Introduction
A major health concern worldwide, skin cancer is one of the destructive types of cancers responsible for a huge number of deaths [1]. As per reports, out of every 5 Americans, one develops skin cancer any time during their life. Surgery and chemotherapy are generally employed for skin cancer treatment. In certain cases, the combination of chemo- and radiotherapy is also used for its management [2]. Despite recent advances, the incidence of skin cancer is increasing at an alarming rate. Additionally, late diagnosis and frequent relapses add to the problems faced during skin cancer treatment. The lack of molecular therapeutic targets and biomarkers for early diagnosis is a further hurdle to proper skin cancer treatment [3]. Over the last few decades, microRNAs (miRs) have gained importance in cancer research and are believed to play essential roles in cancer treatment [4]. The miRs regulate diverse processes in human cells, such as differentiation, proliferation and programmed cell death to name a few [5]. A vast number of studies have confirmed that miR expression levels are remarkably dysregulated in cancer cells. These miRs either promote (oncomiRs) or suppress (tumour suppressor) the progression and growth of cancers [6]. Many miRs have also been shown to act as molecular markers for detection and cancer progression [7]. miR-27a has been shown to be involved in the regulation of growth and metastasis of different cancer types. miR-27a has been shown to act as an oncogene in adenocarcinoma [8]. In pancreatic cancer, miR-27a targets Sprouty2 to control its proliferation [9]. In osteosarcoma, miR-27a modulates the expression of MAP2K4 to suppress its growth [10]. Uveal melanoma growth is inhibited by genistein via inhibition of miR-27a [11]. Despite all these studies, the role of miR-27a has been studied in skin cancer. Against this backdrop, the present study was undertaken to study the function and prospective therapeutic implications of miR-27a in skin cancer. The results showed that miR-27a acts as an oncomiR in skin cancer and may have therapeutic implications in skin cancer treatment.
Material and methods
Cell lines, tissues and culture conditions
Skin cancer tissue specimens and normal adjacent tissues of fifteen skin cancer patients who underwent surgical resection in the First People’s Hospital of Fuyang Hangzhou, Hangzhou, China from May 2017 to June, 2019 were included. Patients were aged 30–69 years with an average age of 44.20 years. The skin cancer cell lines (A431, A-375, A-101D, HMCB, Hf688(A).T) and the normal skin cell line (HEMn-LP) were procured from Type Culture Collection of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China. The cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 µg/ml streptomycin and 100 U/ml penicillin and a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. The study was approved by the research ethics committee of the institute under the approval number 66578-FFH of 2019.
qRT-PCR
The RNA was extracted from the transfected A431 cells using Trizol regent and subsequently cDNA was synthesized using a RevertAid cDNA synthesis kit. The cDNA was then used as a template for RT-qPCR analysis with the assistance of the Taq PCR Master Mix kit (Qiagen, Inc.) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. For determination of the expression, the cycling conditions were as follows: 95°C for 15 s, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 20 s, and 55°C for 1 min. GAPDH was used as an internal control. The relative expression was determined by ΔΔCT methodology as described previously [12].
Transfection
The transfection of miR-NC, NC, miR-27a Inh (inhibitor), pcDNA-MAPK7 and si-MAPK7 were performed with Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) following user guidelines.
Cell viability assay
The transfected A431 cells (2.5 × 103) were cultured in each 96-well plate. Following incubation of 3 days, the cells were subjected to treatment with 25 µl of MTT. The medium was removed after about 4 h and DMSO (170 µl) was added to the culture to enable the solubilisation of the formazan crystals. Finally, the absorbance was taken at 570 nm for the determination of A431 cell viability.
Phase contrast microscopy
The transfected A431 cells were evaluated for changes in morphology by Olympus BX41 (magnification; 400×) and digital images of the cells were taken.
Acridine orange/ethidium bromide (AO/EB) staining
The transfected A431 cells were used for the assessment of the nuclear morphology after staining with a solution of AO/EB for 25 min at 20°C. After fixation with methanol (70%), the nuclear morphology was investigated by fluorescence microscopy. Five different random fields were selected for fluorescence microscopy. The annexin V-FITC assay was performed as determined previously [13].
Immunocytochemical analysis
Firstly the transfected A431 cells were cultured on coverslips until 70% confluence was achieved. The avidin-biotin complex immunoperoxidase methodology was employed for immunohistochemical analysis of the cells. The Bcl-2, Ki-67, caspase-3 and p53 expression was assessed using the respective monoclonal antibodies. Ten random fields were selected for analysis using an Olympus BX 41microscope with 400× magnification.
