Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ONCOLOGY / STATE OF THE ART PAPER
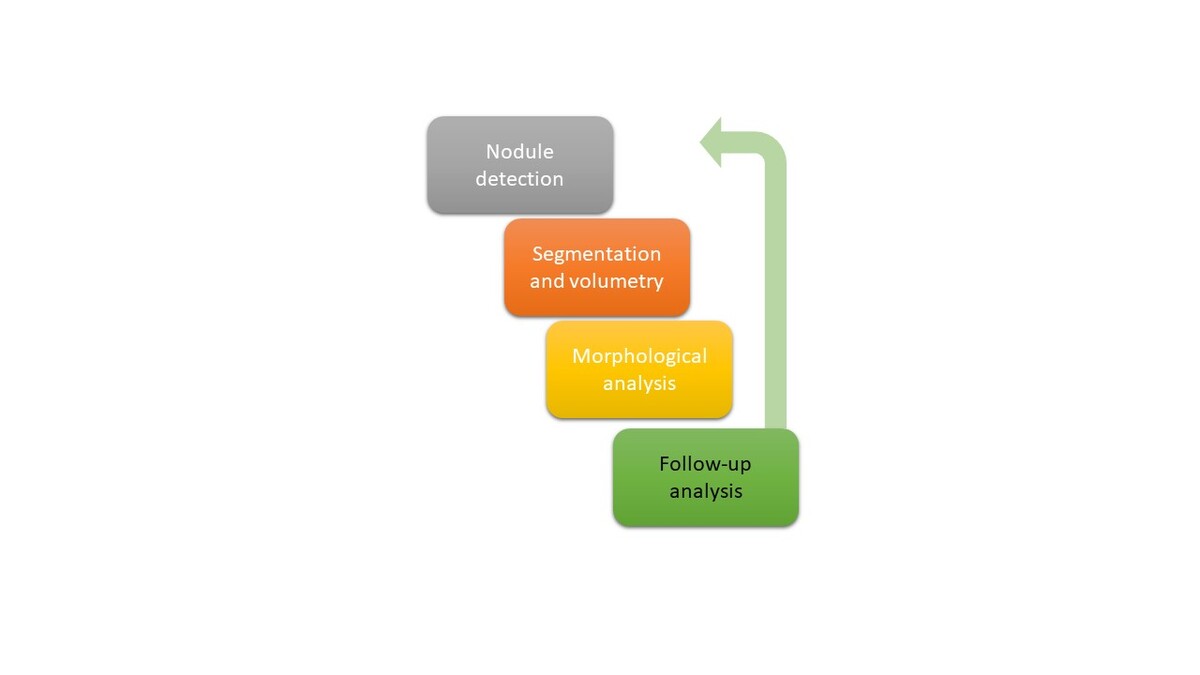
Clinical applications of deep learning in distinguishing benign from malignant pulmonary nodules in computed tomography scans
1
Imaging Department, Yantaishan Hospital, Yantai, Shandong, China
Submission date: 2024-10-09
Final revision date: 2025-02-22
Acceptance date: 2025-03-11
Online publication date: 2025-05-18
Corresponding author
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Early diagnosis is crucial for improving the prognosis of lung cancer, one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths. Lung cancer includes small cell lung cancer (SCLC, ~15% of cases) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC, ~80–85%). Prognosis depends on the stage at diagnosis: the 5-year survival rate is 65% for localized NSCLC but only 9% for distant-stage disease. Radiologists face challenges distinguishing benign from malignant pulmonary nodules on computed tomography scans.
Methods:
This review explores deep learning (DL) methods, including multi-view convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and 3D models for nodule segmentation, emphasizing volumetric assessments for malignancy prediction.
Results:
CNNs effectively analyze CT data, achieving 94.2% sensitivity with 1.0 false positives per scan in lung nodule detection.
Conclusions:
DL enhances diagnostic accuracy, reduces radiologist workload, and enables earlier lung cancer detection. Further research is needed to improve model adaptability across diverse clinical settings.
Early diagnosis is crucial for improving the prognosis of lung cancer, one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths. Lung cancer includes small cell lung cancer (SCLC, ~15% of cases) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC, ~80–85%). Prognosis depends on the stage at diagnosis: the 5-year survival rate is 65% for localized NSCLC but only 9% for distant-stage disease. Radiologists face challenges distinguishing benign from malignant pulmonary nodules on computed tomography scans.
Methods:
This review explores deep learning (DL) methods, including multi-view convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and 3D models for nodule segmentation, emphasizing volumetric assessments for malignancy prediction.
