Introduction
Subacute thyroiditis (SAT), or de Quervain’s thyroiditis, is typically a self-limiting, inflammatory disease, although episodes can last weeks to months in some patients. It is characterized by neck pain that often radiates to the jaw or ear and associated dysphagia, with an enlarged and tender thyroid gland. The neck pain can be bilateral or unilateral, can change location by traveling between lobes, and can be exacerbated by coughing or chin/head movements. As a result, patients might consult for a presumed upper respiratory tract infection and/or receive treatment. SAT also can be confused with ear disorders or even tooth problems, making diagnosis particularly challenging.
Subacute thyroiditis is diagnosed via clinical assessment based on physical and laboratory examinations [1–3]. Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein level (CRP) are typical for SAT. Thyroid function tests can change according to the phase of the disease: the first, acute inflammatory phase can be accompanied by thyrotoxicosis due to destruction of thyroid tissue; a second, typically transient form of hypothyroidism can then occur, followed by euthyroidism [1, 4].
Although most patients recover with a euthyroid state, permanent hypothyroidism can develop in anywhere from 0.5% up to 45% of patients [4–8]. The patient-, disease-, and treatment-related factors associated with permanent hypothyroidism after SAT are not clear. We examined the clinical characteristics in patients with SAT and explored the relationships between such factors and the incidence of permanent post-SAT hypothyroidism at our centre.
Material and methods
We retrospectively analysed medical records from patients diagnosed with SAT in our centre in Trabzon Medical Park Hospital, Turkey. Specifically, we searched the medical records for a listing of the ICD-10 diagnosis code for SAT (E06.1). In all, 283 patients had an ICD-10 diagnosis code of E06.1 recorded between September 2014 and January 2020. Of these, 119 met the inclusion/exclusion criteria and were included in the study. We excluded patients with known previous thyroid disease and those who lacked follow-up data at least 6 months after the SAT episode had resolved. Data were extracted by reviewing each patient’s medical record and follow-up information.
The diagnosis of SAT was made by clinical assessment (neck pain that radiated to the jaw or ear with associated dysphagia, or that changed location between lobes, and enlarged and tender thyroid gland) accompanying laboratory values (increased ESR and CRP, thyrotoxicosis, if present), with ultrasonography (diffusely or focally hypoechogenic areas in normal or enlarged gland with low flow) performed by the same physician (İ.A.) with a linear 12-MHz probe (SonoScape, China), and scintigraphy findings (when available).
We extracted baseline demographic data; characteristics of neck pain and other symptoms (see below); laboratory results including ESR (Vision-A), CRP (Roche Diagnostics, Cobas® 6000, c501, Analyzer Series), complete blood count (CBC) (Mindray BC 6000), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free triiodothyronine (T3), free thyroxine (T4), and antithyroid antibodies (Roche Diagnostics, Cobas® 6000 Analyzer Series); ultrasonography findings; medications received; the need for and duration of steroid therapy; the presence of hypothyroidism; and the incidence and frequency of SAT recurrences.
Flu-like symptoms were defined as joint and/or muscle pain, fatigue, headache, and sore throat. Creeping neck pain was pain that travelled between lobes of the thyroid. Radiating neck pain was pain that travelled to the ear, chin, jaw, or elsewhere in the neck. Symptoms of thyrotoxicosis consisted of at least one of the following: palpitations, weight loss, sweating, tremor, and/or shortness of breath. Permanent hypothyroidism was defined as still requiring thyroid hormone replacement 6 months after SAT completely resolved.
Patients were considered to require steroid treatment if their symptoms did not regress with the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) alone. The starting steroid treatment was methylprednisolone 32 mg every morning by mouth. The dosage was tapered weekly as 24 mg → 16 mg → 12 mg → 8 mg → 4 mg and then stopped. If the patient had recurrence of symptoms, the steroid dosage was increased back to the level the patient had been taking immediately before the symptoms returned. Recurrence of SAT was defined as the reappearance of symptoms after stopping the medical treatment (NSAIDs or steroid).
