Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
HEPATOLOGY / CLINICAL RESEARCH
Survival benefits of chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and chemoradiotherapy in patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a population-based study
1
The Fifth People’s Hospital of Taizhou, China
2
Taizhou Fourth People’s Hospital, China
3
Jiangyin Hospital Affiliated to Nantong University, China
4
The Fifth People’s Hospital of Suzhou, China
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2024-12-04
Final revision date: 2025-02-02
Acceptance date: 2025-02-07
Online publication date: 2025-04-20
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
This population-based study aimed to evaluate the survival benefits of radiotherapy, chemotherapy, chemoradiotherapy, and non-chemoradiotherapy in patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC).
Material and methods:
We used the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database’s SEER*stat software (version 8.3.5) to gather data of patients diagnosed with unresectable ICC from 2000 to 2018. Survival curves were plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method, comparing the overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) among patients who underwent radiotherapy, chemotherapy, chemoradiotherapy, or no therapy at all. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression models were employed to analyze the prognostic factors affecting these unresectable ICC patients.
Results:
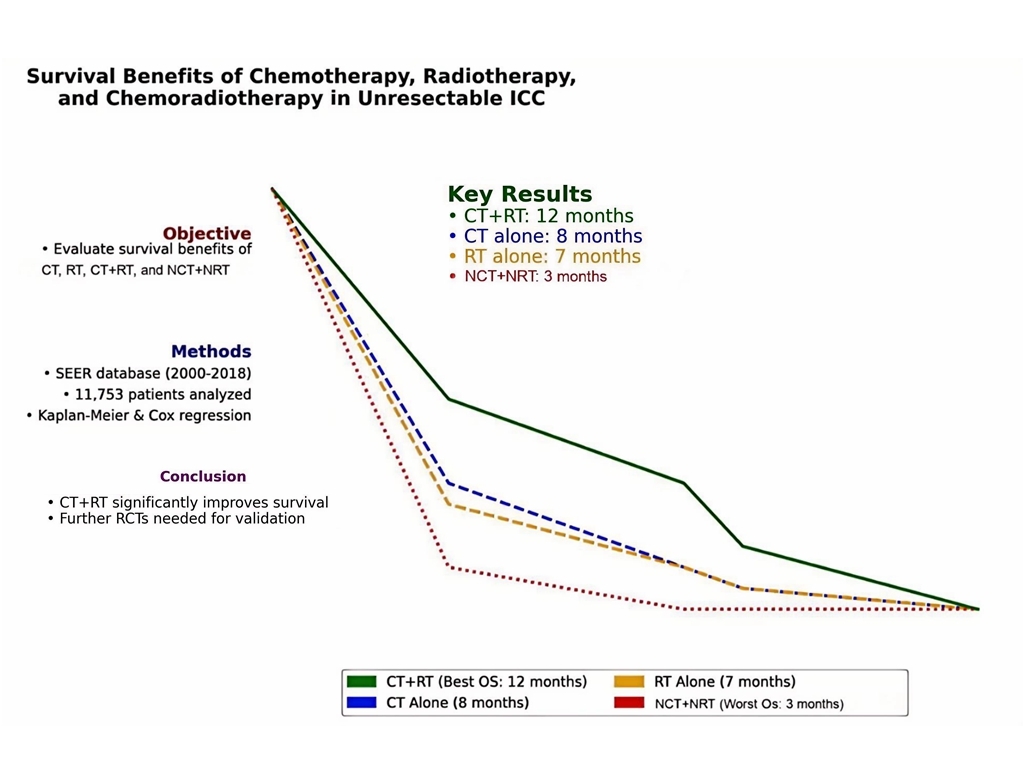
From 2000 to 2018, we identified 11,753 cases of unresectable ICC from the SEER database. Of these, 4,531 (38.5%) patients underwent chemotherapy alone, 482 (4.1%) patients underwent radiotherapy alone, and 996 (8.5%) patients received a combination of both. A total of 5,744 (48.9%) patients did not receive chemoradiotherapy. The median OS was 8 months (95% CI: 8–-9 months) for patients receiving chemotherapy alone, 7 months (95% CI: 6–8 months) for radiotherapy alone, 12 months (95% CI: 11–13 months) for chemoradiotherapy, and 3 months (95% CI: 3–3 months) for those not receiving chemoradiotherapy. The CSS findings were consistent with the OS results. The Cox regression models indicated that patient age, sex, grade classification, tumor diameter, and treatment modality were independent prognostic factors for unresectable ICC patients (p < 0.05).
