Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a prevalent metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia and the prevalence is about 8.8% worldwide [1]. The current managements of T2DM include oral anti-hyperglycemia medications and insulin injection [2, 3]. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have been applied recently to control the hyperglycemic status in T2DM patients [4–6]. According to a previous study, a decrease of 0.71% in glycated hemoglobin level was found after additional application of SGLT2 inhibitors in T2DM individuals compared to dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor monotherapy [7].
In addition to the effect of blood sugar control, SGLT2 inhibitors also illustrate a positive influence on some vital organs [4, 8]. SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetic mice suppressed the autosis of cardiomyocytes, thus reducing the myocardial infarction event rate [9]. Application of SGLT2 inhibitors was also found to decrease the incidence of heart failure in the study by Karagiannis et al. [10]. In addition to cardiovascular diseases, SGLT2 inhibitors can retard the possibility of anemia as well as hyperkalemia in individuals diagnosed with chronic kidney disease [11]. Accordingly, SGLT2 inhibitors might also show a protective effect in other diseases with similar pathophysiology.
Some studies have evaluated the influence of SGLT2 inhibitors on ophthalmic diseases [12, 13]. Development and progression of diabetic retinopathy could be suppressed by the application of SGLT2 inhibitors in some previous research but without a universal consensus [14–18]. It has also been reported that the incidence of dry eye disease could be reduced via use of SGLT2 inhibitors [19, 20]. Still, there is a paucity of studies evaluating the correlation between SGLT2 inhibitors and uveitis development. Since uveitis is an inflammatory ocular disease and SGLT2 inhibitors possess anti-inflammatory ability [21, 22], such a correlation may exist but needs further validation.
Herein, the object of this study is to investigate whether a significant correlation exists between SGLT2 inhibitors and the incidence as well as severity of uveitis via utilization of the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD). The established predisposing factors of uveitis were considered in the multivariable analyses of this study.
Material and methods
Data source
The procedure in this study conformed to the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and related amendments, and this study was approved by both the National Health Insurance Administration of Taiwan and the Institutional Review Board of Chung Shan Medical University Hospital (Project code: CS1-20108). The necessity of written informed consent was waived by the two institutions. Taiwan NHIRD includes insurance-claimed medical data of roughly 23 million individuals from January 1, 2014 to December 31, 2020. The available data of Taiwan NHIRD include International Classification of Diseases-Ninth Revision (ICD-9) as well as International Classification of Diseases-Tenth Revision (ICD-10) diagnostic codes, age, sex, education level, urbanization level of residence, image examination codes, laboratory examination codes, medical department category, procedure codes, surgery codes and international ATC codes for medicines.
Patient selection
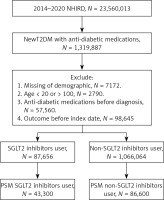
A retrospective cohort study was conducted. Participants with T2DM were regarded as using SGLT2 inhibitors if they achieved the following inclusion criteria: (1) the diagnosis of T2DM via corresponding ICD-9 or ICD-10 codes from 2014 to 2019, (2) visited an internal medicine or family medicine department with an interval of more than 3 months, and (3) the use of SGLT2 inhibitor medications including dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, canagliflozin and ertugliflozin via the ATC codes. The index date of this study was defined as the date 6 months after the initiation of SGLT2 inhibitor treatment. Moreover, the following exclusion criteria were applied to standardize the study population: (1) loss of demographic data, (2) use of anti-diabetic medication before the T2DM diagnosis, (3) patients younger than 20 years or older than 100 years, and (4) the presence of uveitis occurred before the index date. In the next step, each patient in the SGLT2 group was matched to another two T2DM patients who did not use SGLT2 inhibitors, and the latter population constituted the control group. We used the propensity score-matching (PSM) method for matching the two groups, which adjusted for demographic, medical and systemic covariates. After the whole process, 43 300 and 86 600 participants constituted the SGLT2 inhibitor group and the control group, respectively. The flowchart of participant selection is presented in Figure 1.
