Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ONCOLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
Downregulation of CENPK suppresses lung adenocarcinoma by regulating EMT
1
Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China
Submission date: 2020-08-05
Final revision date: 2021-04-23
Acceptance date: 2021-05-28
Online publication date: 2021-06-08
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Centromere protein K (CENPK) plays a key role in regulating the assembly and function of centromeres, which in turn can affect the occurrence and development of various tumors. However, little is known about the biological function of CENPK in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
Material and methods:
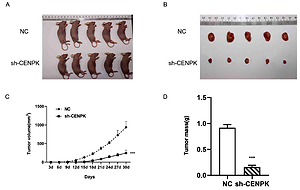
We evaluated the relationship between CENPK expression and the clinicopathological characteristics of LUAD patients via a bioinformatics method based on data taken from the TCGA database. Then, the role of CENPK in LUAD was investigated in vitro by using the human LUAD cell line A549. Cell Counting Kit-8 and colony formation assays were used detect the cell proliferation ability. Wound healing and transwell assays were used to detect the cell migration and invasion ability. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers (E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Snail and vimentin) were measured by western blotting. In addition, a xenograft experiment was used to explore the function of CENPK in vivo.
Results:
CENPK is highly expressed in LUAD tissues and cell lines. Moreover, high expression of CENPK in LUAD is significantly associated with stage, lymph node involvement and poor survival. CENPK knockdown significantly decreases the proliferation, migration and invasion ability of A549 cells by EMT both in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions:
CENPK is highly expressed in LUAD and leads to a poor prognosis. CENPK knockdown can suppress the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cells via EMT, which may be a valid target for treatment.
Centromere protein K (CENPK) plays a key role in regulating the assembly and function of centromeres, which in turn can affect the occurrence and development of various tumors. However, little is known about the biological function of CENPK in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
Material and methods:
We evaluated the relationship between CENPK expression and the clinicopathological characteristics of LUAD patients via a bioinformatics method based on data taken from the TCGA database. Then, the role of CENPK in LUAD was investigated in vitro by using the human LUAD cell line A549. Cell Counting Kit-8 and colony formation assays were used detect the cell proliferation ability. Wound healing and transwell assays were used to detect the cell migration and invasion ability. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers (E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Snail and vimentin) were measured by western blotting. In addition, a xenograft experiment was used to explore the function of CENPK in vivo.
Results:
CENPK is highly expressed in LUAD tissues and cell lines. Moreover, high expression of CENPK in LUAD is significantly associated with stage, lymph node involvement and poor survival. CENPK knockdown significantly decreases the proliferation, migration and invasion ability of A549 cells by EMT both in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions:
CENPK is highly expressed in LUAD and leads to a poor prognosis. CENPK knockdown can suppress the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cells via EMT, which may be a valid target for treatment.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.