Introduction
Despite the advances in awareness and therapeutics, breast cancer remains a top-ranked malignancy in terms of mortality in the USA. Breast cancer incidence is increasing alarmingly and is expected to rise in the future [1]. One of the prime causes is the late planning of pregnancy and then a reduction in breastfeeding duration, stimulating a trigger in the pathogenesis of breast cancer [2, 3]. Owing to having few symptomatic manifestations, breast cancer is very hard to detect in the early stages of the disease and hence commonly diagnosed during advanced stages of the disease. Despite significant improvement in diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, the outcome of breast cancer therapeutics is dismal because of challenges such as advanced stage metastasis, drug resistance, and adverse side effects [2]. The resistance developed against radiotherapy in almost half of the advanced breast cancer patients is due to the hypoxia created deep inside the tumor microenvironment [4, 5]. However, breast cancer heterogeneity is another major factor against the target-specific chemotherapeutics [4, 6, 7]. Based on the gene expression profile breast cancer cells have five different subtypes: normal-like, basal-like, HER-2 positive, luminal type A and luminal type B. Intriguingly, the medical outcome varies within each subtype [8]; e.g. luminal type A and luminal type B represent MCF-7 and BT-474 cells respectively, are androgen receptor (ER)-positive and respond to hormone therapy. However, MCF-7 is negative for HER2 whereas BT-474 is positive for HER2 [9, 10]. Additionally, luminal A subtype is markedly differentiated and this type of breast cancer has a good prognosis, whereas highly proliferative cells of luminal B type have a poor prognosis [11, 12]. Therefore, a multiple target therapeutic strategy, which not only kills cancer cells but also makes inroads in tumor cell metastasis and has less toxic effects on normal cells, is needed.
Owing to low toxicity effects on normal cells, natural compounds are novel, complex structures and can modulate the heterogeneous group of cancer cells by targeting multiple signaling pathways [13]. Numerous studies have demonstrated that phytochemicals have promising antitumor potential against BC; e.g., resveratrol, withaferin A, sulforaphane and curcumin-induced apoptosis mediated cell killing, arrest cell cycle and decrease proliferation of BC cells [14–18]. Moreover, recently various reports have shown that natural compounds not only induce apoptosis in cancer cells but can modulate tumor cell invasion and make inroads in BC metastasis [19]. Thus, natural compounds are considered an attractive agent for comprehensive therapeutics of BC.
AKBA is a key component of gum resin obtained from the plant Boswellia serrata. The Indian traditional Ayurveda system of medicine has long been using AKBA to treat various inflammatory ailments which include ulcerative colitis, bronchial asthma, chronic colitis, Crohn’s disease and osteoarthritis [20, 21]. Recently, AKBA has been shown to exhibit an anti-tumor effect to activate apoptotic mechanisms in numerous types of malignancies such as prostate cancer, pancreatic cancer, glioblastoma, colon cancer, hepatoma and fibrosarcoma [22–26]. However, whether AKBA could modulate tumor cell motility and invasion in BC cells, the underlying mechanisms are still not clear.
Therefore, the current study aims to evaluate and investigate the anti-tumor mechanism induced by AKBA in subtypes luminal A and B cell lines (MCF-7 and BT-474). The current study is the first report to reveal that AKBA exhibits significant antiproliferative potential and simultaneously suppresses migration and cell invasion by decreasing expression as well as activity of MMP-2/9 and potentiates apoptosis in both subtypes luminal A and B cell lines. We also found that AKBA reduces the phosphorylation of EGFR and abrogates PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by suppressing MMP-2/9 expression and upregulates E-cadherin and TIMP1 expression in BC cells. Collectively these results demonstrate that AKBA could be a promising chemotherapeutic natural compound in the therapeutics of BC.
Material and methods
Culturing of cells and their treatments
BC cells (MCF-7, BT-474) and the MCF-10 transformed normal cell line were procured from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and were maintained, cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Essential Medium (DMEM) (#A4192101) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (#16000044), penicillin-streptomycin solution (#15140130), in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. All the cell lines were free from Mycoplasma contamination.
Preparation of AKBA dilutions
20 mg/ml stock solution of AKBA was prepared in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Aliquots of stock solutions were prepared and stored at –20°C. Further, the dilution of stock solution was done in DMEM to prepare a working solution of desired concentrations between 10 and 40 µM for the treatment of cultured cells.
Chemicals, reagents, and antibodies
AKBA (#A9855), gelatin (#G1890), 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-y1)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) (#M5655), Brij-35 (#203728), propidium iodide (PI) (#P4170), Coomassie Brilliant Blue (R-250) (#1125530025), phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) (#78830), dithiothreitol (DTT) (#10197777001), DMSO (#C6164), Bradford reagent (#B6916), Annexin V and FITC kit for the detection of apoptosis (#APOAF), gefitinib (#SML1657), erlotinib (#SML2156) and protease inhibitor cocktail (#P8340), were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Signaling Technology antibodies procured for the current study were: β-actin (#3700S, 1 : 10000 dilution), EGFR (#4267S, 1 : 1000 dilution), p-EGFR-Tyr1173 (#2244S, 1 : 1000 dilution), PARP1 (#9532S, 1 : 1000 dilution), PI3K-p110α (#4255S, 1 : 1000 dilution), caspase-3 (#9662S, 1 : 1000 dilution), Akt (#4685S, 1 : 1000 dilution), p-Akt-Ser473 (#4060S, 1 : 1000 dilution), MMP-9 (#13667S, 1 : 1000 dilution), MMP-2 (#40994S, 1 : 1000 dilution), E-cadherin (#14472S, 1 : 2000 dilution), and TIMP1 (#8946S, 1 : 1000 dilution). Secondary anti-mouse IgG-coupled (#sc-2005, 1 : 2000 dilution) and anti-rabbit coupled (#sc-2357, 1 : 2000 dilution) with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology.
