Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
INTENSIVE CARE MEDICINE / RESEARCH PAPER
The Plasma Metabolite-Mediated Relationship between Inflammatory Cytokines and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
1
Jiangxi Provincial People's Hospital, China
2
Jinggangshan university affiliated hospital, China
Submission date: 2025-01-02
Final revision date: 2025-02-16
Acceptance date: 2025-02-23
Online publication date: 2025-04-27
KEYWORDS
inflammatory cytokinesplasma metabolitesmediationAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeMendelian Analysis
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
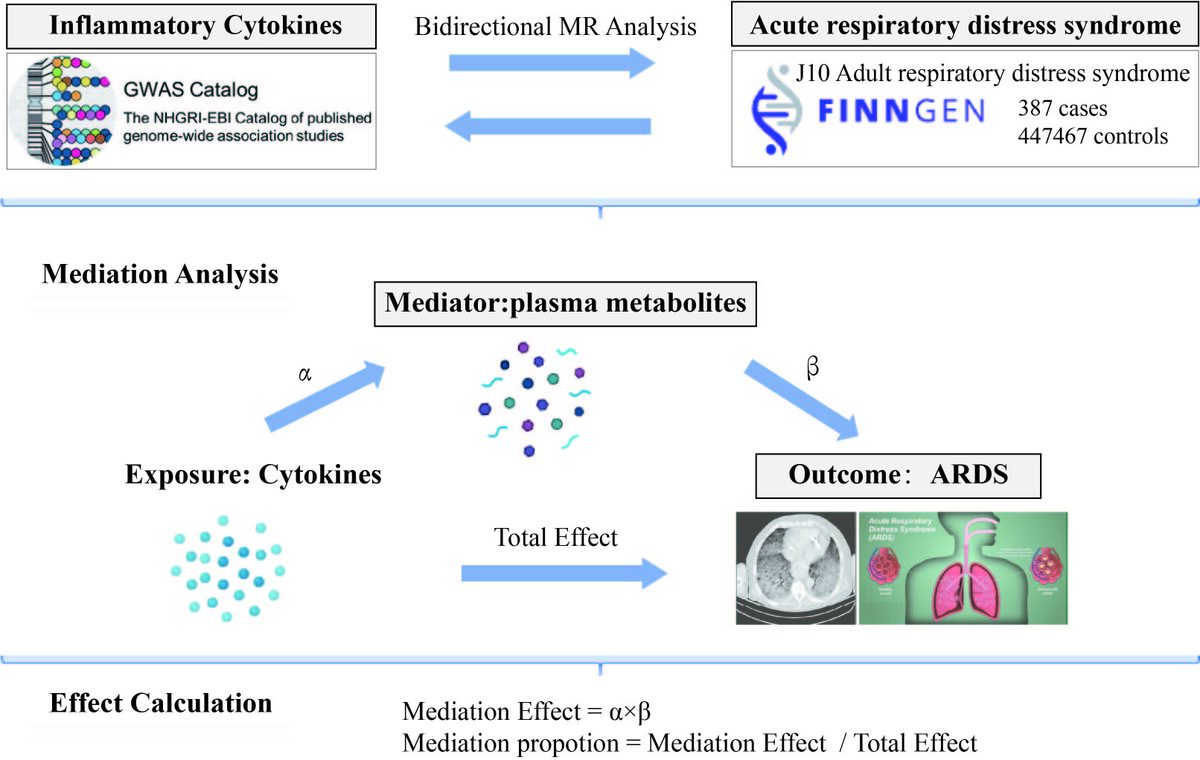
Biomarkers of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) can provide precise treatment options. It is a clinical syndrome of diffuse lung inflammation and edema, usually leading to acute respiratory failure. We use Mendelian randomization (MR) and mediation analysis to infer the potential impact of inflammatory factors and metabolites on ARDS.
Material and methods:
The summary statistics of 1400 plasma metabolite traits and 41 inflammatory cytokine traits were obtained from publicly available GWAS. Inverse Variance Weighted were adopted for bidirectional MR analysis to infer causal relationships. Several sensitivity analyses were also used to ensure reliable MR results. Mediation analysis was used to determine the pathway from inflammatory factors to ARDS mediated by plasma metabolism and the proportion of mediation effects explained by plasma metabolites were estimated.
Results:
MR analysis revealed the causal effects of 5 inflammatory cytokines and 18 plasma metabolites on ARDS. Reverse MR analysis shows that ARDS has no effect on these 5 inflammatory cytokines. In addition, we screened 18 pathogenic metabolites associated with ARDS. Based on known pathogenic metabolites above, it was observed that through mediation analysis that Ceramide levels and Alpha tocopherol to sulfate ratio may mediate the causal pathway from inflammatory factors to ARDS, with mediation ratios of 14.1% and 17.7%, respectively (p<0.05).
Conclusions:
The increase of Ceramide levels and Alpha-tocopherol to sulfate ratio respectively will reduce the risk of ARDS. Our research provide further insights into the complex interactions between inflammatory cytokines and metabolites in the development of ARDS, promoting the development of innovative strategies for ARDS prevention and treatment.
Biomarkers of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) can provide precise treatment options. It is a clinical syndrome of diffuse lung inflammation and edema, usually leading to acute respiratory failure. We use Mendelian randomization (MR) and mediation analysis to infer the potential impact of inflammatory factors and metabolites on ARDS.
Material and methods:
The summary statistics of 1400 plasma metabolite traits and 41 inflammatory cytokine traits were obtained from publicly available GWAS. Inverse Variance Weighted were adopted for bidirectional MR analysis to infer causal relationships. Several sensitivity analyses were also used to ensure reliable MR results. Mediation analysis was used to determine the pathway from inflammatory factors to ARDS mediated by plasma metabolism and the proportion of mediation effects explained by plasma metabolites were estimated.
Results:
MR analysis revealed the causal effects of 5 inflammatory cytokines and 18 plasma metabolites on ARDS. Reverse MR analysis shows that ARDS has no effect on these 5 inflammatory cytokines. In addition, we screened 18 pathogenic metabolites associated with ARDS. Based on known pathogenic metabolites above, it was observed that through mediation analysis that Ceramide levels and Alpha tocopherol to sulfate ratio may mediate the causal pathway from inflammatory factors to ARDS, with mediation ratios of 14.1% and 17.7%, respectively (p<0.05).
Conclusions:
The increase of Ceramide levels and Alpha-tocopherol to sulfate ratio respectively will reduce the risk of ARDS. Our research provide further insights into the complex interactions between inflammatory cytokines and metabolites in the development of ARDS, promoting the development of innovative strategies for ARDS prevention and treatment.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.