Introduction
Lung cancer is the most common cancer in men and one of the most common cancers in women. The lung cancer signs are dysphagia, shortness of breath, cough, coughing up blood, weigh loss, chest pain, shoulder pain, wheezing, fatigue, hoarseness, and weakness. The lung cancer metastasis symptoms are blurred vision, seizures, headaches, and weakness [1–3]. For diagnosis of lung cancer, positron emission tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, low-dose helical computed tomography scan, computed tomography, chest X-ray, molecular testing, blood tests, thoracentesis, needle biopsy, bronchoscopy, sputum cytology, and physical and history examination are used [4]. For the treatment of lung cancer, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy are used [4, 5]. The main anti-human lung cancer chemotherapeutic supplements/drugs are alectinib, ceritinib, crizotinib, and brigatinib [5]. Due to severe side effects of the chemotherapeutic drugs and supplements, the formulation of the chemotherapeutic medications from Ag nanoparticles are the research priority of pharmacology, oncology, and organic chemistry researchers [6–10].
Nanomaterials, which are the subject of our study, have unique competencies different from their macro-scale counterparts due to their low volume/surface ratio and many advanced and new physiochemical properties such as color, solubility, strength, prevalence, toxicity, magnetic, optical, thermodynamics [11–14]. In recent years, biological methods that are non-toxic, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly have become the focus of interest compared to physicochemical nanoparticle synthesis methods [13, 15–21]. Various pathways have been developed for the biogenic or biological formulation of nanomaterials from the salts of different metal ions [14, 19, 20, 22, 23]. The basic principle in the biogenesis of nanoparticles is the reduction of metal ions of several biomolecules found in organisms. In addition to reducing the environmental impact of biological synthesis, it enables the production of large quantities of nanoparticles, which are well defined in size and morphology, independent of contamination. Microorganisms, marine algae, plant extracts, plant tissue, fruits, and all plants are administered to formulate nanomaterials [13, 14, 19–21, 24–29]. The reduction of metal ions using plant extracts has been a known method since the 1900s. Due to the poor understanding of the mechanisms of the reducing agents, there has been increased interest in the past 30 years [14]. Recently, scientists have revealed that medicinal plants’ green-synthesized metallic nanoparticles have excellent anti-cancer properties. Metallic nanoparticles have achieved notable consideration in the field of medicine. Some studies conducted today have shown that some nanoparticles have therapeutic properties and provide an excellent alternative to physicochemically different metal-supported nanoparticles, antibacterial, and especially anticancer drugs. Medicinal plants green-synthesized silver nanoparticles as a special type of well-known metallic nanoparticles have recently been used for the cure of several types of tumors and cancers [13, 19, 20, 21, 26–36]. In this regard, in the study of Ahmeda et al. Melissa officinalis green-formulated Ag nanoparticles were used as a chemotherapeutic drug to treat leukemia [37]. A study reported the anti-acute myeloid leukemia abilities of Ag nanomaterials in the cellular and molecular conditions. Ag nanoparticles significantly killed all malignant leukemia cells (32D-FLT3-ITD, Murine C1498, and Human HL-60/vcr) in nano concentrations [26].
There is no study about the remedial capacities of Ag nanoparticles containing natural compounds in the treatment of human lung cancer. However, there are many studies about the anti-human lung cancer properties of medicinal plants including Hibiscus syriacus, Memecylon umbellatum, Mirabilis multiflora, Oscillatoria acutissima, Chelidonium majus, Nigella sativa, Morinda citrifolia, Bruguiera sexangula, Camellia sinensis, Hypsizygus marmoreus, Lentinus edodes, and Viola odorata [38].
