Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), with characteristics of memory decline, personality impairment and cognitive dysfunction, is known as a pathology that includes β-amyloid (Aβ) (plaques) and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) [1, 2]. It was reported that AD affected approximately 47 million people in 2016, which led to a substantial personal, social and financial burden. Additional non-AD pathological changes, including typically vascular, Lewy bodies, or TDP-43 pathology, were also found in individuals with AD [3]. Numerous efforts have been made to alleviate the plaques and NFTs, but the optimum therapeutic strategy of AD has never been reported up to now [4].
Previous studies have shown that increased neuroinflammation, 1 of the hallmarks in the pathology of AD, could lead to neuronal dysfunction and death [5–7]. The neuroinflammatory hypothesis of AD has been demonstrated [8]. Pro-inflammatory factors exhibited increased levels in AD, including inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) [9]. Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) has been regarded as a prototypical pro-inflammatory transcription factor [10]. Some researchers have found that NF-κB might be an important pro-inflammatory activator in AD, and the progression of AD can be suppressed by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [11–13]. Therefore, reducing neuroinflammation through the NF-κB signaling pathway might be a promising approach to generate novel treatment for this disease [14]. Increasingly, medicinal plants have been reported to possess effective components against AD in many preclinical and clinical trials, and some of those medicinal plants have been traditionally used to treat dementia in China [15].
The traditional Chinese medicine Huatuo Zaizao pill (HTZP) was listed in the pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China Part I, and it consists of red flower, angelica, Ligusticum wallichii, fructus evodiae, borneol, rhizoma arisaematis and nux vomica. It has the functions of activating blood circulation, removing blood stasis, resolving phlegm and dredging collaterals, promoting qi and relieving pain. It is widely used in the treatment and prevention of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and vascular dementia. Furthermore, it can mitigate focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion neurogenesis injury in rats, which showed the potential to promote rehabilitation after stroke [16]. In our study, the efficacy of HTZP for attenuating memory decline and the content of inflammation of AD mice were examined.
Material and methods
Drug
Huatuo Zaizao pill was obtained from Guangzhou Baiyunshan Qixing Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China; the Saudi Food and Drug Authority approval number: Z44020748). Huatuo Zaizao pill has been used in clinical practice for treating cerebral infarction in China [17]. For adult patients, the effective dose of HTZP was 8–16 g (crude materials) per day.
Aβ1-42-induced Alzheimer’s disease mouse model and Huatuo Zaizao pill treatment
3-month-old male C57BL/6 mice were purchased from the Model Animal Research Center of Nanjing University, and were kept at an ambient temperature of 20–23°C. Measures were taken to minimize animal suffering during the research. All procedures used in the AD mouse model were based on a previous study conducted by the investigators [18]. Aβ1-42 (Millipore, CA, USA) was dissolved in 1% NH3 · H2O at a concentration of 1 mg/ml, and incubated at 37°C for 5 days to allow for fibril formation. After being anesthetized with 10% chloral hydrate, 2 µl of Aβ1-42 was injected into the bilateral hippocampus using the following stereotaxic coordinates: AP – 2.0 mm, ML ±1.6 mm, and DV 1.5 mm. The HTZP was smashed over 60 mesh sieves and extracted for 40 min with normal saline as the solvent. The concentration was 2 g/ml in normal saline. Then, these mice were grouped into 4 groups (n = 10, per group): vehicle group with saline, AD model group with saline, and AD model with HTZP (0.5 g/kg/day, 1 g/kg/day, i.p. for 15 days) treatment group after 7 days of Aβ1-42 injection. All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Care Committee of Nanjing University (reference number: 20160108).
Morris water maze test
The Morris water maze test was conducted to detect the spatial learning and memory function of Aβ1-42-induced AD mice [19]. The test was performed on a circular swim tank (122 cm in diameter and 75 cm in depth) filled with warm water (22 ±3°C), with an escape platform inside it (50 cm in depth and 10 cm in diameter). The platform was submerged 1 cm below the surface of the water. During the acquisition phase trials (days 1–5), mice were trained to search for the hidden platform under the water. Within 60 s, the mice were allowed to escape onto platform and stay on it for 5 s, and warmed in the cage. However, if mice did not find the platform, 60 s was recorded as the escape latency. On the 6th day, the platform was removed, and the number of platform crossings and time spent on the target quadrant were recorded and analyzed using a computerized video system (ANY-maze, Stoeling Co, USA).