Migration and invasion assay
Transwell chamber with Matrigel coating was used to assess the invasion of transfected cancer cells. Briefly, a 100 µl cell culture containing 6000 cells was added to the upper chamber of the transwell and lower chamber was given 750 µl of DMEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS. After 48 h incubation at 37oC/5% CO2, cells from the surface of the membrane’s upper side were removed carefully with cotton swabs while those that adhered to the lower side of the membrane were fixed with 70% ethyl alcohol and stained with 0.1% crystal violet. A light microscope (100×) was used for visualization of cells and photographs were taken. At least seven random fields were used for counting of invasive cells. The wound heal assay was used to determine the cell migration as described earlier [13].
Results
Upregulation of miR-27a in skin cancer
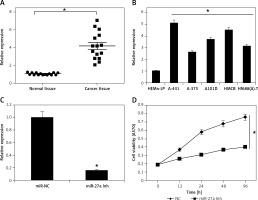
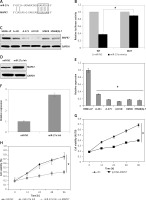
The experiments started with the assessment of the gene expression of miR-27a in the skin cancer tissues and the adjacent normal tissues by qRT-PCR. The outcomes of the qRT-PCR as determined by ΔΔCT methodology revealed remarkable upregulation of miR-27a in skin cancer tissues relative to adjacent normal tissues (Figure 1 A). The upregulation was up to more than 7-fold. Subsequently, the transcripts of miR-27a were also examined in skin cancer cell lines (A431, A-375, A-101D, HMCB, Hf688(A).T) and the normal skin cell line (HEMn-LP) and, interestingly, the results were similar. The expression of miR-27a was significantly enhanced in the skin cancer cells, with the highest upregulation of up to 5.1-fold in A431 cells (Figure 1 B). This aberrant expression of miR-27a encouraged us to further study the function of miR-27a in skin cancer.
Figure 1
Expression of miR-27a in (A) skin cancer and normal adjacent tissues (B) normal and skin cancer cell lines. C – Expression of miR-27a in miR-NC and miR-27a inhibitor transfected A431 cells. D – Viability of miR-NC and miR-27a inhibitor transfected A431 cells. The experiments were performed in triplicate and expressed as mean ± SD (*p < 0.05)
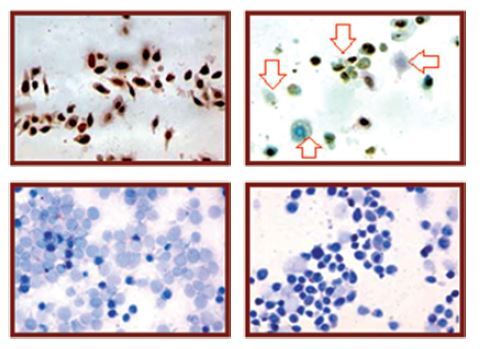
miR-27a regulates apoptosis of skin cancer cells
Since miR-27a was remarkably upregulated in both skin cancer tissues and cell lines, we inhibited the expression of miR-27a to reveal its effects on A431cell viability. Interestingly, the MTT assay showed a time-dependent depletion of the A431 cell viability as the expression of miR-27a was inhibited (Figures 1 C, D). Secondly, different assays such as phase contrast microscopy and AO/EB staining showed signs of apoptosis in the transfected A431 cells (Figure 2 A). The immunohistochemical analysis showed a considerable decrease in the expression of Bcl-2, ki-67 and p-53 proteins, suggesting the induction of apoptosis in A431 cells (Figure 2 A). The annexin V/PI assay showed around 17% apoptosis in miR-27a Inh transfected cells relative to 6% in miR-NC transfected cells (Figure 2 B). The western blot analysis also revealed a decrease in Bcl-2 and increase in caspase-3 and Bax expression upon miR-27a inhibition in A431 cells (Figure 2 C). All these outcomes clearly indicate that suppression of miR-27a in A431 cells promotes apoptosis in A431 cells.
Figure 2
A – miR-NC and miR-27a inhibitor transfected A431 cells showing morphology as revealed by phase contrast microscopy, induction of apoptosis as depicted by AO/EB staining and immunohistochemical analysis showing expression of Bcl-2, Ki-67 and p53. Annexin V/PI staining of miR-NC and miR-27a inh transfected A431 cells (B) and miR-NC and miR-27a inh transfected A431 cells showing the expression of caspase-3, Bcl-2 and Bax (C). The experiments were performed in triplicate
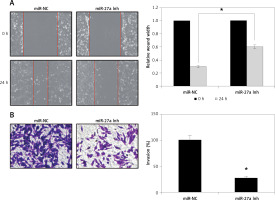
miR-27a regulates the migration and invasion of skin cancer cells
Next, to analyse whether miR-27a has any role in metastasis of A431 cells, we performed the wound healing and transwell assays. The wound healing assay showed remarkable and significant inhibition of the cell migration as obvious from the wound width (Figure 3 A). The transwell chamber assay revealed around 73% inhibition of A431 cell invasion upon miR-27a inhibition (Figure 3 B), indicating the regulation of A31 cell migration and invasion by miR-27a.
