Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
CLINICAL RESEARCH
EGCG suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by reducing PACRG methylation via inhibition of DNA methyltransferases
1
Department of Nutrition, Eye & ENT Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
2
State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering, Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Industrial Microorganisms, School of Life Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Submission date: 2025-05-29
Final revision date: 2025-08-20
Acceptance date: 2025-08-22
Online publication date: 2025-10-28
Corresponding author
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
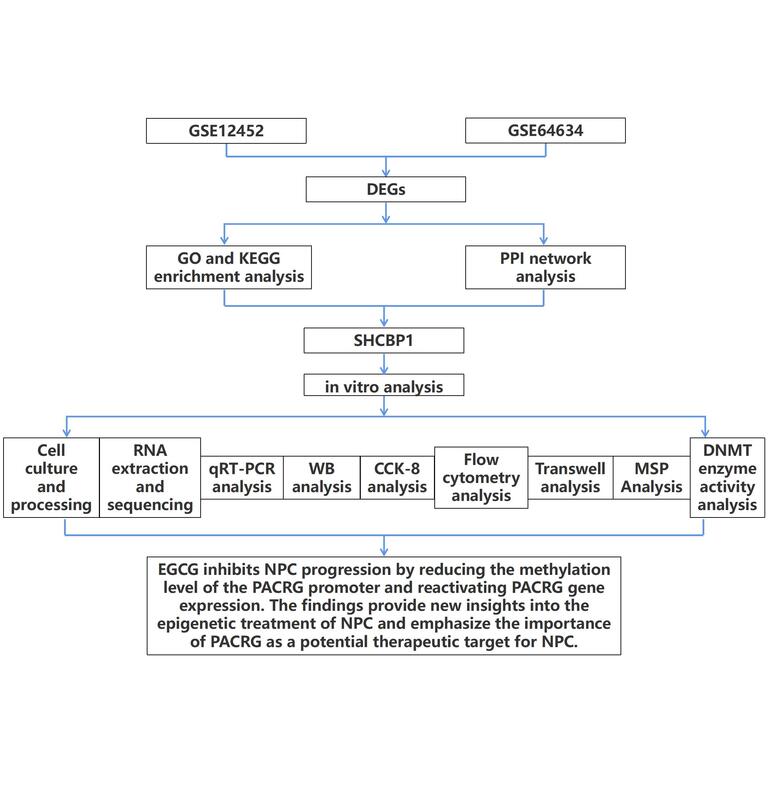
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a serious cancer with a poor prognosis and a significant risk of metastasis. Although its epigenetic control mechanisms are still unknown, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) exhibits strong anticancer properties. Promoter methylation in malignancies often silences PACRG, a putative tumor suppressor gene. This study aimed to determine whether EGCG suppresses cancer by altering PACRG gene expression in NPC cells.
Material and methods:
NPC cells were subjected to EGCG or 5-aza-dC. Cellular functions were assessed by CCK-8, Transwell, and flow cytometry assays. Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) was used to identify PACRG promoter methylation, and gene expression was measured using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blot (WB). The expression of DNA methyltransferase-related genes was evaluated. siRNA targeting PACRG was used to assess its functional involvement in the effects mediated by EGCG.
Results:
EGCG exerted dose- and time-dependent effects on NPC cells by reducing proliferation and migration while inducing apoptosis and G2 phase cell cycle arrest. Mechanistically, EGCG significantly reduced the mRNA expression and enzymatic activity of DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B, resulting in decreased PACRG promoter methylation and restored PACRG expression. Functional assays revealed that knockdown of PACRG diminished the inhibitory effect of EGCG on NPC cells, indicating that the epigenetic reactivation of PACRG partially mediates the tumor-suppressive function of EGCG.
Conclusions:
Our results revealed that EGCG inhibits NPC progression by reducing PACRG promoter methylation, highlighting that PACRG demethylation and reactivation are a promising therapeutic strategy.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a serious cancer with a poor prognosis and a significant risk of metastasis. Although its epigenetic control mechanisms are still unknown, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) exhibits strong anticancer properties. Promoter methylation in malignancies often silences PACRG, a putative tumor suppressor gene. This study aimed to determine whether EGCG suppresses cancer by altering PACRG gene expression in NPC cells.
Material and methods:
NPC cells were subjected to EGCG or 5-aza-dC. Cellular functions were assessed by CCK-8, Transwell, and flow cytometry assays. Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) was used to identify PACRG promoter methylation, and gene expression was measured using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blot (WB). The expression of DNA methyltransferase-related genes was evaluated. siRNA targeting PACRG was used to assess its functional involvement in the effects mediated by EGCG.
Results:
EGCG exerted dose- and time-dependent effects on NPC cells by reducing proliferation and migration while inducing apoptosis and G2 phase cell cycle arrest. Mechanistically, EGCG significantly reduced the mRNA expression and enzymatic activity of DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B, resulting in decreased PACRG promoter methylation and restored PACRG expression. Functional assays revealed that knockdown of PACRG diminished the inhibitory effect of EGCG on NPC cells, indicating that the epigenetic reactivation of PACRG partially mediates the tumor-suppressive function of EGCG.
Conclusions:
Our results revealed that EGCG inhibits NPC progression by reducing PACRG promoter methylation, highlighting that PACRG demethylation and reactivation are a promising therapeutic strategy.
