospital in the period from June 1, 2021 to December 31, 2022 were included. The inclusion criteria of the patients were as follows: The RA diagnosis was in accordance with the diagnostic criteria of RA recommended by the American Rheumatic Society and the European Anti-Rheumatic Alliance (EULAR) [12] and confirmed by clinical laboratory examination and imaging examination; the age of RA patients was ≥ 60 years old; RA patients included were all in a stage of high disease activity with a Disease Activity Score (DAS) 28 > 5.1. the patients knew about and agreed to participate in this study. The exclusion criteria of this study were as follows: patients with tumors; patients with secondary anemia caused by primary hematological diseases and other diseases; patients with other autoimmune diseases; patients who did not want to participate in this study.
According to the index of hemoglobin (Hb), the patients were divided into the anemia group and no anemia group according to whether they were complicated with anemia. The definition of anemia was Hb < 120 g/l in male and < 110 g/l in female patients.
All patients received standard and regular RA treatment. We collected the following information about the patient’s hospitalization: gender, age, body mass index (BMI), RA course, whether the patient had hypertension, diabetes and hyperlipidemia. In addition, we also collected the following relevant test results of the patients: white blood cell count (WBC), C-reactive protein (CRP), platelet count (PLT), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), rheumatoid factor (RF), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), apolipoprotein A (ApoA), apolipoprotein B (ApoB), homocysteine (HCY), platelet/lymphocyte count (PLR), blood glucose (GLU), albumin (Alb), red blood cell count (RBC), lymphocyte count (LC), red blood cell width (RDW), mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH).
Statistical analysis
In this study, all the data were analyzed by SPSS23.0 software. The clinical data of the two groups were analyzed by univariate analysis, the measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and the independent sample t-test was used for comparison between the two groups. The counting data were presented as cases or percentage (%), and the comparisons between groups were conducted using the χ2 test. Pearson correlation analysis of the correlation of anemia and characteristics of elderly patients with RA was conducted. Logistic regression was performed to analyze the related influencing factors of anemia. In this study, the difference between groups was statistically significant when p < 0.05.
Results
A total of 285 RA patients were finally included, of whom 178 patients had been diagnosed with anemia, and the incidence of anemia in patients with high RA activity was 62.46%. As presented in Table I, there was a significant difference in the course of RA (p = 0.015). There were no significant differences in gender, age, BMI, hypertension, diabetes and hyperlipidemia (all p > 0.05).
Table I
Characteristics of elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis (n = 285)
The laboratory test results of elderly patients with RA are presented in Table II. There were significant differences in Hb, LDL-C, PLR and Alb between RA patients with anemia and without anemia (all p < 0.05). There were no significant differences in WBC, CRP, PLT, ESR, AST, ALT, RF, IgA, IgM, IgG, HDL-C, TG, TC, ApoA, ApoB, HCY, GLU, RBC, LC, RDW, MCV and MCH between RA patients with and without anemia (all p > 0.05).
Table II
Laboratory test results of elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis
[i] Hb – hemoglobin, WBC – white blood cell count, CRP – C-reactive protein, PLT – platelet count, ESR – erythrocyte sedimentation rate, AST – aspartate aminotransferase, ALT – alanine aminotransferase, RF – rheumatoid factor, ESR – erythrocyte sedimentation rate, HDL-C – high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C – low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, TG – triglyceride, TC – total cholesterol, ApoA – apolipoprotein A, ApoB – apolipoprotein B, HCY – homocysteine, PLR – platelet/lymphocyte count, GLU – blood glucose, Alb – albumin, RBC – red blood cell count, LC – lymphocyte count, RDW – red blood cell distribution width, MCV – mean corpuscular volume, MCH – mean corpuscular hemoglobin.
As shown in Table III, Pearson correlation analysis indicated that course of RA (r = 0.522), Hb (r = 0.797), LDL-C (r = 0.558), PLR (r = 0.615) and Alb (r = 0.604) were correlated with anemia in patients with high RA activity (all p < 0.05).