Statistical analysis
The data obtained in the study were analysed in IBM Statistical Package for the Social Science (IBM SPSS; Armonk, NY, USA) for Windows v24.0 software. Qualitative data were assessed by χ2 test. Normality of distribution was determined using Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Student’s t-tests were used for the analysis of normally distributed data (age values). We compared Mann-Whitney U test for differences between patients who did and did not develop permanent hypothyroidism for continuous variables data that were not normally distributed. We performed multivariate analysis by using logistic enter model for parameters of which p < 0.20: SAT recurrence, thyrotoxicosis, weeks of steroid use, and temporary hypothyroidism.Qualitative data were presented by number and percentage (%), and quantitative data by arithmetic mean ± standard deviation and/or median (min.–max. values). Statistically, p < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
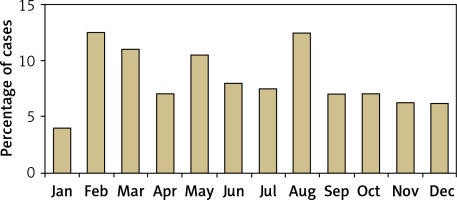
The mean follow-up period was 34.4 ±14.6 weeks (range: 24–104 weeks) after complete resolution of SAT. The patients had a mean age of 42 years (range: 24–78 years), and SAT occurred more than 3 times more often in women than in men (Table I). Although SAT occurred more frequently during the spring and summer, its incidence did not differ significantly by month or season (p = 0.329 and 0.534, respectively; Figure 1).
Table I
Characteristics of patients, overall and by development of permanent hypothyroidism after subacute thyroiditis
| Parameters | Overall (n = 119) | Permanent hypothyroidism | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (n = 10) (%) | No (n = 109) (%) | |||
| Age [years], mean (SD) | 42.3 (10.9) | 40 (11) | 42.8 (10.9) | 0.524 |
| Sex, n (%): | 93 (78.2) | 8 (80) | 84 (77.0) | 1 |
| Female | 8 (8.8) | 83 (91.2) | ||
| Male | 2 (7.1) | 26 (92.9) | ||
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate [mm/hour], median (min.–max.) | 43 (30–78) | 52 (2–128) | 0.731 | |
| C-reactive protein [mg/l], median (min.–max.) | 5.5 (1.2–463) | 4.9 (0.5–998) | 0.824 | |
| Haemoglobin (min.–max.) | 11.5 (10.9–13.0) | 12.5 (9.3–15.0) | 0.276 | |
| Haematocrit (min.–max.) | 35.9 (32.8–39.9) | 38.8 (29.4–329.0) | 0.179 | |
| Mean platelet volume (min.–max.) | 9.8 (8.4–10.7) | 9.7 (7.1–106.0) | 0.788 | |
| Platelet (min.–max.) | 366.5 (310.0–386.0) | 327.0 (207.0–722.0) | 0.681 | |
| Preceding viral/flu-like symptoms, n (%): | 88 (69.7) | 1 | ||
| Yes | 3 (8.6) | 32 (91.4) | ||
| No | 7 (8.3) | 77 (91.7) | ||
| Neck pain characteristics, n (%): | ||||
| Bilateral | 79 (66.4) | |||
| Right | 23 (19.3) | |||
| Left | 14 (11.8) | |||
| Isthmus | 3 (2.5) | |||
| Creeping, n (%): | 66 (55.5) | 0.750 | ||
| Yes | 5 (7.6) | 61 (92.4) | ||
| No | 5 (9.4) | 48 (90.6) | ||
| Radiating, n (%): | 81 (68) | 0.725 | ||
| Yes | 6 (7.5) | 74 (92.5) | ||
| No | 4 (10.5) | 34 (89.5) | ||
| Fever, n (%): | 55 (46.2) | 0.337 | ||
| Yes | 3 (5.5) | 52 (94.5) | ||
| No | 7 (10.9) | 57 (89.1) | ||
| Symptoms of thyrotoxicosis, n (%): | 0.185 | |||
| Yes | 2 (3.9) | 49 (96.1) | ||
| No | 8 (11.8) | 60 (88.2) | ||
| Thyrotoxicosis, n (%): | 76 (63.9) | 0.004 | ||
| Yes | 2 (2.6) | 74 (97.4) | ||
| No | 8 (18.6) | 35 (81.4) | ||
| Antithyroid antibodies, n (%)*: | 1.0 | |||
| Positive | 9 (16.0) | 0 (0) | 9 (100) | |
