Introduction
Colon cancer or colorectal cancer is one of the most important cancers in the gastrointestinal system. Exercising most days of the week, eating a variety of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, stopping smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight reduce the occurrence of colon cancer [1–4]. A history of polyps, obesity, smoking, inflammatory intestinal conditions, inherited syndromes, radiation therapy, diabetes, colon cancer family history, older age, high-fat diet, alcohol, African-American race, and sedentary lifestyle are the main risk factors of colon cancer [1, 2]. Colon cancer signs are weight loss, blood in the stool, nausea or vomiting, worsening constipation, anemia or rectal bleeding, change in bowel movements, loss of appetite, decrease in stool caliber, and feeling tired all the time [1, 2]. Radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and surgery are the therapeutic options for colon carcinoma [4]. Due to the severe side effects of chemotherapy, researchers are studying new formulations such as herbal medicine to treat colon carcinoma [5, 6].
Science history is an enticing field of humanity’s interdisciplinary knowledge and study. Medical science is one of the interesting fields of science history all of the world, as the ancient civilized nation has a long medical history with world-famous citizens [6]. From ancient times and when man entered the world, he always tried to strive for a better livelihood and meet his needs. In this regard, gaining valuable experiences created only by chance has led to the use of nature around them to improve life for consecutive years [6, 7]. The most valuable experience that is now a relic of the ancients and the wealth gained from them by modern man is the use of plants as the most natural substances around him for the treatment and even prevention of diseases, which of course is easier than cure [8, 9]. The science of using medicinal plants is one of the most important medical sciences in the world and its importance was such that some countries tried to plant and harvest some of the most important ones [6, 7]. Today, despite the high volume of chemical products with chemical sources, as well as the occurrence of various and incurable diseases, as well as the rapid treatment of diseases with synthetic drugs that reduce the pain and suffering of the disease, replacing medicinal plants for their treatment, which has an almost longer treatment process than chemical drugs, seems difficult and even unlikely [7–14]. Ethnomedicinal herbs as a source of necessary chemical compositions gained much attention to treat, control, and prevent many ills and promote body health. Many plants are used for their antibacterial property [6–8]. Due to the current progression in the herb extraction methodology, ethnomedicinal plants are extracted in various ways [15–18]. One of the medicinal plant compound extraction methods is an aqueous extract. In recent years, interest in aqueous extracts has increased for pharmacological experiments and it appears that aqueous extracts have been useful to treat, control, and prevent animal and human bacterial infections [16–18].
In recent years, it has been shown that traditional medicine herbs play an important role in the prevention and treatment of various cancers. Some of these plants are used directly to treat cancer, and some reduce the toxic effects of chemotherapeutic drugs [4–6]. One of the plants that has long been considered by humans is Equisetum arvense L. It has two types of aerial stems: the red stem of this plant appears at the beginning of spring and the infertile stem, which is green. The green stem of Equisetum arvense L grows after the red stem and is widely used in medical treatments. The plant is distributed throughout Europe and grows in humid areas and swampy pastures in the Middle East. Equisetum arvense L is a flowerless perennial plant with a black rhizome with two types of stems (a spring stem and a summer stem) and the part used for this plant is its infertile bases that contain chlorophyll particles [19–22]. The chemical composition of the leaves of Equisetum arvense L includes: silicic acid, oxalic, malic, aconitic, glucoside, alkaloids and salts of aluminum and potassium and a type of saponin called equisetin [22]. In traditional medicine, Equisetum arvense L is considered as an effective medicine to treat wounds and ulcers due to its free silica. This plant also has a role in increasing the elasticity and resistance of the skin and can have a beneficial therapeutic effect in tissue death in cases of cell death [19–21]. In contemporary American herbal medicine, Equisetum arvense L is now recommended for external use to heal wounds and for internal use to relieve urinary tract and prostate disorders. In animal husbandry, Equisetum arvense L is used as fodder for lactating cows, which is very effective for increasing milk [19–22]. Studies have shown that colloidal silica in Equisetum arvense L increases the elasticity and resistance of the skin. Equisetum arvense L contains a substance called flavonoids and therefore has antioxidant properties and strengthens blood vessels [20–22]. This plant strengthens hair and nails, and thickens and shines hair. In traditional medicine, due to the extraordinary antioxidant effects of Equisetum arvense L, it is used to treat various cancers such as skin, stomach, colon and prostate cancers [23].