Table III
Pearson correlation analysis on the correlation of anemia and characteristics of elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis
[i] BMI – body mass index, Hb – hemoglobin, WBC – white blood cell count, CRP – C-reactive protein, PLT – platelet count, ESR – erythrocyte sedimentation rate, AST – aspartate aminotransferase, ALT – alanine aminotransferase, RF – rheumatoid factor, ESR – erythrocyte sedimentation rate, HDL-C – high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C – low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, TG – triglyceride, TC – total cholesterol, ApoA – apolipoprotein A, ApoB – apolipoprotein B, HCY – homocysteine, PLR – platelet/lymphocyte count, GLU – blood glucose, Alb – albumin, RBC – red blood cell count, LC – lymphocyte count, RDW – red blood cell distribution width, MCV – mean corpuscular volume, MCH – mean corpuscular hemoglobin.
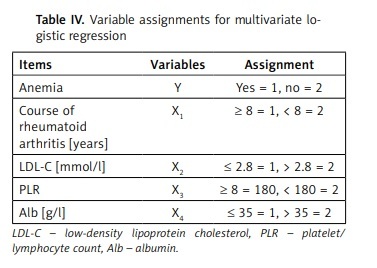
The variable assignments for multivariate logistic regression are shown in Table IV. As shown in Table V, the results of logistic regression analysis indicated that course of RA ≥ 8 years (OR = 2.584, 95% CI: 1.822–3.647), LDL-C ≤ 2.8 mmol/l (OR = 3.202, 95% CI: 2.804–3.431), PLR ≥ 8 (OR = 2.183, 95% CI: 1.744–2.457), and Alb ≤ 35 g/l (OR = 1.716, 95% CI: 1.401–2.006) were risk factors of anemia in elderly patients high RA activity (all p < 0.05).
Table IV
Variable assignments for multivariate logistic regression
| Items | Variables | Assignment |
|---|---|---|
| Anemia | Y | Yes = 1, no = 2 |
| Course of rheumatoid arthritis [years] | X1 | ≥ 8 = 1, < 8 = 2 |
| LDL-C [mmol/l] | X2 | ≤ 2.8 = 1, > 2.8 = 2 |
| PLR | X3 | ≥ 8 = 180, < 180 = 2 |
| Alb [g/l] | X4 | ≤ 35 = 1, > 35 = 2 |
Table V
Logistic regression analysis of the risk factors of anemia in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Discussions
RA is a systemic autoimmune disease with arthritis as the main clinical manifestation, which often involves bone destruction and progressive joint deformities, and the disability rate is very high [12]. It is also accompanied by comorbidities, such as blood system involvement, heart, lung and other organ function [13, 14]. Anemia is a common extraarticular manifestation of RAs, but it is often ignored by clinicians and nurses. The results of this study show that the incidence of anemia in RA patients is 62.46%, and course of RA ≥ 8 years, LDL-C ≤ 2.8 mmol/L, PLR ≥ 8, Alb ≤ 35 g/l are the risk factors of anemia in elderly patients with high RA activity. Medical workers should take early intervention and nursing measures according to these factors to improve the prognosis of patients with high RA activity.
It has been reported that the prevalence of anemia in RA is related to the prognosis of patients. For the parameters to be evaluated, including swelling, joint pain and activity level, there is a positive correlation between the improvement of symptoms and the relief of anemia [15, 16]. Previous studies [17, 18] have shown that the quality of life score of RA patients is significantly improved after anemia treatment, RA patients with anemia may have more severe joint disease, and if anemia is successfully treated, joint disease may also be improved. Therefore, it is very important to identify and deal with the risk factors of RA with anemia. In recent years, it has been found that anemia can be used as a tool for assessing disease progress in patients with RA, and it can also be used to predict the risk of rapid bone erosion in patients with RA [19, 20]. Therefore, the monitoring and management of anemia in patients with RA is of great significance for the prognosis of patients.
PLR was originally used as a biomarker of systemic inflammation to predict the prognosis of neoplastic diseases [21]. In recent years, PLR has been used as a prognostic indicator of cardiovascular disease. Higher PLR in this study is also a major risk factor for anemia in elderly patients with RA [22–24]. The level of lipid in blood is the result of the balance between synthesis and catabolism or absorption. Studies of elderly patients with RA with anemia [25, 26] have shown that the metabolic rate of lipid catabolism in the anemia group is higher than that in the non-anemia group, and LDL-C is an independent risk factor for progression of RA with anemia in the elderly. Therefore, medical workers should pay attention to evaluate the overall impact of elevated blood lipid levels on cardiovascular risk in elderly patients with RA complicated with anemia due to the control of inflammation. It is suggested that blood lipids and inflammatory indexes in elderly RA patients should be monitored regularly, and corrective measures should be taken in time when the baseline blood lipid levels decrease significantly, so as to avoid further deterioration of the RA and anemia [27, 28].