Results:
CNNs effectively analyze CT data, achieving 94.2% sensitivity with 1.0 false positives per scan in lung nodule detection.
Conclusions:
DL enhances diagnostic accuracy, reduces radiologist workload, and enables earlier lung cancer detection. Further research is needed to improve model adaptability across diverse clinical settings.
REFERENCES (167)
1.
Gałązka JK, Czeczelewski M, Kucharczyk T, et al. Obesity and lung cancer – is programmed death ligand-1 (PD-1L) expression a connection? Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 313-6.
2.
Thandra KC, Barsouk A, Saginala K, et al. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Contemp Oncol (Pozn) 2021; 25: 45-52.
3.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 2021; 71: 7-33.
4.
Gould MK, Donington J, Lynch WR, et al. Evaluation of individuals with pulmonary nodules: when is it lung cancer? Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2013; 143 (5 Suppl): e93S-120S.
5.
Bankier AA, MacMahon H, Goo JM, et al. Recommendations for measuring pulmonary nodules at CT: a statement from the Fleischner society. Radiolog 2017; 285: 584-600.
6.
Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon H, et al. Fleischner Society: glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiolog 2008; 246: 697-722.
7.
Lu MS, Chen MF, Yang YH, et al. Appraisal of lung cancer survival in patients with end-stage renal disease. Arch Med Sci 2023; 19: 86-93.
8.
Choi WJ, Choi TS. Automated pulmonary nodule detection based on three-dimensional shape-based feature descriptor. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2014; 113: 37-54.
9.
Peloschek P, Sailer J, Weber M, et al. Pulmonary nodules: sensitivity of maximum intensity projection versus that of volume rendering of 3D multidetector CT data. Radiolog 2007; 243: 561-9.
10.
Kim H, Park CM, Koh JM, et al. Pulmonary subsolid nodules: what radiologists need to know about the imaging features and management strategy. Diagn Interv Radiol 2014; 20: 47-57.
11.
Revel MP, Bissery A, Bienvenu M, et al. Are two-dimensional CT measurements of small noncalcified pulmonary nodules reliable? Radiolog 2004; 231: 453-8.
12.
Han D, Heuvelmans MA, Oudkerk M. Volume versus diameter assessment of small pulmonary nodules in CT lung cancer screening. Transl Lung Cancer Res 2017; 6: 52.
13.
Brzozowska M, Wierzba W, Szafraniec-Buryło S, et al. Overall survival of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib, gefitinib or afatinib under drug programmes in Poland – real-world data. Arch Med Sci 2021; 17: 1618-27.
14.
Henschke CI. Early lung cancer action project: overall design and findings from baseline screening. Lancet 1999; 354: 99-105.
15.
Castellino RA. Computer aided detection (CAD): an overview. Cancer Imaging 2005; 5: 17.
16.
McCarville MB, Lederman HM, Santana VM, et al. Distinguishing benign from malignant pulmonary nodules with helical chest CT in children with malignant solid tumors. Radiolog 2006; 239: 514-20.
17.
Singh S, Maxwell J, Baker JA, et al. Computer-aided classification of breast masses: performance and interobserver variability of expert radiologists versus residents. Radiolog 2011; 258: 73-80.
18.
Giger ML, Karssemeijer N, Schnabel JA. Breast image analysis for risk assessment, detection, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 2013; 15: 327-57.
19.
Joo S, Yang Y, Moon WK, Kim HC. Computer-aided diagnosis of solid breast nodules: use of an artificial neural network based on multi plesonographic features. IEEE Transact Med Imaging 2004; 23: 1292-300.
20.
Way TW, Sahiner B, Chan HP, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of pulmonary nodules on CT scans: improvement of classification performance with nodule surface features. Med Phys 2009; 36: 3086-98.
21.
Way TW, Hadjiiski LM, Sahiner B, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of pulmonary nodules on CT scans: segmentation and classification using 3D active contours. Med Phys 2006; 33: 2323-37.
22.
Giger ML, Ahn N, Doi K, et al. Computerized detection of pulmonary nodules in digital chest images: use of morphological filters in reducing false-positive detections. Med Phys 1990; 17: 861-5.
23.
Ying W, Cunxi C, Tong J, et al. Segmentation of regions of interest in lung CT images based on 2-D OTSU optimized by genetic algorithm in 2009 Chinese Control and Decision Conference. IEEE 2009: 5185-9.
24.