REFERENCES (26)
1.
Wong KC, Hui EP, Lo KW, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2021; 18: 679-95.
2.
Su ZY, Siak PY, Leong CO, Cheah SC. The role of Epstein–Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Front Microbiol 2023; 14: 1116143.
3.
Stan D, Niculet E, Lungu M, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a new synthesis of literature data. Exp Ther Med 2022; 23: 136.
4.
Bayatfard P, Sari SY, Yazici G. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. JAMA Oncol 2024; 10: 1292.
5.
Zhang J, Tang H, Li H, Jiang D, Luo H. Case report of chemoradiotherapy combined with immunotherapy for liver metastasis and lymph node metastases in the head of the pancreas of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Arch Med Sci 2022; 18: 1413-9.
6.
Song X, Wang S, Li J, Yan L, Chen F, Wang J. Induction chemotherapy plus nimotuzumab followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy for advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Arch Med Sci 2021; 17: 1317-24.
7.
Wang S, Li Z, Ma Y, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of green tea polyphenols. Molecules 2021; 26: 3755.
8.
Ferrari E, Bettuzzi S, Naponelli V. The potential of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) in targeting autophagy for cancer treatment: a narrative review. Int J Mol Sci 2022; 23: 6075.
9.
Khiewkamrop P, Surangkul D, Srikummool M, et al. Epigallocatechin gallate triggers apoptosis by suppressing de novo lipogenesis in colorectal carcinoma cells. FEBS Open Bio 2022; 12: 937-58.
10.
Jiang S, Huang C, Zheng G, et al. EGCG inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis through downregulation of SIRT1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Front Nutr 2022; 9: 851972.
11.
Fang CY, Wu CC, Hsu HY, et al. EGCG inhibits proliferation, invasiveness and tumor growth by up-regulation of adhesion molecules, suppression of gelatinases activity, and induction of apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Sci 2015; 16: 2530-58.
12.
Li YJ, Wu SL, Lu SM, et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits nasopharyngeal cancer stem cell self-renewal and migration and reverses the epithelial–mesenchymal transition via NF-B p65 inactivation. Tumor Biol 2015; 36: 2747-61.
13.
He C, Zhou J, Wang D, Wang R, Wu M, Dong T. PLAGL1 gene demethylation induced by epigallocatechin gallate promotes pheochromocytoma cell apoptosis via Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2022; 23: 2119-25.
14.
Morris J, Moseley VR, Cabang AB, et al. Reduction in promotor methylation utilizing EGCG (epigallocatechin-3-gallate) restores RXR expression in human colon cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016; 7: 35313.
15.
Agarwal A, Kansal V, Farooqi H, Prasad R, Singh VK. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), an active phenolic compound of green tea, inhibits tumor growth of head and neck cancer cells by targeting DNA hypermethylation. Biomedicines 2023; 11: 789.
16.
Zhang W, Yang P, Gao F, Yang J, Yao K. Effects of epigallocatechin gallate on the proliferation and apoptosis of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE2. Exp Ther Med 2014; 8: 1783-8.
17.
Zhang L, Rong W, Ma J, et al. Comprehensive analysis of DNA 5-methylcytosine and N6-adenine methylation by nanopore sequencing in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Cell Devel Biol 2022; 10: 827391.
18.
Han B, Yang X, Zhang P, et al. DNA methylation biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One 2020; 15: e0230524.
19.
Toma MI, Wuttig D, Kaiser S, et al. PARK2 and PACRG are commonly downregulated in clear‐cell renal cell carcinoma and are associated with aggressive disease and poor clinical outcome. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013; 52: 265-73.
20.
Agirre X, Román‐Gómez J, Vázquez I, et al. Abnormal methylation of the common PARK2 and PACRG promoter is associated with downregulation of gene expression in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and chronic myeloid leukemia. Int J Cancer 2006; 118: 1945-53.
21.
Noël A, Ghosh A. Carbonyl profiles of Electronic Nicotine Delivery System (ENDS) aerosols reflect both the chemical composition and the numbers of E-Liquid ingredients-focus on the in vitro toxicity of strawberry and vanilla flavors. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022; 19: 16774.
22.
Kafetzopoulos I, Taglini F, Davidson-Smith H, Sproul D. DNMT1 loss leads to hypermethylation of a subset of late replicating domains by DNMT3A. bioRxiv 2024: 2024.12.19.629414.
23.
Lauria A, Meng G, Proserpio V, et al. DNMT3B supports meso-endoderm differentiation from mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Commun 2023; 14: 367.
24.
Araki T, Hamada K, Myat AB, et al. Enhanced cytotoxicity on cancer cells by combinational treatment of PARP inhibitor and 5-azadeoxycytidine accompanying distinct transcriptional profiles. Cancers 2022; 14: 4171.
25.
Li BB, Huang GL, Li HH, Kong X, He ZW. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate modulates microrna expression profiles in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE2 cells. Chin Med J 2017; 130: 93-9.
26.
Ramesh N, Mandal AKA. Encapsulation of epigallocatechin-3-gallate into albumin nanoparticles improves pharmacokinetic and bioavailability in rat model. 3 Biotech 2019; 9: 238.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.