Real-time PCR
Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed as previously described [20]. The hippocampal tissue was sampled, and the total RNA was extracted using Trizol (Invitrogen, USA). The total cDNA was synthesized using the reverse transcriptase kit (Takara, Dalian, China), and real-time quantitative PCR was conducted with a SYBR green kit (Takara, Dalian, China). The primers were as follows:
Measurement of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits were used to measure amounts of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α from serum of each group, according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Cusabio Biotech Co. Ltd, China). Briefly, serum separated from the blood was added to the template pre-coated with mouse IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α antibody, followed by incubating for a certain amount of time at 37°C. The absorbance was detected at 450 nm after adding TMB substrate solution and stop solution in sequence. The levels of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α were assayed by the standard curve.
Western blot
Western blot was performed as previously described [21]. Mice were sacrificed after being anesthetized, and the hippocampi were collected and homogenized with ice cold RIPA lysis buffer. After centrifuging at 12,000 g for 15 min at 4°C, the supernatants were collected, and the protein concentration was measured using a BCA protein assay kit (Bioworld, USA). Equal proteins were separated by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel, transferred onto a PVDF membrane, and incubated in 5% non-fat milk for 2 h at room temperature (RT). Then, the membrane was incubated at 4°C overnight with COX-2 (1 : 2,000, Bioworld, USA), iNOS (1 : 1,000, BD Biosciences, USA), p-IκB (1 : 500, Cell Signaling Technology, USA), IκB (1 : 500, Cell Signaling Technology, USA), p65 (1 : 500, Cell Signaling Technology, USA), GAPDH (1 : 5,000, Bioworld, USA), and lamin B (1 : 2,000, Bioworld, USA). The membrane was washed with TBST for 30 min, and incubated in the proper secondary antibody for 1 h. Then, membranes were washed for 45 min with TBST, and processed with chemiluminescence reagents using an ECL kit (Thermo Fisher, USA). ImageJ (NIH, USA) was used to examine the intensities of the bands.
Immunofluorescence
Mice were perfused with saline and 4% paraformaldehyde after being anesthetized. Immunostaining was performed with antibodies that selectively marked microglial cells (anti-Iba1). After dehydration, the brains were cut into 18-µm slices by a freezing microtome (Leica, Germany). After blocking with 2% BSA, the slices were incubated with Iba1 (1 : 500, Abcam, USA) at 4°C overnight, and kept in the secondary antibody at RT for 1 h. After being washed with PBS, these parts were reacted with DAPI (1 : 1,000; Bioworld, USA) for 15 min. Then, images were obtained by fluorescence microscope (Olympus, Japan). All images were analyzed by Image-Pro Plus for the counting of microglia cells.
Results
Huatuo Zaizao pill attenuates memory deficits in Aβ1-42-induced AD mice
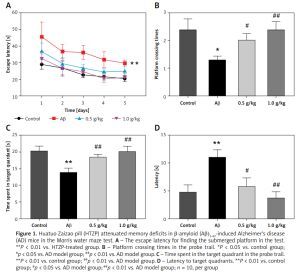
The Morris water maze test was performed to investigate whether HTZP could mitigate cognitive disorder of AD mice. Mean escape latency in AD mice treated with HTZP was decreased, compared to the increasing level in the model group (Figure 1 A, p < 0.01). Furthermore, the crossing platform times (Figure 1 B, p < 0.01), and time spent in the target quadrants (Figure 1 C, p < 0.01) were increased after treatment with HTZP. In addition, latency to arrive at the target quadrants of AD mice also decreased in the HTZP treatment group (Figure 1 D, p < 0.01). This study revealed that HTZP could improve the spatial cognition ability of AD mice.