C. kwangsiensis folium, as one of the well-known plants in all of the world, is from the Plantae kingdom, Zingiberaceae family, Zingiberoideae subfamily, Zingibereae tribe, and Curcuma genus [39]. There are five well-known species in this genus. Species in the Curcuma genus including Curcuma kwangsiensis, Curcuma phaeocaulis Val., Curcuma sichuanensis, C. kwangsiensis folium, Curcuma wenyujin, and Curcuma longa L. All of these species are important due to significant therapeutic properties; of course, the remedial roles of C. kwangsiensis folium are unique. C. kwangsiensis folium is cultivated in Iran, Bangladesh, Taiwan, Nepal, India, and especially China [39, 40]. Recent studies have indicated that C. kwangsiensis folium has notable anti-parasitic, antifungal, antiviral, antibacterial, larvicidal, antioxidant, hypoglycemic, anti-diabetic, nephroprotective, hepatoprotective, immunomodulatory, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activities [40]. This species is shown to have steroids, saponins, tannin, terpenoids, glycosides, proteins, carbohydrates, alkaloids, phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and essential oils as the major phytochemical groups [39]. The antioxidant compounds of the Curcumae genus are oxygenated sesquiterpenes, oxygenated monoterpenes, limonene, sesquiterpene hydrocarbons, trans-caryophyllene, α-zingiberene, p-cymene, α-pinene, monoterpene hydrocarbon, β-pinene, α-terpinolene, trans-β-elemenone, α-terpineol, β-sesquiphellandrene, and camphor. Certainly the above phytochemicals have a unique role in the therapeutic effects of this plant. In Chinese traditional medicine, C. kwangsiensis folium is administered to treat cancers of various types such as ovarian and uterine cancers [39, 40].
Accordingly, the present experiment was conducted to evaluate the possible anti-human lung cancer activity of synthesized Ag nanoparticles using C. kwangsiensis folium leaf aqueous extract against common cell lines of human lung cancer.
Material and methods
Material
Bovine serum, antimycotic antibiotic solution, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), decamplmaneh fetal, 4-(dimethylamino) benzaldehyde, hydrolysate, Ehrlich solution, borax-sulfuric acid mixture, and DMED were all obtained from the US company Sigma-Aldrich.
Synthesis of Curcumae kwangsiensis folium green-synthesized Ag nanoparticles
To obtain the aqueous extract of the plant, 250 g of the dried C. kwangsiensis folium leaves were added to a container containing 2000 ml of boiled water, and the container lid was tightly closed for 4 h. Then, the content of the container was filtered, and the remaining liquid was placed on a bain-marie to evaporate. Finally, a tar-like material was obtained, which was powdered by a freeze dryer.
The extract of the C. kwangsiensis folium leaves was prepared for the green synthesis method and extracted with distilled water in the microwave. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles was started by combination of 200 ml of AgNO3 × H2O at concentrations of 10–3 M and 400 ml of C. kwangsiensis folium leaf aqueous isolate (20 μg/ml) in a cylindrical flask.
The reaction mixture was kept under magnetic stirring for 12 h at room temperature. At the end of the reaction time, the black colored colloidal solution of Ag was formed. The solution was centrifuged at 10 000 rpm for 15 min. The precipitate was sprayed with water and then resuspended [27].
Chemical characterization of Curcumae kwangsiensis folium green-synthesized Ag nanoparticles
Various analytical techniques were used to characterize the Ag nanoparticles: The biomolecules related to the Ag nanoparticle reduction including secondary metabolites were detected by the FT-IR (Shimadzu IR affinity.1). In the UV-Vis spectroscopy analysis, characteristic absorption bands of Ag metal were examined before and after the nanoparticle synthesis process. TEM and FE-SEM analysis of the Ag nanoparticles was performed with JEOL 200 kV by placing them on a carbon-coated copper grid.
Determination of the antioxidant activities of Curcumae kwangsiensis folium green-mediated Ag nanoparticles
The DPPH method is a common method for the assessment of the antioxidant activity of plant species and metallic nanoparticles. It is based on trapping the free radicals of the material, called DPPH, using antioxidant agents which reduce the absorption rate at 520 nm wavelength. When the DPPH solution is mixed with a material that can donate hydrogen atoms, radical formation occurs, which is followed by color reduction. This reaction eliminates the purple color, whose index is the formation of an absorption band at 520 nm [41].