Conclusions:
Chemoradiotherapy can enhance the OS and CSS of patients with unresectable ICC, compared to the use of chemotherapy or radiotherapy alone.
This population-based study aimed to evaluate the survival benefits of radiotherapy, chemotherapy, chemoradiotherapy, and non-chemoradiotherapy in patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC).
Material and methods:
We used the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database’s SEER*stat software (version 8.3.5) to gather data of patients diagnosed with unresectable ICC from 2000 to 2018. Survival curves were plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method, comparing the overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) among patients who underwent radiotherapy, chemotherapy, chemoradiotherapy, or no therapy at all. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression models were employed to analyze the prognostic factors affecting these unresectable ICC patients.
Results:
From 2000 to 2018, we identified 11,753 cases of unresectable ICC from the SEER database. Of these, 4,531 (38.5%) patients underwent chemotherapy alone, 482 (4.1%) patients underwent radiotherapy alone, and 996 (8.5%) patients received a combination of both. A total of 5,744 (48.9%) patients did not receive chemoradiotherapy. The median OS was 8 months (95% CI: 8–-9 months) for patients receiving chemotherapy alone, 7 months (95% CI: 6–8 months) for radiotherapy alone, 12 months (95% CI: 11–13 months) for chemoradiotherapy, and 3 months (95% CI: 3–3 months) for those not receiving chemoradiotherapy. The CSS findings were consistent with the OS results. The Cox regression models indicated that patient age, sex, grade classification, tumor diameter, and treatment modality were independent prognostic factors for unresectable ICC patients (p < 0.05).
Conclusions:
Chemoradiotherapy can enhance the OS and CSS of patients with unresectable ICC, compared to the use of chemotherapy or radiotherapy alone.
REFERENCES (36)
1.
Massarweh NN, El-Serag HB. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Control 2017; 24: 1073274817729245.
2.
Saha SK, Zhu AX, Fuchs CS, Brooks GA. Forty-year trends in cholangiocarcinoma incidence in the U.S.: intrahepatic disease on the rise. Oncologist 2016; 21: 594-9.
3.
Bridgewater J, Galle PR, Khan SA, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol 2014; 60: 1268-89.
4.
Endo I, Gonen M, Yopp AC, et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: rising frequency, improved survival, and determinants of outcome after resection. Ann Surg 2008; 248: 84-96.
5.
Valle J, Wasan H, Palmer DH, et al. Cisplatin plus gemcitabine versus gemcitabine for biliary tract cancer. N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 1273-81.
6.
Zhang XX, Ma HB, Li TH, Huang B, Jia NY, Meng Y. Actual over 3-year survival after stereotactic body radiation therapy in patients with unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol 2023; 25: 731-8.
7.
Brunner TB, Eccles CL. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy as therapeutic strategies in extrahepatic biliary duct carcinoma. Strahlenther Onkol 2010; 186: 672-80.
8.
Edeline J, Touchefeu Y, Guiu B, et al. Radioembolization plus chemotherapy for first-line treatment of locally advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a phase 2 clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 2020; 6: 51-9.
9.
Valle JW, Borbath I, Khan SA, et al. Biliary cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2016; 27 (Suppl 5): v28-37.
10.
Zhuang L, Yan X, Meng Z. Second primary malignancy in patients with cholangiocarcinoma: a population-based study. Cancer Manag Res 2019; 11: 1969-83.
11.
Zheng YH, Xie K, Shen HY, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics, therapeutic modalities and survival outcomes of plasmablastic lymphoma: a real-world study. Arch Med Sci 2021; 20: 1874-86.
12.
Yang X, RY, Yang R, Xu Y, Zang S. Development and validation of the treatment expectation scale for patients with liver cancer. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 1831-40.
13.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020; 70: 7-30.
14.
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021; 71: 209-49.
15.
Rizzo A, Brandi G. Neoadjuvant therapy for cholangiocarcinoma: a comprehensive literature review. Cancer Treat Res Commun 2021; 27: 100354.