Helen R, Kamaraj N, Selvi K, et al. Segmentation of pulmonary parenchyma in CT lung images based on 2D Otsu optimized by PSO. in 2011 international conference on emerging trends in electrical and computer technology. IEEE 2011; 536-54.
25.
Liu Y, Wang Z, Guo M, et al. Hidden conditional random field for lung nodule detection. in 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). IEEE 2014; 3518-21.
26.
John J, Mini M. Multilevel thresholding based seg mentation and feature extraction for pulmonary nodule detection. Procedia Technolog 2016; 24: 957-63.
27.
Teramoto A, Fujita H, Yamamuro O, et al. Automated detection of pulmonary nodules in PET/CT images: ensemble false-positive reduction using a convolutional neural network technique. Med Phys 2016; 43: 2821-7.
28.
Mastouri R, Neji H, Hantous-Zannad S, et al. A morphological operation-based approach for Sub-pleural lung nodule detection from CT images. in 2018 IEEE 4th Middle East Conference on Biomedical Engineering (MECBME). IEEE 2018; 84-89.
29.
Santos AM, de Carvalho Filho AO, Silva AC, et al. Automatic detection of small lung nodules in 3D CT data using Gaussian mixture models, Tsallis entropy and SVM. Eng Appl Artif Intell 2014; 36: 27-39.
30.
Madero Orozco H, Vergara Villegas OO, et al. Automated system for lung nod ules classification based on wavelet feature descriptor and support vector machine. Biomed Eng Online 2015; 14: 9.
31.
Lu L, Tan Y, Schwartz LH, et al. Hybrid detection of lung nodules on CT scan images. Med Phys 2015; 42: 5042-54.
32.
Farahani FV, Ahmadi A, Zarandi MF. Lung nodule diagnosis from CT images based on ensemble learning. in 2015 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bio informatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB). IEEE 2015; 1-7.
33.
Klik MA, v Rikxoort EM, Peters JF, et al. Improved classification of pulmonary nod ules by automated detection of benign subpleural lymph nodes. in 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: Nano to Macro. IEEE 2006: 494-7.
34.
Froz BR, de C. Filhoa AO, Silva AC, et al. Lung nodule classification using artificial crawlers, directional texture and support vector machine. Expert Syst Appl 2017; 69: 176-88.
35.
Wu J, Qian T. A survey of pulmonary nodule detection, segmentation and classification in computed tomography with deep learning techniques. J Med Artif Intell 2019; 2.
36.
Liu K, Li Q, Ma J, et al. Evaluating a fully automated pulmonary nodule detection approach and its impact on radiologist performance. Radiol Artif Intell 2019; 1: e180084.
37.
Shen W, Zhou M, Yang F, et al. Multi-scale convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification. In: International conference on information processing in medical imaging 2015; 588-599. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
38.
Ciompi F, Chung K, Van Riel SJ, et al. Towards automatic pulmonary nodule management in lung cancer screening with deep learning. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 46479.
39.
Causey JL, Zhang J, Ma S, et al. Highly accurate model for prediction of lung nodule malignancy with CT scans. Sci Rep 2018; 8: 9286.
40.
Hua KL, Hsu CH, Hidayati SC, et al. Computer-aided classification of lung nodules on computed tomography images via deep learning technique. Onco Targets Ther 2015; 4: 2015-22.
41.
Hensley CP, Emerson AJ. Non-small cell lung carcinoma: clinical reasoning in the management of a patient referred to physical therapy for costochondritis. Phys Ther 2018; 98: 503-9.
42.
Dhara AK, Mukhopadhyay S, Khandelwal N, et al. Computer-aided detection and analysis of pulmonary nodule from CT images: a survey. IETE Tech Rev 2012; 29: 265-75.
43.
Sluimer I, Schilham A, Prokopet M, et al. Computer analysis of computed tomography scans of the lung: a survey. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2006; 25: 385-405.
44.
Valente IRS, Cortez PC, Neto EC, et al. Automatic 3D pulmonary nodule detection in CT images: a survey. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2016; 124: 91-107.
45.
Amitava H, Dey D, Sadhu AK. Lung nodule detection from feature engineering to deep learning in thoracic CT images: a comprehensive review. J Digit Imaging 2020; 33: 655-77.
46.
Guobin Z, Jiang S, Yang Z, et al. Automatic nodule detection for lung cancer in CT images: a review. Comput Biol Med 2018; 103: 287-300.
47.