To determine the radical scavenging activity of the silver salt, C. kwangsiensis folium leaf extract, and Ag nanoparticles, 1 ml of 50 μm DPPH was combined with 1 ml of variable concentrations (0–1000 μg/ml) of silver salt, C. kwangsiensis folium leaf extract, and Ag nanoparticles. Then, they were transferred to the 37°C condition for 1 h. The samples’ absorption rate was determined at 520 nm by a spectrophotometer, and the antioxidant activity was calculated by the below formula: Inhibition (%) = (Sample A/Control A) × 100.
The blank sample contained 1 ml of methanol and 1 ml of silver salt, C. kwangsiensis folium leaf extract, and Ag nanoparticles, and a sample of 1 ml of DPPH and 2 ml of silver salt, C. kwangsiensis folium leaf extract, and Ag nanoparticles with the applied concentrations was regarded as the negative control [41].
Determination of the IC50 of Curcumae kwangsiensis folium green-mediated Ag nanoparticles in the antioxidant test
Calculation of half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is a suitable method for comparison of the activity of pharmaceutical materials. In this method, the measurement and comparison criterion is the concentration at which 50% of the final activity of the drug occurs. In this experiment, the IC50 of various repeats is estimated and compared with the IC50 of BHT, which is introduced as the antioxidant activity index. The closer the obtained value is to the IC50 of BHT, the stronger is the antioxidant activity of the material. The graph of the IC50 of the extract was produced by drawing the percent inhibition curve versus the extract concentration. First, three stock samples with variable concentrations (0–1000 μg/ml) of silver salt, C. kwangsiensis folium leaf extract, and Ag nanoparticles were prepared. Then, a serial dilution was prepared from each sample, and IC50 of the above samples was measured separately, following which their mean was calculated. BHT, with different concentrations, was considered positive control. All experiments were performed in triplicate [41].
Evaluation of anti-lung cancer properties of Curcumae kwangsiensis folium green-mediated Ag nanoparticles
The human lung cancer cell lines (lung well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma: HLC-1, lung moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma: LC-2/ad, and lung poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma: PC-14) and the normal cell line (HUVEC) in the MTT assay were used as follows. They were cultured as a monolayer culture in 90% RPMI-1640 medium and 10% fetal serum and supplemented with 200 mg/ml streptomycin, 125 mg/ml penicillin, and 8 mg/ml amphotericin B. The culture was then exposed to 0.5 atm carbon dioxide at 37°C, on which the tests were performed after at least ten successful passages. MTT assay is a method used to investigate the toxic effects of various materials on various cell lines, including non-cancer and cancer cells. To evaluate the cell toxicity effects of the compounds used in this research, the cells were transferred from the T25 flask to the 96-well flasks. In each cell of the 96-cell flasks, 7000 cells of cancer and fibroblast cell lines were cultured, and the volume of each cell was eventually increased to 100 μl. Before the treatment of the cells in the 96-well flask, the density of cells was increased to 70%, so the 96-well flasks were incubated for 24 h to obtain the cell density of 7 × 103. Next, the initial culture medium was discarded, and variable concentrations (0–1000 μg/ml) of silver salt, C. kwangsiensis folium leaf extract, and Ag nanoparticles were incubated at 37°C and 0.5 CO2 for 24, 48, and 72 h. Then, 20 μl of MTT was added to each well after a certain amount of time. Next, 100 μl of DMSO solvent was added to each well. They were then kept at room temperature for 25 min and read at 490 and 630 nm by a microtitre plate reader.
The cell lines were treated with the hydroalcoholic extract (1.25 mg/ml), which inhibited about 20% of the cell growth. The Annexin/PI method was used to determine the apoptosis level in the treated and control cell lines using a flow cytometry machine. To perform the experiment, the cell lines were treated with a variable concentrations (0–1000 μg/ml) of silver salt, C. kwangsiensis folium leaf extract, and Ag nanoparticles for 24 h. Cells were irrigated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). After centrifugation, buffer binding solution was added to the obtained precipitate. Then, 5 μl of Annexin V dye was added and incubated for 15 min at 25°C. Cells were washed with the binding solution, following which 10 μl of PI dye was added. Finally, cell analysis was done by a flow cytometry machine according to the formula below: Cell viability (%) = (Sample A/Control A) × 100.