Primary outcome
The primary outcome in our study was uveitis development based on the following criteria: (1) the uveitis diagnosis according to related ICD-9 diagnostic codes or ICD-10 diagnostic codes, (2) the performance of slit-lamp biomicroscopy examination before or at the time of uveitis diagnosis via the procedure codes, (3) the utilization of topical steroid, intravitreal steroid or immunosuppressant after the uveitis diagnosis via the ATC codes, (4) the uveitis diagnosis was made by an ophthalmologist. Participants in this study were traced until (1) uveitis diagnosis, (2) withdrawal from the National Health Insurance program or (3) deadline of NHIRD: December 31, 2020.
Demographic and systemic confounders
In addition to the primary outcome, we considered specific demographic data and systemic diseases in the statistical model to adjust the effect of these confounders on uveitis occurrence and progression: age, sex, economic level, hypertension, coronary heart disease (CHD), hyperlipidemia, cerebrovascular disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and Sjogren syndrome according to the associated diagnostic codes in the NHIRD. To guarantee that the duration of systemic diseases in our research is long enough to elevate or retard the risk of uveitis occurrence, only systemic diseases with a disease interval longer than 2 years before the index date were included in the statistical analyses.
Statistical analysis
SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC, USA) was employed in statistical analyses of this study. Descriptive analyses were adopted to show the demographics and baseline systemic diseases in the two groups, and the absolute standardized difference (ASD) was used to analyze the difference between the two groups. An ASD value more than 0.1 was set as a significant difference between the two groups. In the next step, Cox proportional hazard regression was used to determine the adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) of uveitis incidence between the two groups, and the effects of all demographic characters and systemic co-morbidities were adjusted in Cox proportional hazard regression. The incidence of anterior and posterior uveitis was further analyzed separately for the two groups. In the subgroup analyses, all the participants were matched by age and sex, and the Cox proportional hazard regression was used again to investigate the incidences of uveitis among different subgroups. The interaction test was conducted to analyze the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on uveitis development in different subgroups. Statistical significance was determined at p < 0.05 in this research and a p-value less than 0.0001 was determined as p < 0.0001.
Results
The demographic characters of the three groups are presented in Table I. The patient distribution of each age interval between the SGLT2 and control groups showed no significant difference (all ASD < 0.1). The male ratio was 65.61% in both the SGLT2 and control groups, which revealed identical distribution (ASD = 0.0000). In addition, the systemic and medical confounders including hypertension, CHD, hyperlipidemia, cerebrovascular accident, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, and ankylosing spondylitis between the two groups demonstrated similar distribution due to the PSM process (all ASD < 0.1) (Table I).
Table I
Characteristic in SGLT2 group and matched diabetes population
There were 147 and 371 new uveitis episodes in the SGLT2 and control groups after the follow-up period up to 5 years (Table II). According to the Cox proportional hazard regression, the incidence of uveitis in the SGLT2 group (aHR = 0.736, 95% CI: 0.602–0.899, p = 0.0007) was significantly lower than that in the control group after adjusting for the effect of all the confounders (Table II). The incidence rates of anterior uveitis (aHR = 0.787, 95% CI: 0.589–0.885, p = 0.0018) and posterior uveitis (aHR = 0.764, 95% CI: 0.626–0.911, p = 0.0014) were also significantly lower in the SGLT2 group than the control group. The other factors that influenced the incidence of uveitis development included rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis (p = 0.0300 and 0.0232) (Table III).