Figure 1
Huatuo Zaizao pill (HTZP) attenuated memory deficits in β-amyloid (Aβ)1-42-induced Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mice in the Morris water maze test. A – The escape latency for finding the submerged platform in the test. **P < 0.01 vs. HTZP-treated group. B – Platform crossing times in the probe trail. *P < 0.05 vs. control group; #p < 0.05 vs. AD model group; ##p < 0.01 vs. AD model group. C – Time spent in the target quadrant in the probe trail. **P < 0.01 vs. control group; ##p < 0.01 vs. AD model group. D – Latency to target quadrants. **P < 0.01 vs. control group; #p < 0.05 vs. AD model group; ##p < 0.01 vs. AD model group; n = 10, per group
Huatuo Zaizao pill reduced the expression of inflammatory factors in the hippocampi and serum of Aβ1-42-induced AD mice
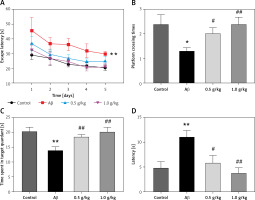
After the treatment with HTZP, the mRNA expression of the inflammatory factors in the hippocampi of AD mice was evaluated. Aβ1-42 injection improved the mRNA expression of COX-2, iNOS, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α (Figure 2) [22]. However, the content of inflammatory factors in AD mice had decreased after treatment with HTZP (Figures 2 A–E). Furthermore, the amounts of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α from serum were increased after Aβ1-42 injection, which was attenuated by HTZP treatment (Figures 3 A–C). The protein content of COX-2 and iNOS in AD mice decreased after treatment with HTZP (Figures 3 D, E). These results demonstrated that HTZP could inhibit neuroinflammation by reducing the content of inflammatory factors in AD mice.
Figure 2
Huatuo Zaizao pill reduced mRNA expression of inflammatory factors in β-amyloid (Aβ)1-42-induced Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mice. The mRNA levels of cyclooxygenase-2 (A), interleukin (IL)-1β (B), IL-6 (C), inducible nitric oxide synthase (D) and tumor necrosis factor α (E) were determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Each bar represents the mean ± standard error of the mean from 3 independent experiments. **P < 0.01 vs. control group; #p < 0.05 vs. AD model group; ##p < 0.01 vs. AD model group; n = 10, per group
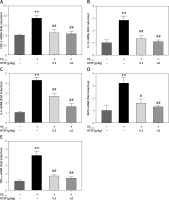
Figure 3
Huatuo Zaizao pill reduced protein expression of inflammatory factors in hippocampi of β-amyloid1-42-induced Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mice. The level of interleukin-1β (A), IL-6 (B) and tumor necrosis factor α (C) from serum of each group was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. D – The protein content of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase was analyzed by western blot. GAPDH was used as the loading control. E – Quantitative analysis of the western blot bands. Each bar represents mean ± standard error of the mean from 3 independent experiments. **P < 0.01 vs. control group; ##p < 0.01 vs. AD model group; n = 10, per group
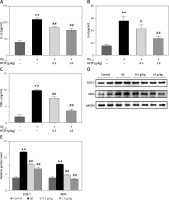
Huatuo Zaizao pill inhibits inflammatory pathway activation in the hippocampi of Aβ1-42-inducedAD mice
The NF-κB pathway plays an important role in regulating the neuroinflammation of AD [11–13]. Aβ1-42 increased the accumulation of the NF-κB p65 nuclear component and IκB phosphorylation (Figure 4). However, the expression levels of p65 and p-IκB were decreased in the hippocampus of AD mice after HTZP injecting (Figures 4 A–D). These results indicate that the effect of HTZP in inhibiting these inflammatory factors might contribute to the NF-κB pathway.