We assessed the effects of Equisetum arvense L in cytotoxicity studies against common human colorectal carcinoma cell lines, i.e., HT-8 [HRT-18], Ramos.2G6.4C10, HT-29, and HCT 116, in vitro. Also, the antioxidant properties of Equisetum arvense L against DPPH free radicals were assessed.
Material and methods
Material
Bovine serum, antimycotic antibiotic solution, 2,2-diphenyl-1-pikrilhydrazil (DPPH), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), fetal bovine serum, 4-(dimethylamino) benzaldehyde, hydrolysate, Ehrlich solution, borax-sulfuric acid mixture, and Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) were all obtained from the US company Sigma-Aldrich.
Preparation of plant extract
The leaves of Equisetum arvense were ground and macerated in ethanol : water (70 : 30) for 48 h. Next, the solvent was evaporated using a Heidolph evaporator (50°C). Then the obtained extract was dried under a hood.
Determination of total phenolic content (TPC)
Methods described by Mohsen Abadi et al. were used to evaluate the total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), radical scavenging activity (RSA) and ferrous ion chelating (FIC) of the plant extract [23].
1 ml of Folin-Ciocalteu’s reagent (10% in distilled water) was added to 1 ml of the plant extract (100 µg/ml in methanol) and 3 ml of distilled water. After 10 min, 4 ml of Na2CO3 (5%) was added and shaken vigorously, The reaction mixture was put in a dark place for 2 h at room temperature. The absorbance was read at 760 nm using a Cary 50 UV-Vis. instrument. The analyses were repeated three times. The TPC extract was measured in mg GAE/g extract (GAE), that is, mg of gallic acid equivalent per gram of dried extract.
Determination of total flavonoid content (TFC)
1 ml of AlCl3 in methanol (2%) was poured into 2 ml of the plant extract solution (100 µg/ml). The mixture was kept at room temperature for 30 min. Next, the absorbance was read at 415 nm. The analyses were carried out in triplicate. A standard curve rutin was used to calculate the extract TFC in terms of mg RuE/g extract.
Determination of radical scavenging activity (RSA)
3 ml of the extract in methanol (20–100 µg/ml) was added to 2 ml of DPPH (0.1 mM). Then, the reaction mixture was stirred and kept in a dark place for 1.5 h. Next, the optical density was read at 517 nm. The result was compared to the positive controls of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) and α-tocopherol (Toc). The assay was run in triplicate. The following equation was used to calculate the RSA: RSA% = [(Ac – As)/Ac] × 100, Ac = control (DPPH solution without extract) absorbance; As = extract absorbance (extract with DPPH solution).
Ferrous ion chelating ability assay
200 µl of ferrozine (5 mM) was added to 100 µl of FeSO4 (2 mM), 1 ml of the plant extract solution in methanol (80–320 µg/ml), and 2 ml of distilled water. The reaction mixture was vibrated and incubated at room temperature for 10 min. The mixture absorbance was analyzed at 562 nm. All measurements were carried out three times. EDTA and AscA (ascorbic acid) were used as the positive controls. The following equation was used to express the plant extract FIC: % Inhibition = [(Ac – As)/Ac] × 100, Ac = control (contains FeSO4, ferrozine, and water) absorbance, and As = sample absorbance.
Assessment of anti-human colorectal carcinoma potentials of Equisetum arvense L
MTT is a colorimetric technique. Based on the fact that living cells can carry out oxidative metabolism, as a result, oxidation breaks down the MTT dye and produces a dye ranging from yellow to blue. This test determines the number of living cells [8].