Yu G, Chi J, Liu J, et al. A survey of computer-aided diagnosis of lung nodules from CT scans using deep learning. Comput Biol Med 2021; 137: 104806.
48.
Patrice M, Qi S, Ma H, et al. Detection and classification of pulmonary nodules using convolutional neural networks: a survey. IEEE Access 2019; 7: 78075-91.
49.
Rubin GD. Lung nodule and cancer detection in computed tomography screening. J Thorac Imaging 2015; 30: 130-8.
50.
Th SE, Horeweg N, de Koning HJ, et al. Computed tomographic characteristics of interval and post-screen carcinomas in lung cancer screening. Eur Radiol 2015; 25: 81-8.
51.
Arjun N, Screaton NJ, Holemans JA, et al. The impact of trained radiographers as concurrent readers on performance and reading time of experienced radiologists in the UK Lung Cancer Screening (UKLS) trial. Eur Radiol 2018; 28: 226-34.
52.
Matsumoto S, Ohno Y, Aoki T, et al. Computer-aided detection of lung nodules on multidetector CT in concurrent-reader and second-reader modes: a comparative study. Eur Radiol 2013; 82: 1332-7.
53.
Yixin Y, Feng X, Chi W, et al. Deep learning aided decision support for pulmonary nodules diagnosing: a review. J Thorac Dis 2018; 10: S867.
54.
Nanda H, Scholten ET, de Jong PA, et al. Detection of lung cancer through low-dose CT screening (NELSON): a prespecified analysis of screening test performance and interval cancers. Lancet Oncol 2014; 15: 1342-50.
55.
Goo JM. A computer-aided diagnosis for evaluating lung nodules on chest CT: the current status and perspective. Korean J Radiol 2011; 12: 145-55.
56.
Korst RJ, Lee BE, Krinsky GA, et al. The utility of automated volumetric growth analysis in a dedicated pulmonary nodule clinic. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2011; 142: 372-7.
57.
Ko JP, Berman EJ, Kaur M, et al. Pulmonary nodules: growth rate assessment in patients by using serial CT and three-dimensional volumetry. Radiology 2012; 262: 662-71.
58.
Kuhnigk JM, Dicken V, Bornemann L, et al. Morphological segmentation and partial volume analysis for volumetry of solid pulmonary lesions in thoracic CT scans. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2006; 25: 417-34.
59.
Devaraj A, van Ginneken B, Nair A, et al. Use of volumetry for lung nodule management: theory and practice. Radiology 2017; 284: 630-44.
60.
de Hoop B, Gietema H, van Ginneken B, et al. A comparison of six software packages for evaluation of solid lung nodules using semi-automated volumetry: what is the minimum increase in size to detect growth in repeated CT examinations. Eur Radiol 2009; 19: 800-8.
61.
Callister MEJ, Baldwin DR, Akram AR, et al. British Thoracic Society guidelines for the investigation and management of pulmonary nodules: accredited by NICE. Thorax 2015; 70 (Suppl 2): ii1-54.
62.
Kadir T, Gleeson F. Lung cancer prediction using machine learning and advanced imaging techniques. Transl Lung Cancer Res 2018; 7: 304-12.
63.
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021; 71: 209-49.
64.
Birring SS, Peake MD. Symptoms and the early diagnosis of lung cancer. Thorax 2005; 60: 268-9.
65.
Cataldo JK. High-risk older smokers’ perceptions, attitudes, and beliefs about lung cancer screening. Cancer Med 2016; 5: 753-9.
66.
National Lung Screening Trial Research Team. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med 2011; 365: 395-409.
67.
de Koning HJ, van der Aalst CM, de Jong PA, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with volume CT screening in a randomized trial. N Engl J Med 2020; 382: 503-13.
68.
Gould MK, Tang T, Liu IA, et al. Recent trends in the identification of incidental pulmonary nodules. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2015; 192: 1208-14.
69.
Hendrix W, Rutten M, Hendrix N, et al. Trends in the incidence of pulmonary nodules in chest computed tomography: 10-year results from two Dutch hospitals. Eur. Radiol 2023; 33: 8279-88.
70.
Bruls RJM, Kwee RM. Workload for radiologists during on-call hours: dramatic increase in the past 15 years. Insights Imaging 2020; 11: 121.
71.
Murchison JT, Ritchie G, Senyszak D, et al. Validation of a deep learning computer-aided system for CT-based lung nodule detection, classification, and growth rate estimation in a routine clinical population. PLoS One 2022; 17: e026679.
72.