Table II
Comparison of risk of uveitis between SGLT2 and control groups
| Uveitis event | Control group | SGLT2 group | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Person-months | 1784500 | 901886 | |
| Uveitis: | |||
| Event | 371 | 147 | |
| Crude HR (95% CI) | Reference | 0.783 (0.647–0.948)* | |
| aHR (95% CI) | Reference | 0.736 (0.602–0.899)* | 0.0007 |
| Anterior uveitis: | |||
| Event | 296 | 125 | |
| Crude HR (95% CI) | Reference | 0.798 (0.659–0.986)* | |
| aHR (95% CI) | Reference | 0.787 (0.589–0.885)* | 0.0018 |
| Posterior uveitis: | |||
| Event | 75 | 22 | |
| Crude HR (95% CI) | Reference | 0.752 (0.640–0.929)* | |
| aHR (95% CI) | Reference | 0.764 (0.626–0.911)* | 0.0014 |
Table III
Effect of each parameter on development of uveitis
| Parameters | aHR | 95% CI | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 0.736 | 0.602–0.899 | 0.0007* |
| Age | 1.044 | 0.874–1.740 | 0.3110 |
| Male sex | 1.348 | 0.892–2.007 | 0.0987 |
| Economic level | 0.925 | 0.667–1.568 | 0.9030 |
| Co-morbidity: | |||
| Hypertension | 1.169 | 0.792–1.220 | 0.8817 |
| CHD | 1.295 | 0.836–1.909 | 0.2461 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.843 | 0.556–1.561 | 0.7948 |
| Cerebrovascular accident | 0.916 | 0.702–1.576 | 0.6599 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 1.562 | 1.176–2.543 | 0.0300* |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | 1.698 | 0.517–3.480 | 0.1529 |
| Sjogren syndrome | 1.211 | 0.835–1.934 | 0.2258 |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | 1.377 | 1.266–2.305 | 0.0232* |
In the subgroup analyses, the T2DM patients under SGLT2 inhibitor treatment and aged under 50 years old demonstrated significantly lower incidence of uveitis than the T2DM patients under SGLT2 inhibitor treatment but over 50 years old (p = 0.0012) (Table IV). Nevertheless, the uveitis incidence of sex subgroups did not show a significant difference between patients who received different T2DM treatments (p = 0.6716) (Table IV).
Table IV
Subgroup analyses of T2DM patients under SGLT2 inhibitor treatment for uveitis development stratified by age and sex
| Parameters | aHR | 95% CI | P-value for interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age: | 0.0012* | ||
| < 50 | 0.628 | 0.572–0.844 | |
| ≥ 50 | 0.808 | 0.662–0.958 | |
| Sex: | 0.6716 | ||
| Male | 0.759 | 0.618–0.920 | |
| Female | 0.722 | 0.600–0.876 |
Discussion
In this study, the incidence of uveitis was significantly lower in the T2DM patients who received SGLT2 inhibitors compared to the patients who received other T2DM treatment after adjusting for multiple confounders. The incidence rates of anterior uveitis and posterior uveitis were also significantly lower in the SGLT2 group. Furthermore, the influence of SGLT2 inhibitors on the uveitis incidence was more prominent in patients younger than 50 years.
SGLT2 inhibitors exert a protective effect in many sites of the human body in addition to T2DM control [11, 23, 24]. Patients with T2DM and chronic kidney disease were found to have a significantly lower risk of macroalbuminuria, kidney transplantation and kidney death under the application of SGLT2 inhibitors [25]. SGLT2 inhibitors could ameliorate proximal tubule hyperreabsorption and decrease diabetic glomerular hyperfiltration [8]. SGLT2 inhibitors also had a protective effect on the cardiovascular system in which the incidence of myocardial infarction significantly decreased in mice that received SGLT2 inhibitor application [9]. Furthermore, the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events and cardiovascular death was decreased in individuals under SGLT2 inhibitor therapy [26]. In addition, a study showed that the microvascular damage as well as endothelial dysfunction in cardiac ischemia could be retarded by the utilization of SGLT2 inhibitors [27]. In the molecular aspect, SGLT2 inhibitors could decrease the inflammatory reaction, including adipose tissue-mediated inflammation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production [22]. In other research, SGLT2 inhibitors ameliorated the inflammatory response in arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy and autoimmune myocarditis [28, 29]. In addition, suppression of inflammation was observed in patients with diabetic kidney disease using SGLT2 inhibitors [30]. Similarly, uveitis is an ocular disease that manifests with inflammation in the iris, ciliary body and choroid [21]. Several immunosuppressants, including antimetabolites and calcineurin inhibitors, were applied to treat severe uveitis, with acceptable outcome [31]. Since SGLT2 inhibitors can suppress the inflammatory reaction in CHD [32], they may also reduce the inflammation in uveitis and lead to lower incidence of uveitis. The above concept was supported by the findings of this study.