As a possible abnormal index of anemia in elderly patients with RA, PLR and hs-CRP have no significant correlation with the increase of immunoglobulin, while hs-CRP, as an important indicator of inflammatory response in the early stage of RA, and LDL-C and TC as important monitoring indexes of abnormal lipid metabolism, can better reflect the possibility of atherosclerosis [29, 30]. Therefore, anemia in elderly patients with RA is closely related to lipid metabolism and inflammatory reaction [31–33]. In clinical treatment one should pay close attention to lipid metabolism and inflammation in RA patients.
In this study, it was found that the serum albumin of RA patients with anemia is lower than that of non-anemic patients. Previous studies [34, 35] have found that RA patients with hypoproteinemia have severe inflammatory reaction, high disease activity, poor nutritional status, and are often complicated with varying degrees of anemia. The specific mechanism of the decrease of serum albumin in RA patients is not clear. It may be related to the disease activity and nutritional deficiency of RA patients, which mainly includes two aspects: firstly the protein intake of patients is insufficient. RA itself is a chronic inflammatory wasting disease; coupled with long-term use of corticosteroids and other drugs, it readily causes gastrointestinal reactions, resulting in protein intake deficiency [36]. The second is the possibility of decline of liver protein in patients with RA. Patients with active RA can produce a variety of inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α, IL-6 and so on [37–39]. These cytokines cause direct or indirect damage to hepatocytes, inhibit the expression of right protein mRNA protein, and cause albumin formation disorder. The higher the activity of RA disease, the more inflammatory factors are produced, the more serious is damage to hepatocytes, and the less albumin is produced. Some studies [40, 41] have found that serum albumin decreases progressively with the increase of RA disease activity. Therefore, the monitoring of albumin in patients with RA is of great significance for the treatment and care of RA patients. It must be noted that medication has a double effect on anemia. On one hand, medication decreased inflammation and diminished the pro-anemic influence of proinflammatory cytokines. On the other hand, medication, especially with classical synthetic drugs, may by itself be myelotoxic. It is possible that medication in elderly individuals is different due to higher sensitivity to adverse reactions. It is also well known that biological medication (without methotrexate) is less myelotoxic than therapy with synthetic drugs. Therefore, the effects of medication on anemia in RA patients need further investigations.
There are some shortcomings in this study that are worth considering. First of all, this study is a single-center study, the sample size of RA patients included is small, and there may be insufficient effects to detect the potential differences between groups. Secondly, there may be some other factors affecting anemia in RA patients that cannot be included in the study analysis. Anemia is caused mostly by inflammation. IL-6, a major proinflammatory cytokine, is a significant factor responsible for anemia. An increase in hepcidin, due to higher circulating levels of IL-6, leads to iron sequestration, decreased iron absorption, and lack of iron availability for erythropoiesis. But IL-6 is not routinely monitored in our hospital, and we do not have enough data on IL-6. Thirdly, evaluation of erythrocyte sedimentation rate as an inflammatory index should be done with caution because anemia by itself increased sedimentation of red cells, some patients lack data on the inflammatory index and we cannot include it in the analysis. Therefore, the results of this study should be treated with caution, and large sample and multicenter studies are still needed to verify the findings in the future.
In conclusion, in this study it was found that the incidence of anemia in RA patients is high, and for RA patients with course of RA ≥ 8 years LDL-C ≤ 2.8 mmol/l, PLR ≥ 8, and Alb ≤ 35 g/l, they may have higher risk of anemia. Understanding of the role of anemia in RA, condition assessment and prognosis judgment are of great significance for clinicians to guide clinical diagnosis and treatment choice for RA. Clinical medical workers should strengthen the detection and tracking of LDL-C, PLR and Alb levels in patients with RA in order to guide the treatment of clinical RA and improve the prognosis of patients with RA.