Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ONCOLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
Anti-human lung cancer activities and survey
of glutathione reductase and glutathione S transferase
inhibition properties with molecular modeling studies
of 2′-hydroxy-5′-methyl-3′-nitroacetophenone:
a pre-clinical trial study
1
Department of Thoracic Surgery, Shaanxi Province People’s Hospital, Xi ‘an city,
China
2
Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Xijing Hospital, The Fourth Military Medical
University, Xi’an, China
3
Biology Department, College of Science, King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia
4
Zoology Department, College of Science, Damanhour University, Damanhour, Egypt
5
Pathology Department, College of Medicine, Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia
Submission date: 2021-04-15
Final revision date: 2021-05-01
Acceptance date: 2021-05-03
Online publication date: 2021-05-14
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
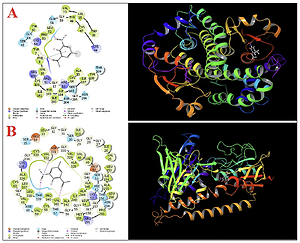
The molecular docking method was found to calculate the biological activity of the 2′-hydroxy-5′-methyl-3′-nitroacetophenone (2′-H-5′- M-3′-N) molecule against the enzymes studied.
Material and methods:
In these calculations, the enzymes used were glutathione reductase (GR) and glutathione S-transferase (GT). After the modeling calculations were completed, the ADME/T parameters were examined to calculate the future drug use properties of the 2′-H-5′-M-3′-N molecule. To survey the antioxidant properties of 2′-H-5′-M-3′-N, the DPPH test was used. Several human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines, i.e., lung moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (LC-2/ad), lung poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma (PC-14), and lung well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma (HLC-1) cell lines, were used to determine the anticancer properties of the molecule.
Results:
Cell viability of 2′-H-5′-M-3′-N was very low against PC-14, LC-2/ad, and HLC-1 cell lines without any cytotoxicity towards the normal cell line. The IC50 values of 2′-H-5′-M-3′-N against LC-2/ad, PC-14, and HLC-1 cell lines were 475, 250, and 691 µg/ml, respectively. The best anti-human lung cancer properties of 2′-H-5′-M-3′-N against the above cell lines were observed in the case of the PC-14 cell line.
Conclusions:
2′-H-5′-M-3′-N was found to have significant antioxidant and anti-human lung cancer properties. It appears that the anti-human lung carcinoma effect of 2′-H-5′-M-3′-N is due to its antioxidant effects.
The molecular docking method was found to calculate the biological activity of the 2′-hydroxy-5′-methyl-3′-nitroacetophenone (2′-H-5′- M-3′-N) molecule against the enzymes studied.
Material and methods:
In these calculations, the enzymes used were glutathione reductase (GR) and glutathione S-transferase (GT). After the modeling calculations were completed, the ADME/T parameters were examined to calculate the future drug use properties of the 2′-H-5′-M-3′-N molecule. To survey the antioxidant properties of 2′-H-5′-M-3′-N, the DPPH test was used. Several human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines, i.e., lung moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (LC-2/ad), lung poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma (PC-14), and lung well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma (HLC-1) cell lines, were used to determine the anticancer properties of the molecule.
Results:
Cell viability of 2′-H-5′-M-3′-N was very low against PC-14, LC-2/ad, and HLC-1 cell lines without any cytotoxicity towards the normal cell line. The IC50 values of 2′-H-5′-M-3′-N against LC-2/ad, PC-14, and HLC-1 cell lines were 475, 250, and 691 µg/ml, respectively. The best anti-human lung cancer properties of 2′-H-5′-M-3′-N against the above cell lines were observed in the case of the PC-14 cell line.
Conclusions:
2′-H-5′-M-3′-N was found to have significant antioxidant and anti-human lung cancer properties. It appears that the anti-human lung carcinoma effect of 2′-H-5′-M-3′-N is due to its antioxidant effects.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.