Jacobs C, Schreuder A, van Riel SJ, et al. Assisted versus manual interpretation of low-dose CT scans for lung cancer screening: impact on lung-RADS agreement. Radiol Imaging Cancer 2021; 3: e200160.
73.
Hempel HL, Engbersen MP, Wakkie J, et al. Higher agreement between readers with deep learning CAD software for reporting pulmonary nodules on CT. Eur J Radiol Open 2022; 9: 10043.
74.
Kozuka T, Matsukubo Y, Kadoba T, et al. Efficiency of a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system with deep learning in detection of pulmonary nodules on 1-mm-thick images of computed tomography. Jpn J Radiol 2020; 38: 1052-61.
75.
Cellina M, Cacioppa LM, Ce M, et al. Artificial intelligence in lung cancer screening: the future is now. Cancers 2023; 15: 4344.
76.
Way T, Chan HP, Hadjiiski L, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of lung nodules on CT scans: ROC study of its effect on radiologists’ performance. Acad Radiol 2010; 17: 323-32.
77.
Vu H, Kim HC, Jung M, et al. fMRI volume classification using a 3D convolutional neural network robust to shifted and scaled neuronal activations. Neuroimage 2020; 223: 117328.
78.
Celeghin A, Borriero A, Orsenigo D, et al. Convolutional neural networks for vision neuroscience: significance, developments, and outstanding issues. Front Comput Neurosci 2023; 17: 1153572.
79.
Lundervold AS, Lundervold A. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging focusing on MRI. Z Med Phys 2019; 29: 102-27.
80.
Thanoon MA, Zulkifley MA, Mohd Zainuri MAA, et al. A review of deep learning techniques for lung cancer screening and diagnosis based on CT images. Diagnostics 2023; 13: 2617.
81.
Brown MS, Mcnitt-Gray MF, Mankovich NJ, et al. Method for segmenting chest CT image data using an anatomical model: preliminary results. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2002; 16: 828-39.
82.
Brown MS, Goldin JG, McNitt-Gray MF, et al. Knowledge-based segmentation of thoracic computed tomography images for assessment of split lung function. Med Phys 2000; 27: 592-8.
83.
Hu S, Hoffman EA, Reinhardt JM. Automatic lung segmentation for accurate quantitation of volumetric X-ray CT images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2001; 20: 490-8.
84.
Leader JK, Zheng B, Rogers RM, et al. Automated lung segmentation in X-ray computed tomography: development and evaluation of a heuristic threshold-based scheme. Acad Radiol 2003; 10: 1224-36.
85.
Sun X, Zhang H, Duan H. 3D computerized segmentation of lung volume with computed tomography. Acad Radiol 2006; 13: 670-7.
86.
Swierczynski P, Papież BW, Schnabel JA, et al. A level-set approach to joint image segmentation and registration with application to CT lung imaging. Comput Med Imaging Graph 2018; 65: 58-68.
87.
Farag AA, Abd El Munim HE, Graham JH, et al. A novel approach for lung nodules segmentation in chest CT using level sets. IEEE Trans Image Process 2013; 22: 5202-13.
88.
Shen S, Bui AA, Cong J, et al. An automated lung segmentation approach using bidirectional chain codes to improve nodule detection accuracy. Comput Biol Med 2015; 57: 139-49.
89.
Zhang W, Wang X, Zhang P, et al. Global optimal hybrid geometric active contour for automated lung segmentation on CT images. Comput Biol Med 2017; 91: 168-80.
90.
Rebouças Filho PP, Cortez PC, da Silva Barros AC, et al. Novel and powerful 3D adaptive crisp active contour method applied in the segmentation of CT lung images. Med Image Anal 2017; 35: 503-16.
91.
Zhang C, Sun X, Dang K, et al. Toward an expert level of lung cancer detection and classification using a deep convolutional neural network. Oncologist 2019; 24: 1159-65.
92.
Nasser IM, Abu-Naser SS. Lung cancer detection using an artificial neural network. Int J Eng Inf Syst 2019; 3: 17-23.
93.
Cifci MA. SegChaNet: a novel model for lung cancer segmentation in CT scans. Appl Bionics Biomech 2022; 2022: 1139587.
94.
Jakimovski G, Davcev D. Using double convolution neural network for lung cancer stage detection. Appl Sci 2019; 9: 427.
95.
Wang J, Wang J, Wen Y, et al. Pulmonary nodule detection in volumetric chest CT scans using CNNs-based nodule-size-adaptive detection and classification. IEEE Access 2019; 7: 46033-44.