Results
In the present study, Ag nanoparticles were formulated using C. kwangsiensis folium leaf extract. Also, we assessed the anti-human lung cancer activities of Ag nanoparticles against common human lung cancer cell lines in in vitro conditions.
Chemical characterization of Ag nanoparticles
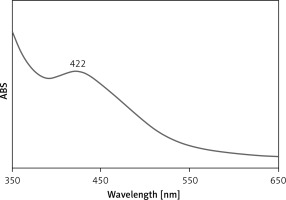
UV-Vis spectroscopic analysis showed the presence of an absorption peak at 422 nm which confirmed the formation of the Ag nanoparticles (Figure 1). Mohammadi et al. (2019) observed the peak of Ag nanoparticles containing Phoenix dactylifera seed ethanolic extract at the wavelength of 438 nm [28]. Hamelian et al. reported Thymus kotschyanus aqueous extract synthesized AgNPs with a peak at 440 nm in the UV-Vis spectrum [26]. Zangeneh et al. observed the absorbance at 462 nm for Ag nanoparticles synthesized by Spinacia oleracea L. [20]. These reports support the results of the current work. The C. kwangsiensis folium mediated synthesis of Ag nanoparticles showed excellent stability even after 20 days and no considerable changes occurred in UV absorbance.
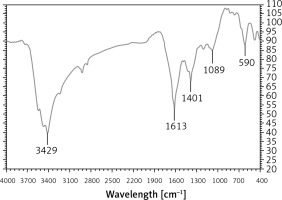
In the FT-IR test, the antioxidant and secondary compounds are determined based on several peaks in special wavelengths. The analysis of the IR spectra of the Ag nanoparticles revealed peaks at 590, 1089, 1401, 1613, and 3429 cm–1 related to Ag-O, C-OH, C=O, C-O, and OH, respectively (Figure 2).
The IR spectra investigated for the Ag nanoparticles revealed absorption peaks at (I) 3287 cm–1 (OH group of alcohols and phenols); (II) 1623 cm–1 (C-O group of carboxylic acid group); (III) 1383 cm–1 (C=O stretching of carboxylic acid group); (IV) 1038 cm–1 (C-OH vibrations of the protein/polysaccharide).
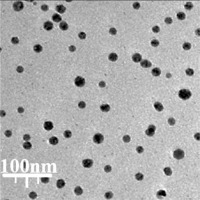
The size of the nanoparticles (15–21 nm) was calculated through TEM images (Figure 3). Furthermore, the histogram plot from the TEM image showed the particle size distribution of biosynthesized Ag nanoparticles in the range of 11 to 24 nm. In previous studies, the size of Ag nanoparticles formulated by aqueous extract of medicinal plants had been calculated in the range of 5–50 nm with the spherical shape [26, 37]. These reports support the results of the current work.
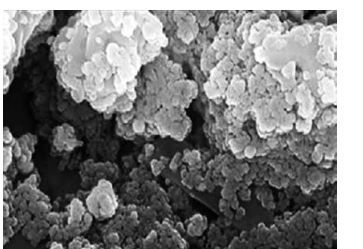
In the present study, the FE-SEM image of Ag nanoparticles is shown in Figure 4. The Ag nanoparticles appeared as an agglomerated structure. The hydroxyl groups present in C. kwangsiensis folium could be responsible for agglomeration [26, 37]. Also, FE-SEM images indicated a diameter of 15–21 nm and the spherical shape for Ag nanoparticles.
Antioxidant properties of Ag nanoparticles synthesized using Curcumae kwangsiensis folium leaf aqueous extract
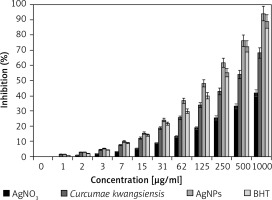
For determining antioxidant properties of several materials such as medicinal plants and metallic nanoparticles green-synthesized by medicinal plants the free radicals are used; the main one is DPPH. In the high antioxidant capacities of several materials, the color of the DPPH molecules changes from violet to the pale yellow or colorless [19–21, 28].