| Negative | 47 (83.9) | 4 (8.5) | 43 (91.5) | |
| Ultrasound involvement, n (%): | ||||
| Bilateral | 74 (62.2) | |||
| Unilateral | 40 (33.6) | |||
| None – normal | 5 (4.2) | |||
| Days from symptom onset to SAT diagnosis, median (min.–max.) | 7 (0–60) | 20 (0–90) | 0.294 | |
| Temporary hypothyroidism, n (%) | 2 (20) | 5 (4.6) | 0.107 | |
| Yes | 2 (28.6) | 5 (71.4) | ||
| No | 8 (7.1) | 104 (92.9) | ||
| Medicine, n (%): | ||||
| Only NSAI | 31 (26) | |||
| NSAI + antibiotics | 15 (13) | |||
| Steroid | 55 (46) | |||
| Antibiotics + steroid | 18 (15) | |||
| Steroid use, n (%): | 71 (59.7) | 1 | ||
| Yes | 8 (9.1) | 80 (90.9) | ||
| No | 2 (6.7) | 28 (93.3) | ||
| Days from diagnosis to start of steroids | 28.7 (27.6) | 26.7 (19.4) | 0.766 | |
| Weeks of steroid use | 17.7 (16.4) | 8.9 (5.9) | 0.021 | |
| SAT recurrence, n (%): | 43 (36) | 0.035 | ||
| Yes | 7 (16.3) | 36 (83.7) | ||
| No | 3 (4) | 72 (96) | ||
More than two-thirds of the patients reported having viral/flu-like symptoms before neck pain started. Neck pain was predominantly bilateral (66%), with the right side being slightly more common than the left as the site of unilateral pain.
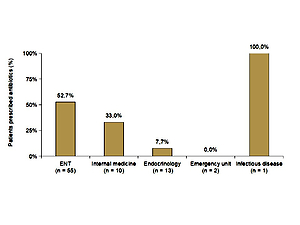
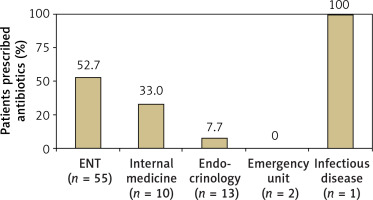
Slightly more than half of the patients (n = 68; 57%) had initially visited a specialty other than endocrinology before SAT was diagnosed: 55 presented to otolaryngology (ENT), 10 to internal medicine, 2 to emergency units, and 1 to infectious disease. Half of the patients in this subgroup were prescribed antibiotics for a misdiagnosed upper respiratory tract infection or high ESR/CRP (Figure 2). Another 7 (10.3%) patients were prescribed antithyroid medicine for a misdiagnosis of hyperthyroidism.
The mean time from symptom onset to correct diagnosis was 22.9 ±1.9 days (range: 0–90 days). The presence of thyrotoxicosis or pain was not associated with the time to diagnosis (p = 0.749 and p = 0.137, respectively). Correct diagnosis was significantly delayed in patients who had been prescribed antibiotics (27 ±19 days vs. 21 ±21.7 days, p = 0.028) and who had fever (25 ±18 vs. 21 ±23.4 days, p = 0.042).
Overall, 61% of our patients required steroid treatment (Table I). Steroids were used for a mean of 6 weeks, and more than 6 weeks for patients with persistent or recurrent symptoms, as much as they needed.
Subacute thyroiditis recurred in 43 patients (36%): 28 (23.5%) had 1 recurrence, 10 (8.4%) had 2 recurrences, and 5 (4.2%) had 1 attack.
In all, 10 (8.4%) patients developed permanent hypothyroidism after SAT. Although the incidence of steroid use was similar overall, patients who developed permanent hypothyroidism had received them for twice as long as patients who did not (mean 17.7 weeks vs. 8.9 weeks; p = 0.021). Permanent hypothyroidism was also significantly more frequent among patients who did not have laboratory-based thyrotoxicosis during SAT (p = 0.004) and who had recurrent SAT (p = 0.035) (Table II).
Table II
Logistic regression enter model* for the development of hypothyroidism
Development of permanent hypothyroidism was not significantly associated with age, sex, flu-like symptoms, neck pain characteristics, presence of fever, symptoms of thyrotoxicosis, baseline ESR or CRP, time to SAT diagnosis, location of ultrasonic involvement, or development of temporary hypothyroidism.