96.
Wang C, Chen D, Hao L, et al. Pulmonary image classification based on inception-v3 transfer learning model. IEEE Access 2019; 7: 146533-41.
97.
Liu Y, Hao P, Zhang P, et al. Dense convolutional binary-tree networks for lung nodule classification. IEEE Access 2018; 6: 49080-88.
98.
Li L, Liu Z, Huang H, et al. Evaluating the performance of a deep learning-based computer-aided diagnosis (DL-CAD) system for detecting and characterizing lung nodules: comparison with the performance of double reading by radiologists. Thorac Cancer 2019; 10: 183-92.
99.
Jin H, Li Z, Tong R, et al. A deep 3D residual CNN for false-positive reduction in pulmonary nodule detection. Med Phys 2018; 45: 2097-107.
100.
Teramoto A, Tsukamoto T, Kiriyama Y, et al. Automated classification of lung cancer types from cytological images using deep convolutional neural networks. Biomed Res Int 2017; 2017: 4067832.
101.
Dou Q, Chen H, Yu L, et al. Multilevel contextual 3-D CNNs for false positive reduction in pulmonary nodule detection. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2016; 64: 1558-67.
102.
Wang S, Shi J, Ye Z, et al. Predicting EGFR mutation status in lung adenocarcinoma on computed tomography image using deep learning. Eur Respir J 2019; 53: 1800986.
103.
Wang C, Shao J, Lv J, et al. Deep learning for predicting subtype classification and survival of lung adenocarcinoma on computed tomography. Transl Oncol 2021; 14: 101141.
104.
Ardila D, Kiraly AP, Bharadwaj S, et al. End-to-end lung cancer screening with three-dimensional deep learning on low-dose chest computed tomography. Nat Med 2019; 25: 954-61.
105.
Shao J, Wang G, Yi L, et al. Deep learning empowers lung cancer screening based on mobile low-dose computed tomography in resource-constrained sites. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2022; 27: 212.
106.
Wang C, Xu X, Shao J, et al. Deep learning to predict EGFR mutation and PD-L1 expression status in non-small-cell lung cancer on computed tomography images. J Oncol 2021; 2021: 5499385.
107.
Li R, Xiao C, Huang Y, et al. Deep learning applications in computed tomography images for pulmonary nodule detection and diagnosis: a review. Diagnostics 2022; 12: 298.
108.
Lakshmanaprabu SK, Mohanty SN, Shankar K, et al. Optimal deep learning model for classification of lung cancer on CT images. Future Gener Comput Syst 2019; 92: 374-82.
109.
Lee SM, Seo JB, Yun J, et al. Deep learning applications in chest radiography and computed tomography: current state of the art. J Thorac Imaging 2019; 34: 75-85.
110.
Bhatia S, Sinha Y, Goel L. Lung cancer detection: a deep learning approach. In: Soft Comput for Problem Solving: SocProS 2017, Vol 2. Singapore: Springer Singapore; 2018: 699-705.
111.
Tian P, He B, Mu W, et al. Assessing PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer and predicting responses to immune checkpoint inhibitors using deep learning on computed tomography images. Theranostics 2021; 11: 2098.
112.
Hu D, Zhang H, Li S, et al. Automatic extraction of lung cancer staging information from computed tomography reports: deep learning approach. JMIR Med Inform 2021; 9: e27955.
113.
Ashraf SF, Yin K, Meng CX, et al. Predicting benign, preinvasive, and invasive lung nodules on computed tomography scans using machine learning. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2022; 163: 1496-505.
114.
Subramanian RR, Mourya RN, Reddy VPT, et al. Lung cancer prediction using deep learning framework. Int J Control Autom 2020; 13: 154-60.
115.
Rajasekar V, Vaishnnave MP, Premkumar S, et al. Lung cancer disease prediction with CT scan and histopathological images feature analysis using deep learning techniques. Results Eng 2023; 18: 101111.
116.
Wankhade S, Vigneshwari S. A novel hybrid deep learning method for early detection of lung cancer using neural networks. Healthc Anal 2023; 3: 100195.
117.
Abunajm S, Elsayed N, ElSayed Z, et al. Deep learning approach for early stage lung cancer detection. arXiv 2023; arXiv:2302.02456.
118.
Avanzo M, Stancanello J, Pirrone G, et al. Radiomics and deep learning in lung cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 2020; 196: 879-87.
119.
Chao H, Shan H, Homayounieh F, et al. Deep learning predicts cardiovascular disease risks from lung cancer screening low dose computed tomography. Nat Commu. 2021; 12: 2963.
