Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ONCOLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
Effect of IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17A on Predicting Treatment Outcomes in PD-1 Blockade Immunochemotherapy in Advanced Gastric Cancer
1
Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Affiliated People’s Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, 212002 Jiangsu People’s Republic of China
2
School of Medicine, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China
3
School of Medicine, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, 212013, China
4
Department of Oncology, Institute of Digestive Diseases, The Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu 212001, China
5
Department of Breast Surgery, Jiangsu University Affiliated People's Hospital, Zhenjiang, 212013, China
Submission date: 2025-02-13
Final revision date: 2025-05-15
Acceptance date: 2025-05-24
Online publication date: 2025-06-25
Corresponding author
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Advanced gastric cancer (AGC) treatment outcomes are improved with PD-1 blockade immunochemotherapy, but predicting responders remains challenging. Cytokines, key immune response regulators, may predict treatment outcomes. Aims: This study investigates the potential of cytokines as predictive biomarkers in AGC patients.
Material and methods:
In this retrospective analysis, 241 patients with AGC were included, with 136 patients receiving an immunochemotherapy regimen that included PD-1 blockade, while 105 patients constituted the control group receiving chemotherapy alone. Serum levels of various cytokines (IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-1β, IL-17A, IFN-α2, IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-12p70) were measured using a Luminex after the initiation of treatment.
Results:
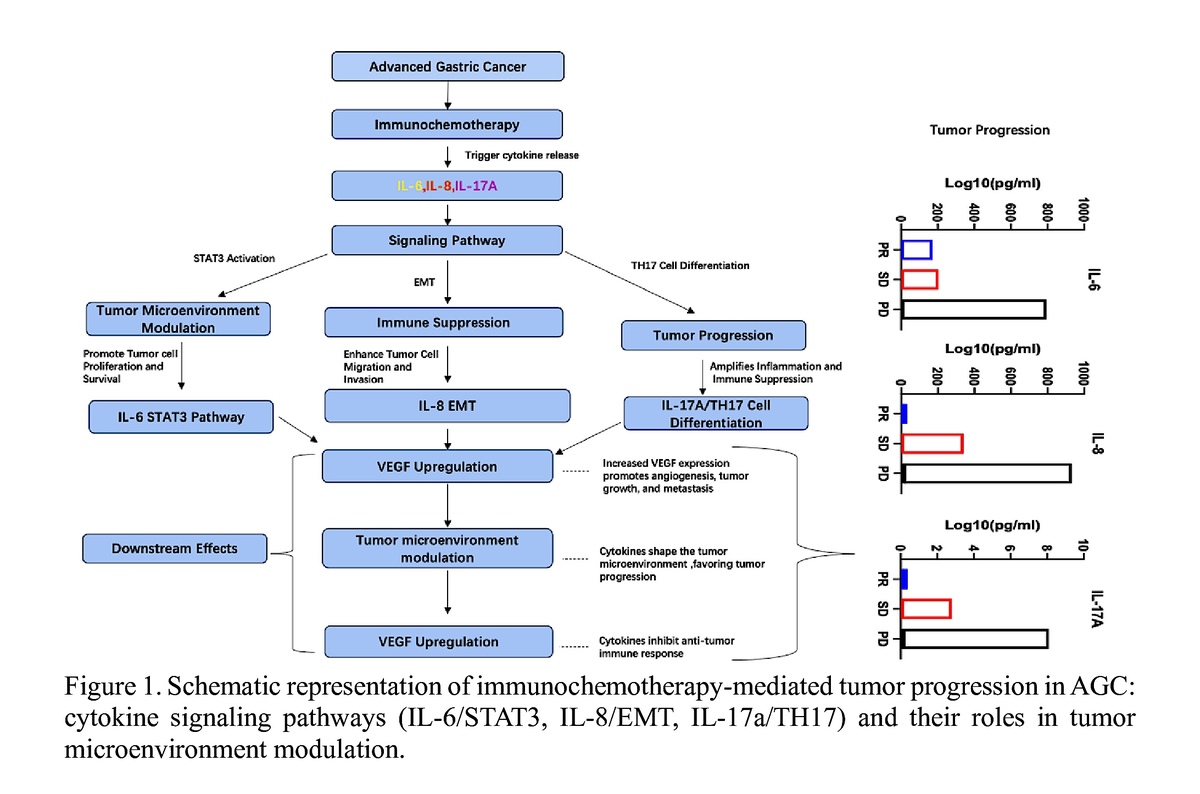
Patients undergoing PD-1 blockade immunochemotherapy demonstrated a significant elevation in the levels of IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17A, especially within the group that exhibited a therapeutic response, when compared to the control group. Notably, among those who responded to the immunochemotherapy, there was a marked reduction in the concentrations of IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17A over the course of the treatment. In contrast, such reductions were not observed in the non-response group. Among the assessed cytokines, the combined evaluation of IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17A, in conjunction with CA-125, demonstrated the highest predictive accuracy for assessing the efficacy of immunochemotherapy in AGC patients.
Conclusions:
Our study identifies IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17A cytokines as predictive biomarkers for treatment outcomes in AGC patients receiving immunochemotherapy. Combining these cytokines with CA-125 significantly enhances predictive accuracy, enabling tailored treatment strategies to improve patient outcomes.
Advanced gastric cancer (AGC) treatment outcomes are improved with PD-1 blockade immunochemotherapy, but predicting responders remains challenging. Cytokines, key immune response regulators, may predict treatment outcomes. Aims: This study investigates the potential of cytokines as predictive biomarkers in AGC patients.
Material and methods:
In this retrospective analysis, 241 patients with AGC were included, with 136 patients receiving an immunochemotherapy regimen that included PD-1 blockade, while 105 patients constituted the control group receiving chemotherapy alone. Serum levels of various cytokines (IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-1β, IL-17A, IFN-α2, IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-12p70) were measured using a Luminex after the initiation of treatment.
Results:
Patients undergoing PD-1 blockade immunochemotherapy demonstrated a significant elevation in the levels of IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17A, especially within the group that exhibited a therapeutic response, when compared to the control group. Notably, among those who responded to the immunochemotherapy, there was a marked reduction in the concentrations of IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17A over the course of the treatment. In contrast, such reductions were not observed in the non-response group. Among the assessed cytokines, the combined evaluation of IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17A, in conjunction with CA-125, demonstrated the highest predictive accuracy for assessing the efficacy of immunochemotherapy in AGC patients.
Conclusions:
Our study identifies IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17A cytokines as predictive biomarkers for treatment outcomes in AGC patients receiving immunochemotherapy. Combining these cytokines with CA-125 significantly enhances predictive accuracy, enabling tailored treatment strategies to improve patient outcomes.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.