miR-27a exerts its effects via MAPK7 signalling
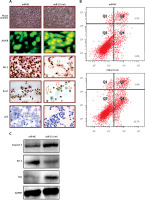
The informatics revealed miR-27a targets MAPK7 (Figure 4 A). The dual luciferase showed a strong interaction between miR-27a and MAPK7 (Figure 4 B). The western blot analysis showed that MAPK7 was remarkably suppressed in all the skin cancer cell lines (Figure 4 C). Nonetheless, the expression of MAPK7 was considerably increased upon suppression of miR-27a (Figure 4 D). Similar results were also obtained by qRT-PCR (Figures 4 E, F). Furthermore, MAPK7 overexpression also reduced the A431 cell viability time dependently (Figure 4 G). Nonetheless, silencing of MAPK7 could avoid the growth inhibitory effects of miR-27a inhibition (Figure 4 H). All these findings point towards the role of MAPK7 signalling in miR-27a mediated effects on A431 cells.
Figure 4
A – Bioinformatic analysis showing MAPK7 as the target of miR-27a. B – Dual luciferase assay. C – Western blot analysis showing expression of MAPK7 in normal and skin cancer cell lines. D – Western blot analysis showing expression of MAPK7 in miR-NC and miR-27a inhibitor transfected A431 cells. E – qRT-PCR analysis showing expression of MAPK7 in normal and skin cancer cell lines. F – qRT-PCR analysis showing expression of MAPK7 in miR-NC and miR-27a inhibitor transfected A431 cells. G – Viability of NC and pcDNA-MAPK7 transfected cells. H – Viability of miR-NC, miR-27a inhibitor and miR-27a inhibitor + MAPK7 transfected A431 cells. The experiments were performed in triplicate and expressed as mean ± SD (*p < 0.05)
Discussion
Skin cancers constitute one of the prevalent types of human cancer and therefore are responsible for tremendous human mortality across the world [14]. The rising incidence rates of skin cancer are probably caused by a combination of increased exposure to ultraviolet (UV) or sun light, increased outdoor activities, changes in clothing style, increased longevity, ozone depletion, genetics and in some cases, immune suppression [15, 16]. Owing to the discovery of a multitude of roles of miRs in cancer development and progression, their therapeutic implications are being explored for the management of different cancer types [17]. This study showed that transcript levels of miR-27a are aberrantly enhanced in skin cancer tissues and cell lines. A number of previous studies have also revealed the aberrant upregulation of miR-27a in cancer cells. For instance, upregulation of miR-27a has been observed in the case of prostate and colon cancer [6, 18]. We inhibited the expression of miR-27a to reveal its effects on A431cell viability and, interestingly, the MTT assay showed time-dependent depletion of A431 cell viability. These findings clearly indicate that miR-27a acts as an oncomiR in skin cancer. Apoptosis is an important process that is essential for an organism to remove malignant cells [19]. A number of proteins are considered to be biomarkers of apoptosis such as Bax, caspase-3 and Bcl-2, to name a few [20]. The findings of this study showed that miR-27a suppression promoted apoptosis in the A431 cells as evident from the phase contrast, AO/EB and annexin V/PI staining. The immunohistochemical analysis showed that the Bcl-2, p53 and Ki-67 expression decreased upon inhibition of miR-27a. The Bax and Bcl-2 proteins are considered to be biomarker proteins for the induction of apoptosis [12]. Herein, the western blots also showed the alteration in expression of apoptosis-related proteins, as Bax and caspase-3 increased and Bcl-2 decreased.
A previously carried out research study revealed that miR-27a inhibition led to suppression of the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells [10]. This study also revealed that the inhibition of miR-27a suppressed the migration and invasion of A431 skin cancer cells. The bioinformatics and dual luciferase assays showed that miR-27a targets MAPK7, which is in consistent with a previous study wherein MAP2K3 was shown to be a target of miR-27a in osteosarcoma [10]. This study revealed that MAPK7 was considerably increased upon suppression of miR-27a. Additionally, MAPK7 overexpression also reduced the A431 cell viability time dependently. Nonetheless, silencing of MAPK7 could avoid the growth inhibitory effects of miR-27a inhibition. This is in agreement with previous studies wherein MAPK7 has been shown to regulate the growth and metastasis of different cancer types [21].
In conclusion, taking the evidence together, miR-27a is considerably upregulated in skin cancer cells. Silencing of miR-27a suppresses the viability of skin cancer cells via promotion of apoptosis. Inhibition of miR-27a also suppresses the migration and invasion of skin cancer cells by targeting MAPK7. miR-27a has therapeutic implications in skin cancer.