120.
Shakeel PM, Burhanuddin MA, Desa MI. Lung cancer detection from CT image using improved profuse clustering and deep learning instantaneously trained neural networks. Meas 2019; 145: 702-12.
121.
Zhang Q, Wang H, Yoon SW, et al. Lung nodule diagnosis on 3D computed tomography images using deep convolutional neural networks. Procedia Manuf 2019; 39: 363-70.
122.
Zhao L, Qian J, Tian F, et al. A weighted discriminative extreme learning machine design for lung cancer detection by an electronic nose system. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 2021; 70: 1-9.
123.
Chen L, Liu K, Shen H, et al. Multimodality attention-guided 3-D detection of nonsmall cell lung cancer in 18 F-FDG PET/CT images. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci 2021; 6: 421-32.
124.
Gindi A, Al Attiatalla TA, Sami MM. A comparative study for comparing two feature extraction methods and two classifiers in classification of early-stage lung cancer diagnosis of chest x-ray images. J Am Sci 2014; 10: 13-22.
125.
Suzuki K, Kusumoto M, Watanabe SI, et al. Radiologic classification of small adenocarcinoma of the lung: radiologic-pathologic correlation and its prognostic impact. Ann Thorac Surg 2006; 81: 413-9.
126.
Wang H, Guo XH, Jia ZW, et al. Multilevel binomial logistic prediction model for malignant pulmonary nodules based on texture features of CT image. Eur J Radiol 2010; 74: 124-9.
127.
Horeweg N, Scholten ET, de Jong PA, et al. Detection of lung cancer through low-dose CT screening (NELSON): a prespecified analysis of screening test performance and interval cancers. Lancet Oncol 2014; 15: 1342-50.
128.
Gartman EJ, Jankowich MD, Baptiste J, et al. Providence VA lung cancer screening program: performance: comparison of local false positive and invasive procedure rates to published trial data. In: Clin strategies to improve lung cancer early detection: who is at risk here? Am Thoracic Soci 2018: A2477.
129.
Robbins SL, Kumar V, Abbas AK, et al. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 8th ed. 2010.
130.
Travis WD. Update on small cell carcinoma and its differentiation from squamous cell carcinoma and other non-small cell carcinomas. Mod Pathol 2012; 25: S18-30.
131.
Chan BA, Coward JI. Chemotherapy advances in small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 2013; 5 (Suppl 5): S565.
132.
Sagawa M, Nakayama T, Tsukada H, et al. The efficacy of lung cancer screening conducted in 1990s: four case–control studies in Japan. Lung Cancer 2003; 41: 29-36.
133.
Fontana R. Lung cancer screening: the Mayo Program. J Occup Med 1986; 28: 46-50.
134.
Kubik A, Parkin DM, Khlat M, et al. Lack of benefit from semi-annual screening for cancer of the lung: follow-up report of a randomized controlled trial on a population of high-risk males in Czechoslovakia. Int J Cancer 1990; 45: 26-33.
135.
Raghu VK, Zhao W, Pu J, et al. Feasibility of lung cancer prediction from low-dose CT scan and smoking factors using causal models. Thorax 2019; 74: 643-9.
136.
Risse EK, Vooijs GP, Van’t Hof MA. Relationship between the cellular composition of sputum and the cytologic diagnosis of lung cancer. Acta Cytol 1987; 31: 170-6.
137.
MacDougall B, Weinerman B. The value of sputum cytology. J Gen Intern Med 1992; 7: 11-3.
138.
Kennedy TC, Hirsch FR, Miller YE, et al. A randomized study of fluorescence bronchoscopy versus white-light bronchoscopy for early detection of lung cancer in high-risk patients. Lung Cancer 2000; 29: 244-5.
139.
Toyoda Y, Nakayama T, Kusunoki Y, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of lung cancer screening using chest low-dose computed tomography. Br J Cancer 2008; 98: 1602-7.
140.
Hinton G. Deep learning – a technology with the potential to transform health care. JAMA 2018; 320: 1101-2.
142.
Ueda D, Shimazaki A, Miki Y. Technical and clinical overview of deep learning in radiology. Jpn J Radiol 2019; 37: 15-33.
143.
Nam JG, Park S, Hwang EJ, et al. Development and validation of deep learning–based automatic detection algorithm for malignant pulmonary nodules on chest radiographs. Radiology 2019; 290: 218-28.
144.