In this assay, following human colorectal carcinoma and normal cell lines were used to study the cytotoxicity and anticancer potential of Equisetum arvense L against human colorectal cancer using a common cytotoxicity test, i.e., MTT assay in in vitro conditions:
Human colorectal carcinoma cell lines: colorectal adenocarcinoma (HT-29), colorectal carcinoma (HCT 116), ileocecal colorectal adenocarcinoma (HCT-8 [HRT-18]), and Burkitt’s lymphoma (Ramos.2G6.4C10).
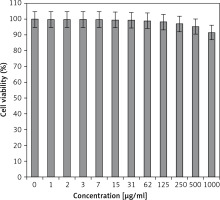
Normal cell line: HUVEC.
15 ml of RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% FSC (10 mg/ml penicillin and 100 mg/ml streptomycin) in a culture flask, placed in a CO2 incubator for 2 h to equilibrate the medium. Under safe conditions (using insulated gloves and goggles) the frozen cell vial was removed from the nitrogen storage tank. In order to avoid the possibility of explosion of the vial (due to the possible entry of liquid nitrogen into the vial), loosen the lid, after disinfecting the outer surface of the vial with 70% alcohol, under the hood to remove nitrogen gas. The closed vial lid again and immediately melted it in a pan at 37°C. The melting process was completed in about 1 min and the cells was avoided from overheating. The medium was added dropwise to the vial and then its contents were taken out and centrifuged with the medium in 15 ml sterile test tubes. After centrifugation, the supernatant was removed and the cells were suspended again in the medium and transferred to a pre-prepared flask containing the medium and FBS and incubated [8].
The cell line used in RPMI 1640 medium containing penicillin (100 IU/ml), streptomycin (100 IU/ml), glutamine (2 mmol) and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). They were incubated at 37°C and in an atmosphere containing 0.5 CO2. Cells began to grow in 75 cm2 T-flasks in 15 ml of medium with an initial number of 1–2 × 106 cells. After 3 days and covering the flask bed with the cells, the adhesive layer to the bottom of the flask was separated enzymatically using trypsin-version and transferred to a sterile test tube for 10 min at 1200 rpm. The cells were then suspended in a fresh culture medium using a Pasteur pipette and the suspension was poured into 100-well plate flat wells (for cell culture) using an 8-channel sampler of 100 μl.
One column of wells was kept cell-free, containing only culture medium. Another column contain culture medium and healthy cells; next columns contain culture medium and cell line cells. One of these columns, which contained culture medium and cells and did not contain Equisetum arvense L aqueous extract, was considered as a control [8].
The plates were incubated in the incubator for 24 h to return the cells to normal from the stress of trypsinization. After this time, suitable dilutions of the prepared Equisetum arvense L aqueous extract (0–1000 µl/ml) and 100 μl of each dilution were added in columns to the plate wells. The cells were incubated for 37 h at 37°C and 5% CO2 in the atmosphere. After 72 h, 20 μl of MTT solution (5 mg/ml) was added to each well. The plates were incubated for 3 to 4 h and then the residue was removed and 100 μl of DMSO was added to each well to dissolve the resulting formazan. After 10 min, using shaking of the plates, the optical absorption of formazan at 570 nm was read using a plate reader. Wells containing cells without Equisetum arvense L aqueous extract were considered as controls and the optical density of wells without cells and only culture medium were considered as blanks. The percentage of cell viability was calculated using the following formula [8]: Cell viability (%) = (Sample A/Control A) × 100.
Qualitative measurement
After collecting data, Minitab statistical software was used for statistical analysis. Evaluation of cytotoxicity results in a completely randomized design and comparison of means was performed using Duncan’s post-hoc test with a maximum error of 5%. To measure the percentage of cell survival in factorial experiments with the original design of completely randomized blocks and compare the means, Duncan’s post-hoc test with a maximum error of 5% was used. The 50% cytotoxicity (IC50) was estimated with ED50 plus software (INER, V: 1.0). Measurements were reported as mean ± standard deviation.
