Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
NEPHROLOGY / BASIC RESEARCH
A novel seven-immune-gene-based model to improve prediction of prognosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
1
Department of Urology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Quanzhou, Fujian, China
2
Department of Plastic Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Quanzhou, Fujian, China
3
Department of Ultrasound, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Quanzhou, Fujian, China
4
Department of Urology, Jinjiang Municipal Hospital, No. 16 Luoshan Section, Jinguang Road, Jinjiang, Quanzhou, Fujian, China
Submission date: 2022-08-23
Final revision date: 2022-12-08
Acceptance date: 2022-12-24
Online publication date: 2022-12-29
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
The aim of our study was to investigate the correlation of immune-related genes with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) prognosis and the role of immune-related genes in the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) and to build a new prognostic model and prognostic scoring system for renal cancer.
Material and methods:
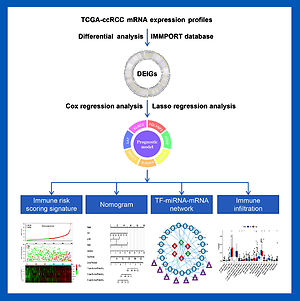
We downloaded the mRNA expression data of 610 samples (538 ccRCC and 72 normal tissues) from the TCGA database and constructed an immune-related prognostic model using Cox regression analysis and LASSO analysis. Then we internally verified the scientific validity and accuracy of the model using Kaplan-Meier (KM) analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Subsequently, Cytoscape was used to construct a TF-miRNA-mRNA network. The “CIBERSORT” package was used to perform the immune infiltration analysis. Finally, validation of key gene expression was performed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR).
Results:
The prognostic model constructed for ccRCC includes 7 genes (KLRC2, PGLYRP2, AGER, CHGA, AVPR1B, IL20RB, LAT). It was proven to have good prognostic performance through the K analysis and the ROC curves. We also constructed an accurate prognostic predictive scoring system by establishing a nomogram. Furthermore, the TF-miRNA-mRNA network revealed the potential mechanism of the model and the immune infiltration analysis revealed a correlation between this model and TIME.
Conclusions:
The results suggest that the newly developed 7-immune-related-gene model can be a practical and reliable prognostic tool for ccRCC. It also shows T cell infiltration characteristics in TIME and can therefore be used as an immune biomarker for the diagnosis and treatment of ccRCC.
The aim of our study was to investigate the correlation of immune-related genes with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) prognosis and the role of immune-related genes in the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) and to build a new prognostic model and prognostic scoring system for renal cancer.
Material and methods:
We downloaded the mRNA expression data of 610 samples (538 ccRCC and 72 normal tissues) from the TCGA database and constructed an immune-related prognostic model using Cox regression analysis and LASSO analysis. Then we internally verified the scientific validity and accuracy of the model using Kaplan-Meier (KM) analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Subsequently, Cytoscape was used to construct a TF-miRNA-mRNA network. The “CIBERSORT” package was used to perform the immune infiltration analysis. Finally, validation of key gene expression was performed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR).
Results:
The prognostic model constructed for ccRCC includes 7 genes (KLRC2, PGLYRP2, AGER, CHGA, AVPR1B, IL20RB, LAT). It was proven to have good prognostic performance through the K analysis and the ROC curves. We also constructed an accurate prognostic predictive scoring system by establishing a nomogram. Furthermore, the TF-miRNA-mRNA network revealed the potential mechanism of the model and the immune infiltration analysis revealed a correlation between this model and TIME.
Conclusions:
The results suggest that the newly developed 7-immune-related-gene model can be a practical and reliable prognostic tool for ccRCC. It also shows T cell infiltration characteristics in TIME and can therefore be used as an immune biomarker for the diagnosis and treatment of ccRCC.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.