In the present study, the concentration of 1000 μg/ml or high concentration showed the best result. Also, the antioxidant properties increased dose-dependently (Figure 5). Among all samples examined (silver salt, C. kwangsiensis folium leaf aqueous extract, and Ag nanoparticles), the Ag nanoparticles revealed the most remarkable inhibition activities against free radicals. BHT revealed similar antioxidant activities compared to the AgNPs. The exact IC50 values of C. kwangsiensis folium, butylated hydroxytoluene, and AgNPs were 399, 207, and 135 μg/ml, respectively (Table I).
Anti-human lung cancer potentials of Ag nanoparticles synthesized using Curcumae kwangsiensis folium leaf aqueous extract
In our research, the cell lines treated with silver salt, C. kwangsiensis folium, and Ag nanoparticles were tested by a well-known cytotoxicity test, i.e. the MTT test, for 72 h regarding the cytotoxicity activities on normal (HUVEC) and common human lung cancer (well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma (HLC-1), moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (LC-2/ad), and poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma (PC-14)) cell lines (Figures 6–9). Ag silver salt, C. kwangsiensis folium leaf aqueous extract, and Ag nanoparticles did not show any cytotoxicity against HUVEC cells in the MTT assay.
Figure 6
Cytotoxic effects of silver salt, Curcumae kwangsiensis folium, and Ag nanoparticles against HUVEC cell line
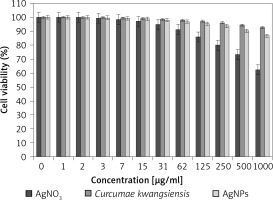
Figure 7
Anti-human lung cancer effects of silver salt, Curcumae kwangsiensis folium, and Ag nanoparticles against lung well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma (HLC-1) cell line
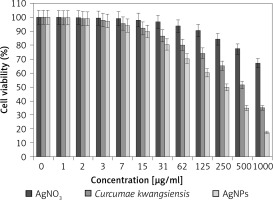
Figure 8
Anti-human lung cancer effects of silver salt, Curcumae kwangsiensis folium, and Ag nanoparticles against lung moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (LC-2/ad) cell line
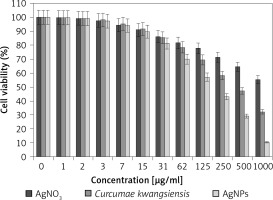
Figure 9
Anti-human lung cancer effects of silver salt, Curcumae kwangsiensis folium, and Ag nanoparticles against lung poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma (PC-14) cell line
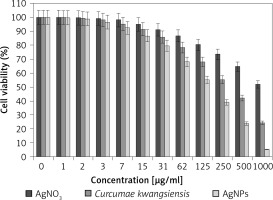
Regarding human lung cancer cell lines, the cell viability dose-dependently decreased in the presence of silver salt, C. kwangsiensis folium, and Ag nanoparticles. The IC50 values of C. kwangsiensis folium and Ag nanoparticles against the HLC-1 cell line were 461 and 358 μg/ml, respectively; against the LC-2/ad cell line were 431 and 300 μg/ml, respectively; and against the PC-14 cell line were 480 and 252 μg/ml, respectively. The best results of cytotoxicity and anti-human lung cancer potentials of Ag nanoparticles against the above cell lines were seen in the case of the PC-14 cell line (Table II).
Discussion
One of the reasons for the synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by plants is the significant antioxidant properties of them. Several studies have reported that plants’ green-formulated Ag nanoparticles can trap the free radicals and save the body cells [42, 43]. The reason behind the antioxidant activity of green or biosynthesized nanoparticles could be due to the presence of metabolites compounds [42–45]. In the previous study, it was revealed that C. kwangsiensis folium leaf has many antioxidant compounds such as oxygenated sesquiterpenes, oxygenated monoterpenes, germacrone, iso-curcumenol, cis-α-elemenone, caryophyllene oxide, germacrene A, β-selinene, α-humulene, β-bourbonene, myrtenol, endo-borneol, limonene, camphene, sesquiterpene hydrocarbons, β-turmenone, curzerenone, trans-calamenene, β-bisabolene, AR-curcumene, trans-caryophyllene, α-zingiberene, aromadendrene, p-cymene, α-pinene, monoterpene hydrocarbon, epi-curzerenone, 2-undecanol, isoborneol, pinocarveol, β-pinene, ar-turmenone, germacrene B, curzerene, β-elemene, 2-undecanone, 4-vinyl-2-methoxy-phenol, p-cymen-8-ol, α-terpinolene, trans-β-elemenone, α-selinene, germacrene D, α-terpineol, β-sesquiphellandrene, borneyl acetate, and Camphor [39]. Various studies have been performed in the nanobiotechnology field using several herbs, but still no report is available on C. kwangsiensis folium green-formulated Ag nanoparticles.