Results and Discussion
Antioxidant activity
Free radicals are atoms, molecules, or ions with unpaired electrons and are therefore very active, unstable, and highly reactive. Free radicals are formed by breaking a bond of a stable molecule. Free radicals collide with other molecules to achieve stability and can separate electrons from them; as a result, they form a chain of more unstable molecules. A free radical can have a positive, negative or neutral charge [8]. During the body’s natural metabolism or under conditions such as smoking, pollution, the entry of unnecessary chemicals into the body in any way, radiation and stress, the body produces free radicals. The most important free radical in the human body is oxygen, which can damage DNA and other molecules. Oxidative stress is the victory of free radicals over the body’s antioxidant defense and is a biological attack on the body [8–10].
Antioxidants are molecules that can donate an electron to a free radical without destabilizing themselves. This stabilizes the free radical and makes it less reactive. The result of oxidative stress in the body is various degeneration, eye damage, premature aging, muscle problems, brain damage, heart failure, diabetes, cancer, and overall weakness of the immune system [9, 11]. Oxygen radicals are continuously produced in all living organisms and with destructive effects, leading to cell damage and death. The production of oxidant species under physiological conditions has a controlled rate, but this production increases under oxidative conditions [11]. Various studies have shown that antioxidant compounds have very significant anti-cancer effects by neutralize of the free radicals. Herbs are rich in antioxidant compounds and reduce the risk of some chronic diseases such as cataracts, rheumatoid arthritis, memory loss, stroke, heart disease, and cancer by protecting cells and increasing the power of plasma antioxidants. Flavonoids and alkaloids commonly found in medicinal plants have high antioxidant activity [8–12].
In the present study, the antioxidant activity results of the plant extract are tabulated in Table I. According to the results the extract was rich in phenolic compounds with TPC of 396.2 ±3.2 mg GAE/g. The value of 62.3 ±1.4 mgRuE/g was measured for the plant TFC. The plant extract scavenged the free radical of DPPH with IC50 of 12.3 ±0.7 µg/ml, which is more than BHT and α-tocopherol as the positive controls. The chelating activity of the plant extract was measured for IC50 of 163.3 ±1.9 µg/ml.
Table I
Total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), DPPH radical scavenging activity (RSA), and ferrous ion chelating ability (FIC) of Equisetum arvense extract
| Variable | TPC [mg GAE/g extract] | TFC [mgRuE/g extract] | RSA IC50 [µg/ml] | FIC IC50 [µg/ml] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LUE | 396.2 ±3.2 | 62.3 ±1.4 | 12.3 ±0.7 | 163.3 ±1.9 |
| BHT | – | – | 23.9 ±1.2 | – |
| TOC | – | – | 46.2 ±2.6 | – |
| EDTA | – | – | – | 59.2 ±1.5 |
| AscA | – | – | – | 1247.2 ±2.8 |
Anti-human colorectal carcinoma potential of Equisetum arvense L
The MTT assay is a colorimetric procedure based on reducing and breaking of yellow tetrazolium crystals by the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase to form insoluble purple crystals. In this method, unlike other methods, the steps of washing and collecting cells, which often cause the loss of a number of cells and increase the work error, have been eliminated and all test steps from the beginning of cell culture to reading the results with a photometer are performed on a microplate, so the repeatability, accuracy and sensitivity of the test are high [7]. If the test is performed on cells attached to the plate, an appropriate number of cells (about 2,000 cells) must first be cultured in each of the wells. Then we select the control and test wells and add the appropriate amount of mitogen or drug to the test wells and place the plate in the incubator for the required time so that the desired substance affects the cells [10–13]. At the end of the incubation time, the supernatant was discarded and 200 μl of culture medium (containing half an mg/ml of MTT solution) was add to each well and placed in a CO2 incubator for 2 to 4 h at 37°C. During incubation, MTT is regenerated by one of the enzymes of the mitochondrial respiratory cycle i.e., succinate dehydrogenase. The regeneration and breakage of this ring produce purple-blue crystals of formazan that are easily detectable under a microscope. At the end, the optical absorption of the resulting solution can be read at 570 nm and the number of cells can be calculated using a standard curve. For each cell line, there is a linear relationship between the number of cells and the light absorption of the final solution. Therefore, to examine each cell type, a standard curve related to the same cell line must be drawn and used [8].