Unfortunately, we had data regarding antithyroid antibodies for only 56 patients. Of the 9 patients who had positive results, none developed permanent hypothyroidism. Of the 47 antibody-negative patients, 4 (8.5%) developed permanent hypothyroidism. There was no significant difference between antibody-positive and -negative groups in the development of permanent hypothyroidism.
Discussion
Although SAT is typically a self-limiting disease, patients may develop permanent hypothyroidism and may require thyroid hormone replacement [4–8]. In our study, 8.4% of our patients developed permanent hypothyroidism after SAT. Risk factors associated with development included longer duration of steroid therapy (but not overall use), recurrences of SAT, and lack of thyrotoxicosis during SAT. Development of temporary hypothyroidism during SAT was not associated with subsequent permanent impairment of thyroid function, nor were the presence and severity of typical SAT symptoms or the time to SAT diagnosis.
In our study, the mean age and sex distribution of the patients were similar to those of previous studies [4, 8–10]. And although it was not statistically significant, SAT occurred more frequently during the spring and summer months in our study, consistent with the data from previous studies [9–12].
Martino et al., who initially drew attention to the seasonal pattern to SAT, concluded that the distribution of SAT is superimposable to that of certain enteroviruses (echovirus, Coxsackie A and B viruses), and thus these viral infections might be partly responsible for some SAT cases [11]. More than two-thirds of our patients described a viral/flu-like illness before their neck pain began, which may also be a clue toward a viral infection-SAT relationship. Upper respiratory tract infection or flu-like symptoms were described in 21% of one cohort [4] and in 30.7% of another [7]. Most recently, infection with SARS-CoV-2 has been implicated in the development of SAT [13].
Diagnosis of SAT may be challenging, and patients can lose substantial time before they receive the correct diagnosis. Some case reports have described diagnoses of fever of unknown origin, temporal arteritis, or even dental problems before thorough investigations revealed the presence of SAT [14–16]. In our study, the mean time from symptom onset to correct diagnosis was nearly 23 days, and in some of our cases it took up to 90 days.
Few studies have focused on delayed diagnosis of SAT. Stasiak et al. found that the pre-diagnosis period was prolonged by up to 70 days [17], and Bostan et al. [18] found a mean time to diagnosis of 23 days (range: 6–70 days), which was similar to our findings. In a study by Görges et al. the time to diagnosis ranged from 2 days to 1 year [7]. In Bostan’s study, 73.6% of patients were admitted to other specialties before receiving the correct diagnosis [18], a larger proportion than the 57.1% of our patients who saw other specialists first, but their distribution of specialties was similar to ours (internal medicine, otolaryngology, emergency departments, and infectious disease) [18]. The percentages of radiating pain and fever were also similar between Bostan’s study and ours (71% vs. 68% for radiating pain, respectively, and 46% in both studies for fever). Although Bostan et al. concluded that correct diagnosis occurred sooner in patients with thyrotoxicosis, symptoms of thyrotoxicosis, fever, or neck pain, we did not find a difference for these variables.
Thirty-four (28.6%) of our patients, 58.7% of Bostan’s patients [18], and 46.7% of Stasiak’s patients [17] had been prescribed antibiotics erroneously. In our study, the time to a correct diagnosis was significantly longer in such patients compared with patients not prescribed antibiotics. Similar findings were noted in the Bostan study [18]. However, Stasiak et al. did not find any difference in time to diagnosis by antibiotic use [17]. Giving antibiotics to patients who had fever or elevated inflammatory markers might have delayed diagnosis via a false sense of relief for both the doctors and the patients. After seeing their symptoms persist, however, patients would have sought other physicians. This misuse of antibiotics not only delayed diagnosis but also resulted in unnecessary healthcare expenses, risk to the patients, and wasted time for physicians and patients. It is also important to re-evoke the importance of physical examination again to avoid unnecessary work-up or interventions.
Nearly all of our patients (95.8%) showed ultrasonic involvement (hypoechoic areas), consistent with previous studies [19–25]. Thyroid involvement was bilateral in 62% and unilateral in 34% of our patients. Schenke et al. found similar proportions (64% and 22%, respectively) [22], as did Sencar et al. (62% and 38%, respectively) [23]. Although Nishihara et al. found that bilateral involvement was related to the development of permanent hypothyroidism [24], we did not, similarly to Schenke et al. [22], Omori et al. [20], Bennedbaek et al. [25], and Sencar et al. [23]. This latter group attributed their disparate results to the relatively short follow-up period used in the Nishihara study [24].