Figure 4
Huatuo Zaizao pill suppressed nuclear factor-κB activation in β-amyloid1-42-induced Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mice. A – Nuclear p65 was evaluated by western blot. Lamin B was used as the loading control. B – Quantitative analysis of western blot. C – Phosphorylation of IκB and total IκB was measured by western blot. D – Quantitative analysis of western blot. Each bar represents mean ±standard error of the mean from 3 independent experiments. **P < 0.01 vs. control group; #p < 0.05 vs. AD model group; ##p < 0.01 vs. AD model group; n = 10, per group
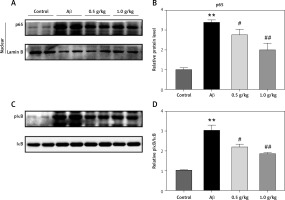
Figure 5
Huatuo Zaizao pill reduced activation of microglia in the hippocampus of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mice. A – Microglia in the hippocampus of mice were analyzed by immunofluorescence using Iba1 antibodies. B – Quantitative analysis of Iba1 staining. **P < 0.01 vs. control group; #p < 0.05 vs. AD model group; ##p < 0.01 vs. AD model group; n = 10, per group
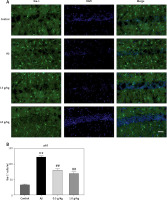
Huatuo Zaizao pill diminishes the activities of microglia in the hippocampus of AD mice
The inflammatory response is mainly mediated by microglia in the brain [23]. In order to investigate whether HTZP could inhibit the activation of microglia, immunofluorescence was carried out. The results suggest that HTZP diminished the microglia activation induced by Aβ1-42 (Figures 5 A, B, p < 0.01).
Discussion
Aβ1-42 could induce an inflammatory response, which ultimately leads to memory decline and neurodegeneration [24]. In the Morris water maze test, the escape latency of the 2 HTZP groups was decreased, and this effect was particularly evident with increasing HTZP concentration. In addition, compared to the control group, the crossing platform times of the AD model group were significantly decreased. The crossing platform times were significantly increased when the AD mice were treated with HTZP. All these data illustrated that HTZP could improve the learning and memory disorder of the AD mice.
In our study, we also investigated the therapeutic mechanism of HTZP in treating the Aβ1-42-induced AD mice. Neuroinflammation is a critical factor in pathology of AD, and Aβ-induced toxicity could lead to glial cell activation and elevation of pro-inflammatory factors [25]. Microglia could lead to the accumulation of pro-inflammatory factors when the inflammatory cascade is started [26]. The increase in inflammatory factors is regarded as 1 mechanism leading to cognitive dysfunction [27]. Compared to the control group, the mRNA expression levels of COX-2, iNOS, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α of the AD model group were significantly higher. However, the mRNA expression levels of these inflammatory factors were significantly decreased when being treated with HTZP in a concentration-dependent manner in AD mice. The present results further indicate that HTZP can inhibit microglia and inflammatory factors, which could attenuate Aβ1-42-induced cognitive disorder.
It has been reported that NF-κB is associated with the degeneration of neurons in the brain of AD patients [28]. NF-κB, a transcription factor, is a heterodimer of p50 and p65 subunits. The phosphorylation of IκB induces its nuclear translocation [29]. NF-κB, the main regulator of pro-inflammatory factors, modulates expression of NAPDH oxidase, interleukins and COX-2 [10]. NF-κB activation can be found in glial cells, which are close to the Aβ plaque areas of AD patients, suggesting the importance of NF-κB activation in AD [14]. NF-κB activities in the hippocampi of AD mice were also evaluated after treatment with HTZP. It was found that HTZP could suppress NF-κB by reducing nuclear accumulation of phosphorylation of IκB and NF-κB p65, indicating that HTZP might suppress Aβ1-42-induced neuroinflammation through the inhibition of NF-κB activation.
Traditional Chinese medicine contains multiple active components, which can treat disease with multiple pathways and targets [30]. In the present study, it was found that HTZP could attenuate Aβ1-42-induced memory decline, and the neuroprotective effect might be associated with the reduction in the inflammatory response and downregulation of the NF-κB pathways. To our best knowledge, the efficacy of Chinese medicine in ameliorating the clinical symptoms of AD has been reported by many studies [31, 32]. So HTZP, as one of the traditional Chinese medicines, has been shown to be effective for an Aβ1-42-induced AD mouse model, suggesting its potential for treating AD [19].
In conclusion, it was shown that HTZP could mitigate cognitive disorder, diminish the activation of microglia, and inhibit the content of inflammatory factors through the NF-κB pathway in Aβ1-42-induced AD mice. HTZP might be an appropriate agent for AD treatment in the future.