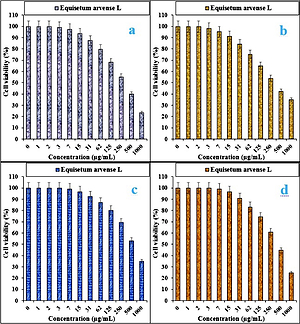
In the present study, the cytotoxicity of Equisetum arvense L was explored by studying its interaction with normal (HUVEC) and human colorectal carcinoma cell lines, i.e. colorectal adenocarcinoma (HT-29), colorectal carcinoma (HCT 116), ileocecal colorectal adenocarcinoma (HCT-8 [HRT-18]), and Burkitt’s lymphoma (Ramos.2G6.4C10) by MTT assay for 48 h. The interactions expressed as cell viability (%) were observed at different Equisetum arvense L concentrations (0–1000 μg/ml) with the five cell lines which are shown in detail in Figures 1 and 2. In all the cases, the % cell viability decreased with increasing Equisetum arvense L sample concentrations.
Figure 1
Anti-colorectal carcinoma properties of Equisetum arvense L against HT-29 (A), HCT 116 (B), HCT-8 [HRT-18] (C), and Ramos.2G6.4C10 (D) cell lines
The IC50 values of Equisetum arvense L against Ramos.2G6.4C10, HCT-8 [HRT-18], HCT 116, and HT-29 were 439, 584, 341, and 337 µg/ml, respectively (Table II).
Table II
IC50 of Equisetum arvense L in the anti-colorectal carcinoma test
| IC50 | Equisetum arvense L [µg/ml] |
|---|---|
| HUVEC | – |
| HT-29 | 337 ±0a |
| HCT 116 | 341 ±0a |
| HCT-8 [HRT-18] | 584 ±0c |
| Ramos.2G6.4C10 | 439 ±0b |
The best cytotoxicity results and anti-human colorectal carcinoma potentials of our Equisetum arvense L were observed in the case of the HT 29 cell line (Table I).
Oxidation from reactive oxygen species can cause cell membrane disintegration, damage to membrane proteins, and DNA mutation, the result of which is the onset or exacerbation of many diseases such as cancer, liver damage, and cardiovascular disease. Although the body has a defense system, constant exposure to chemicals and contaminants can lead to an increase in the number of free radicals outside the body’s defense capacity and irreversible oxidative damage [14–16]. Therefore, antioxidants with the property of removing free radicals play an important role in the prevention or treatment of oxidation-related diseases or free radicals. Extensive molecular cell research on cancer cells has developed a targeted approach to the biochemical prevention of cancers whose goal is to stop or return cells to their pre-cancerous state without any toxic doses through nutrients and drugs. Numerous studies have been performed on the use of natural compounds as anti-cancer agents in relation to appropriate antioxidant activity [14–18]. It seems that the high anti-human colon carcinoma properties of Equisetum arvense L aqueous extract are related to its antioxidant activities.
In conclusion, Equisetum arvense L extract was found to be rich in phenolic compounds and a potent herbal product to scavenge free radicals of DPPH. The Equisetum arvense seed was also assessed in biological applications such as radical scavenging and anticancer activities. The Equisetum arvense seed exhibited good antioxidant properties, even better than the reference standard molecule. The oncological part of the recent study revealed significant cytotoxicity and anti-human colorectal carcinoma properties of Equisetum arvense L against common human colorectal carcinoma cell lines, i.e., colorectal adenocarcinoma (HT-29), colorectal carcinoma (HCT 116), ileocecal colorectal adenocarcinoma (HCT-8 [HRT-18]), and Burkitt’s lymphoma (Ramos.2G6.4C10) in in vitro conditions. The IC50 values of Equisetum arvense L against Ramos.2G6.4C10, HCT-8 [HRT-18], HCT 116, and HT-29 were 439, 584, 341, and 337 µg/ml, respectively. Possibly the anti-human colorectal carcinoma properties of Equisetum arvense L are related to its antioxidant effects.