Some patients with SAT recover without the need for treatment; however, for many of them NSAIDs or steroids are indicated for relief of pain and other symptoms [26]. There is no consensus regarding therapies for SAT. The American Thyroid Association guidelines call for the use of glucocorticoid therapy (prednisone 40 mg/day for 1–2 weeks, then tapered over 2–4 weeks or longer, according to the symptoms) when NSAIDs are not effective for the relief of symptoms or when patients have moderate to severe symptoms at onset [26]. This is a strong recommendation, but it has low-quality evidence supporting it. Because a clear definition of treatment (for the beginning or maintenance phases) according to objective criteria for symptoms is lacking, treatment decisions are usually made based on clinical assessments. The course recommended for steroid treatment is about 6–8 weeks, but some patients may need steroid therapy beyond 8 weeks. Most of our patients required steroid treatment, perhaps because of the delay in obtaining the correct diagnosis or the fact that our facility is a referral centre.
The effect of steroid therapy on the course of SAT is controversial. In one study, steroid therapy shortened the recovery time relative to patients given only NSAIDs [8]. In the same study, however, the prevalence of permanent hypothyroidism was 10%, and the use of steroids had no effect on its development [8]. A more recent study had similar findings of a lack of steroid treatment effect on permanent hypothyroidism [27]. Conversely, in the studies by Fatourechi et al. [4] and Görges et al. [7], permanent hypothyroidism was more common among patients who received steroids, and significantly so when the total steroid dose exceeded 4 g [7]. We did not calculate the total steroid dosages for our patients, but those who had one or more SAT recurrences – who would have required steroids for longer overall durations – were more likely to develop permanent hypothyroidism than patients who had only one SAT episode. The studies finding a link between steroid usage and permanent hypothyroidism speculated that patients who received steroids had more severe symptoms, which reflected the presence of more severe inflammation of the thyroid gland, which in turn caused the hypothyroidism [4, 7]. However, one recent study found that steroid treatment offered an apparent protective effect against the development of permanent hypothyroidism [28]. In this retrospective study, the decision to treat patients with NSAIDs versus steroids was made according to the attending specialists’ individual preferences, and the time from symptom onset to diagnosis was unknown. Thus, it was not possible to evaluate the severity of patients’ symptoms relative to the severity of the thyroiditis [28]. A head-to-head, prospective, randomised trial comparing the effect of the steroid treatment to NSAIDs is needed to reveal the impact of steroid therapy on the development of hypothyroidism after SAT.
We have demonstrated that the presence of thyrotoxicosis may protect patients from developing hypothyroidism, and the absence of thyrotoxicosis increases the risk for permanent hypothyroidism. To our knowledge a relationship between thyrotoxicosis and development of hypothyroidism has not been previously described in literature. We may speculate on some hypotheses: to have thyrotoxicosis, one needs sufficient stored thyroid hormones, which means healthy and well functioning follicular thyroid cells. If the patient does not have thyrotoxicosis due to the destruction during SAT, we may explain this by the presence of an ongoing possible autoimmune course caused by already injured follicular cells. Although we did not find a statistical significance in terms of making a diagnosis earlier for thyrotoxic patients, as we mentioned before, another possible reason may be that patients with thyrotoxicosis may have had symptoms arising from thyrotoxicosis causing them to admit earlier and receive treatment earlier. All these hypotheses need confirmation by randomized, prospective, controlled trials. We should consider the long time to diagnosis in patients; some of the patients might have already had thyrotoxic phase (acute destruction phase) before a diagnosis of SAT.
Our study has limitations. First, this was a retrospective study; no causality can be inferred from our findings. In addition, given that our centre is a referral hospital, our findings do not capture the entire spectrum of patients who might develop permanent hypothyroidism after SAT, particularly given the small number of our patients so affected. There are likely to be other factors – such as comorbid conditions or environmental aspects – that contribute to the development of this complication. Given the low number of cases, our study population is relatively a small group, and so prospective studies including larger study groups are needed.
In conclusion, the patients in our study who received steroids for SAT for longer periods, those who had recurrent SAT, and those who did not have thyrotoxicosis during SAT were more likely to develop permanent hypothyroidism afterward. Such patients should be closely monitored for signs of developing hypothyroidism. Prospective studies should examine this question in greater detail.