Among the different parameters of metallic nanoparticles such as the nature of surface functions, texture, size, and morphology, the size effect is most necessary in the anticancer test using standard cancer cells. Previous reports revealed that the anticancer activity increases with a decrease in particle size based on their better penetration ability over the cell lines. It has been reported that particle size lower than 50 nm displays better activity in the corresponding cancer cell lines [46]. As can be observed in Figures 4 and 5 of our study, the sizes of Ag nanoparticles synthesized by C. kwangsiensis folium leaf aqueous extract are in the range of 15–21 nm.
The anticancer effects of green-formulated Ag nanoparticles have been confirmed in the previous studies [47–49]. The study of Suman et al. (2013) clarified the anti-cervix cancer effects of Ag nanoparticles containing a natural compound (Morinda citrifolia) against the HeLa cell line. In the previous study, the Ag nanoparticles killed all HeLa cells in high doses [48]. In another study, the anti-liver cancer properties of Ag nanoparticles containing Piper longum leaf against Hep-2 cell lines were proved [47]. In a previous experiment it was reported that Ag nanoparticles green-synthesized by Annona quamosal leaf have excellent anti-breast cancer potential against the MCF-7 cell line [49].
Likely the significant anti-human lung cancer potential of Ag nanoparticles synthesized by C. kwangsiensis folium against human lung cancer cell lines is linked to their antioxidant activities. Similar research revealed the antioxidant materials such as metallic nanoparticles especially Ag nanoparticles and ethno-medicinal plants reduce the volume of tumors by removing free radicals [50]. In detail, the high presence of free radicals in the normal cells causes many mutations in their DNA and RNA, destroys their gene expression and then accelerates the proliferation and growth of abnormal cells or cancerous cells [25, 51]. The free radicals’ high presence in all cancers such as skin cancers, throat, ovarian, testicular, bladder, colon, small intestine, gastrointestinal, stromal, stomach, breast, lung, vaginal, prostate, pancreatic, liver, gallbladder, hypopharyngeal, fallopian tube, thyroid, esophageal, parathyroid, bile duct, and rectal indicates the significant role of these molecules in causing tumorigenesis and angiogenesis [25, 52]. Many researchers reported that Ag nanoparticles synthesized by ethno-medicinal plants have a remarkable role in removing free radicals and growth inhibition of all cancerous cells [52, 53].
In this research, the Ag nanoparticles were attained from the reaction between AgNO3 and C. kwangsiensis leaf aqueous extract in in vitro conditions. TEM, FE-SEM, UV-Vis, and FT-IR methods were used to evaluate nanoparticle characteristics. The results of these techniques revealed that Ag nanoparticles had been synthesized in the best way. Based on the FT-IR spectrum the presence of a great number of antioxidant compounds produced appropriate conditions for the reduction of silver. In the TEM technique, the mean size of Ag nanoparticles was assessed to be 18 nm, which is favorable.
The Ag nanoparticles showed the best antioxidant activities against DPPH. Ag nanoparticles had appropriate anti-lung cancer activities dose-dependently against HLC-1, LC-2/ad, and PC-14 cell lines without any cytotoxicity on the normal cell line (HUVEC). After clinical study Ag nanoparticles containing C. kwangsiensis leaf aqueous extract can be used as an efficient drug in the treatment of lung cancer and diseases in humans.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic conditions, we could not investigate the anti-human lung adenocarcinoma effects of other metallic nanoparticles such as palatine, gold, iron and copper green-synthesized by C. kwangsiensis leaf aqueous extract in the in vitro conditions.