16.
Beal EW, Tumin D, Moris D, et al. Cohort contributions to trends in the incidence and mortality of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 2018; 7: 270-6.
17.
Altman AM, Kizy S, Marmor S, Huang JL, Denbo JW, Jensen EH. Current survival and treatment trends for surgically resected intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. J Gastrointest Oncol 2018; 9: 942-52.
18.
Mukkamalla SKR, Naseri HM, Kim BM, Katz SC, Armenio VA. Trends in incidence and factors affecting survival of patients with cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2018; 16: 370-6.
19.
Yao KJ, Jabbour S, Parekh N, Lin Y, Moss RA. Increasing mortality in the United States from cholangiocarcinoma: an analysis of the National Center for Health Statistics Database. BMC Gastroenterol 2016; 16: 117.
20.
Shaib YH, El-Serag HB, Davila JA, Morgan R, McGlynn KA. Risk factors of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States: a case-control study. Gastroenterology 2005; 128: 620-6.
21.
Burak K, Angulo P, Pasha TM, Egan K, Petz J, Lindor KD. Incidence and risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2004; 99: 523-6.
22.
Toy E, Balasubramanian S, Selmi C, Li CS, Bowlus CL. The prevalence, incidence and natural history of primary sclerosing cholangitis in an ethnically diverse population. BMC Gastroenterol 2011; 11: 83.
23.
Liao X, Zhang D. The 8th Edition American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging for Hepato-pancreato-biliary Cancer: a review and update. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2021; 145: 543-53.
24.
Hwang S, Lee YJ, Song GW, et al. Prognostic Impact of tumor growth type on 7th AJCC Staging System for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: a single-center experience of 659 cases. J Gastrointest Surg 2015; 19: 1291-304.
25.
Spolverato G, Ejaz A, Kim Y, et al. Tumor size predicts vascular invasion and histologic grade among patients undergoing resection of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg 2014; 18: 1284-91.
26.
Okusaka T, Nakachi K, Fukutomi A, et al. Gemcitabine alone or in combination with cisplatin in patients with biliary tract cancer: a comparative multicentre study in Japan. Br J Cancer 2010; 103: 469-74.
27.
Ioka T, Kanai M, Kobayashi S, et al. Randomized phase III study of gemcitabine, cisplatin plus S-1 versus gemcitabine, cisplatin for advanced biliary tract cancer (KHBO1401- MITSUBA). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2023; 30: 102-10.
28.
Chen YX, Zeng ZC, Tang ZY, et al. Determining the role of external beam radiotherapy in unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a retrospective analysis of 84 patients. BMC Cancer 2010; 10: 492.
29.
Zheng X, Chen B, Wu JX, et al. Benefit of adjuvant radiotherapy following narrow-margin hepatectomy in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma that adhere to major vessels. Cancer Manag Res 2018; 10: 3973-81.
30.
Barney BM, Olivier KR, Miller RC, Haddock MG. Clinical outcomes and toxicity using stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for advanced cholangiocarcinoma. Radiat Oncol 2012; 7: 67.
31.
Schartz DA, Porter M, Schartz E, et al. Transarterial yttrium-90 radioembolization for unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2022; 33: 679-86.
32.
Kim YI, Park JW, Kim BH, et al. Outcomes of concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced-stage unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Radiat Oncol 2013; 8: 292.
33.
Torgeson A, Lloyd S, Boothe D, et al. Chemoradiation therapy for unresected extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a propensity score-matched analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 2017; 24: 4001-8.
34.
Song J, Di Y, Kang X, Ren G, Wang Y. Development and validation of a nomogram to predict cancer-specific survival with unresected cholangiocarcinoma undergoing external radiotherapy. Front Public Health 2023; 11: 1012069.
35.
Ben-Josef E, Normolle D, Ensminger WD, et al. Phase II trial of high-dose conformal radiation therapy with concurrent hepatic artery floxuridine for unresectable intrahepatic malignancies. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 8739-47.
36.
Chang WW, Hsiao PK, Qin L, Chang CL, Chow JM, Wu SY. Treatment outcomes for unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Nationwide, population-based, cohort study based on propensity score matching with the Mahalanobis metric. Radiother Oncol 2018; 129: 284-92.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.