The application of SGLT2 inhibitors correlates with a significantly lower incidence of uveitis in T2DM patients compared to other anti-diabetic treatment. To our knowledge, this is a relatively novel finding suggesting the possible association between SGLT2 inhibitor usage and lower uveitis incidence. Furthermore, several known risk factors for uveitis development including age, sex, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and Sjögren syndrome were adjusted in the Cox proportional hazard regression, and we excluded pre-existing uveitis before the index date in this study. As a consequence, SGLT2 inhibitor usage may be an independent protective factor for uveitis development in T2DM individuals. A previous study demonstrated that SGLT2 inhibitors were not associated with uveal disease, but the small number of cases of uveal disease in that study may have caused statistical bias [13]. A possible explanation for our finding is that the anti-inflammatory effect of SGLT2 inhibitors suppresses the inflammatory reaction [30], and the inflammation is correlated with uveitis development [21]. Regarding the incidence of anterior uveitis and posterior uveitis, both rates showed a significantly lower value in the SGLT2 group, which may indicate the universal effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on uveitis suppression. Since individuals with T2DM have a higher baseline inflammatory level than the normal population [33], SGLT2 inhibitors may play a crucial role in such a population, but this need further validation.
Concerning the subgroup analyses stratified by different conditions, the T2DM patients receiving SGLT2 inhibitors and aged younger than 50 years displayed significantly lower incidence of uveitis development than the control group. There is a paucity of studies examining this correlation in different age populations. A previous study demonstrated that the SGLT2 inhibitors yielded a better therapeutic outcome in T2DM patients younger than 40 years compared to T2DM individuals older than 40 years [34]. It was postulated that the higher urinary glucose excretion may be the reason for the better response of SGLT2 inhibitors in the youth [34], and this may explain the lower dry eye disease (DED) incidence in the young population of our study, since hyperglycemia could contribute to DED [35]. The sex-stratified subgroup analyses did not reveal a statistically significant difference in the incidence of uveitis in the SGLT2 subgroup compared to the control subgroups. This finding corresponded to the results reported in previous publications that the SGLT2 inhibitors showed a similar effect in systemic co-morbidities [36, 37]. Perhaps the result would become significant with more participants, which needs further research to clarify.
In the epidemiological aspect, T2DM is one of the most prevalent chronic diseases in the world [1]. According to previous publications, the incidence of T2DM was approximately 8.8% in Europe while the highest incidence was found in the Caribbean region, at about 13% [1]. In addition, an increasing trend was predicted for the prevalence of all diabetes, which may grow by about 50% by 2040 compared to 2015 [38]. Uveitis, although not as prevalent as T2DM, still has an incidence from 17 to 52 per 100,000 individuals every year [39]. In addition, the incidence of uveitis-induced unilateral blindness was 2.93 per 1,000 person-years in the uveitis population [40]. Since neither T2DM nor uveitis is a rare disease and progression of uveitis could cause blindness, T2DM treatment that is associated with lower risk of uveitis might be illustrated.
Nevertheless, this study still has some limitations. Firstly, we used the reported data rather than the real medical document; thus several critical aspects of information including the severity of T2DM, the level of blood sugar, the change of blood sugar after anti-diabetic treatment, the severity of uveitis, the exact etiology of uveitis, the results of uveitis-related laboratory examination, the treatment outcome of uveitis and the severity of systemic co-morbidities cannot be accessed. Secondly, intermediate uveitis and panuveitis were not analyzed in the current study due to the extremely low numbers of cases. Finally, in some cases uveitis may have been misdiagnosed as conjunctivitis or keratitis before the index date and recurred after the index date, and was recognized at that time. However, the design of our database cannot separate these cases from the fresh uveitis cases after the index date, which thus could contribute to some bias.
In conclusion, the use of SGLT2 inhibitors is correlated with a lower incidence of uveitis including anterior uveitis and posterior uveitis development in T2DM patients after adjusting for multiple risk factors of uveitis. Furthermore, the protective effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on uveitis development is more significant in patients younger than 50 years. Consequently, the use of SGLT2 inhibitors might be considered in T2DM patients with predisposing factors for uveitis. Further large-scale prospective research to investigate the potential influence of SGLT2 inhibitors on the therapeutic outcome and prognosis of uveitis is necessary.