Manser R, Lethaby A, Irving LB, et al. Screening for lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013; 2013: CD001991.
145.
Berlin L. Radiologic errors, past, present and future. Diagnosis 2014; 1: 79-84.
146.
Schwartz LH, Litière S, De Vries E, et al. RECIST 1.1 – Update and clarification: From the RECIST committee. Eur J Cancer 2016; 62: 132-7.
147.
Schwyzer M, Ferraro DA, Muehlematter UJ, et al. Automated detection of lung cancer at ultralow dose PET/CT by deep neural networks – initial results. Lung Cancer 2018; 126: 170-3.
148.
Sun W, Zheng B, Qian W. Automatic feature learning using multichannel ROI based on deep structured algorithms for computerized lung cancer diagnosis. Comput Biol Med 2017; 89: 530-9.
149.
Hosny A, Parmar C, Coroller TP, et al. Deep learning for lung cancer prognostication: a retrospective multi-cohort radiomics study. PLoS Med 2018; 15: e1002711.
150.
Tiwari L, Raja R, Awasthi V, et al. Detection of lung nodule and cancer using novel Mask-3 FCM and TWEDLNN algorithms. Meas 2021; 172: 108882.
151.
Wu B, Zhou Z, Wang J, et al. Joint learning for pulmonary nodule segmentation, attributes and malignancy prediction. In: IEEE 15th Int Symp Biomed Imaging (ISBI 2018). 2018: 1109-13.
152.
Liu H, Cao H, Song E, et al. Multi-model ensemble learning architecture based on 3D CNN for lung nodule malignancy suspiciousness classification. J Digit Imaging 2020; 33: 1242-56.
153.
Li J, Tao Y, Cai T. Predicting lung cancers using epidemiological data: a generative-discriminative framework. IEEE/CAA J Autom Sinica 2021; 8: 1067-78.
154.
Xie Y, Zhang J, Xia Y. Semi-supervised adversarial model for benign–malignant lung nodule classification on chest CT. Med Image Anal 2019; 57: 237-48.
155.
Abdani SR, Zulkifley MA. Shahrimin MI, et al. Computer-assisted pterygium screening system: a review. Diagnostics (Basel) 2022; 12: 639.
156.
Zulkifley MA, Moubark AM, Saputro AH, et al. Automated apple recognition system using semantic segmentation networks with group and shuffle operators. Agriculture 2022; 12: 756.
157.
Stofa MM, Zulkifley MA, Zainuri MA. Skin lesions classification and segmentation: a review. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 2021; 12: 532-41.
158.
Stofa MM, Zulkifley MA, Zainuri MA, et al. U-net with atrous spatial pyramid pooling for skin lesion segmentation. in Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Electrical, Control and Computer Engineering: InECCE2021, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia, 23rd August. 2022. Springer.
159.
Xu M, Qi S, Yue Y, et al. Segmentation of lung parenchyma in CT images using CNN trained with the clustering algorithm generated dataset. Biomed Engineering Online 2019; 18: 1-21.
160.
Liu C, Pang M. Automatic lung segmentation based on image decomposition and wavelet transform. Biomed Signal Process Control 2020; 61: 102032.
161.
Khanna A, Londhe ND, Gupta S, et al. A deep residual U-Net convolutional neural network for automated lung segmentation in computed tomography images. Biocybern Biomed Eng 2020; 40: 1314-27.
162.
Comelli A, Coronnello C, Dahiya N, et al. Lung segmentation on high-resolution computerized tomography images using deep learning: a preliminary step for radiomics studies. J Imaging 2020; 6: 125.
163.
Ait Skourt B, El Hassani A, Majda A. Lung CT image segmentation using deep neural networks. Procedia Comput Sci 2018; 127: 109-13.
164.
Hu Q, Souza LFD, Holanda GB, et al. An effective approach for CT lung segmentation using mask region-based convolutional neural networks. Artif Intell Med 2020; 103: 101792.
165.
Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Litjens G, et al. Pulmonary nodule detection in CT images: false positive reduction using multi-view convolutional networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2016; 35: 1160-9.
166.
Negahdar M, Beymer D, Syeda-Mahmood T. Automated volumetric lung segmentation of thoracic CT images using fully convolutional neural network. In: Med Imaging 2018: Comput-Aid Diagn. 2018; 10575: 356-61.
167.
Roy R, Chakraborti T, Chowdhury AS. A deep learning-shape driven level set synergism for pulmonary nodule segmentation. Pattern Recogn Lett 2019; 123: 31-8.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.