Cell viability assay
The proliferation of cells was analyzed by MTT assay as per the standard protocol [27]. Briefly, BC cells (MCF-7, BT-474) along with the transformed normal (MCF-10A) cells were plated at a density of 5 × 103 cells per well of a 96-well plate. The cells were treated with varying concentrations of AKBA (0.2–200 µM) and control DMSO for 24 h in an incubator containing 5% CO2. Subsequently, cells were incubated with MTT dye (2.5 mg/ml) for 3 h at 37°C. The formazan crystals formed were solubilized in DMSO, mixed properly by vortex and absorbance was measured at 570 nm by a multiplate reader. The percentage of cell proliferation was analyzed as the percent cell viability of treated cells compared with the control DMSO cells.
Detection of apoptosis
BC cells were seeded at a density of 0.5 × 106 cells per well in a 6-well plate and treated with different concentrations (20, 30, 40 µM) of AKBA along with control DMSO. After 24 h, cells were harvested with a cell scraper, processed and incubated with annexin V and PI as directed in the protocol. After completion of the staining process, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry to quantify the apoptotic cell population.
Scratch motility (wound healing) assay
Briefly, BC cells (MCF-7 and BT-474) were plated at a density of 5.5 × 105 cells per well of a 6-well plate and allowed to adhere to make a complete monolayer for 24 h. The monolayer formed was scratched with a sterile micropipette tip (200 µl) to create a wound and was gently washed with serum-free medium to wash out detached cells. Photographs were taken at the time of creating wound (0 h). Cells were incubated in low-serum medium (1%) and simultaneously exposed to varying concentrations of AKBA (10, 20, 30 µM) along with control DMSO for 24 h. The photographs were taken with an inbuilt camera of the microscope from the areas where wounds were created at 0 h. The closure of the wound was determined as a percentage by using the formula: Closure wound % age = [1 – (area of wound after 24 h/area of wound at 0 h) × 100%].
Gelatin zymography
BC cells (MCF-7 and BT-474) at a density of 0.5 × 106 were seeded in a 6-well plate and allowed to adhere to the surface overnight. Cells were exposed to varying concentrations (10, 20, 30 µM) of AKBA along with control DMSO for 24 h. The conditional medium was collected from the cells exposed to varying concentrations of AKBA along with control untreated cells, after the completion of the time. Conditional medium samples were subjected to protein estimation and an equal quantity of protein was mixed with sample loading dye (25% glycerol, 2.0% SDS, 60 mM Tris-HCl, 0.1% bromophenol blue and pH 6.8). Gelatin zymography was performed with SDS-polyacrylamide gels having composition 7.5%, gelatin 0.1%, running at 4°C for 3 h at 100 V. After resolving the gel completely under a given condition of temperature and voltage, the gel was washed at room temperature with buffer containing 2 ml of Triton X-100 in 98 ml of double-distilled water, to wash out SDS. The gel was then incubated for 24 h at 37°C in incubation buffer (0.02% NaN3, 10 mM CaCl2, 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0) and stained for 1–1.5 h in Coomassie staining solution followed by destaining with a destaining solution. Detection of gelatinase activity was analyzed by spotting stainless bands on a dark blue background on a gel stained with Coomassie brilliant blue.
Matrigel invasion assay
To evaluate the anti-invasive potential of AKBA, Transwell Boyden chamber plates obtained from BD Bioscience were used. Briefly, BC cells (1.25 × 106) were seeded, incubated and exposed to varying concentrations of AKBA (10, 20, 30 µM) along with control DMSO for 24 h in serum-free medium in the upper chamber and the lower chamber was filled with 10% complete medium as a chemoattractant. After 24 h, the Matrigel-coated polycarbonate biological porous membrane inserts were removed and the cells attached from the upper side of the chamber were scraped completely with a swab of cotton. The porous inserts containing cells from the lower chamber side were fixed in ice-cold methanol for 10 min and stained by dipping the inserts in 0.1% crystal violet solution. The migration of the cells was analyzed by taking photographs of the bottom side of the attached migrated cells and the migrated stained cells were counted under the phase-contrast microscope.
Phase-contrast microscopy
BC cells (5 × 104) were cultured on coverslips with varying (20, 30, 40 µM) concentrations of AKBA along with control DMSO for 24 h to analyze the changes in the cellular morphology. Cells were processed for the phase-contrast microscope to analyze the morphological changes in treated cells.
Immunoblotting
After overnight plating of 50 × 105 cells/well in a humidified 5% CO2 incubator at 37°C, BC cells were exposed to varying concentrations (20, 30, 40 µM) of AKBA along with control DMSO. After 24 h, cells were harvested and washed with ice-cold PBS. The cells were lysed and processed at 4°C for centrifugation at a speed of 13000 g for 10 min. Supernatants collected from centrifugation in a separate tube were subjected to the Bradford method of protein estimation. Then 20 µg of protein from each treated sample was loaded in the wells of SDS-PAGE gel. After resolving properly, SDS-PAGE gel was subjected to transfer onto the PVDF membrane, and incubated in fat-free milk (5%) blocking solution dissolved in TBST. After blocking nonspecific proteins, the PVDF membrane was incubated and probed with the desired antibodies (1 : 1000 dilutions) for at least 3–4 h at room temperature or 4oC overnight. The PVDF membrane was washed with TBST buffer three times. The pre-incubated membrane with primary antibody was probed with horseradish peroxidase-labeled secondary antibody for at least 1 h. After washing three times with TBST buffer, immunosubstance proteins were visualized using ECL Plus on the PVDF membrane.
Statistical analysis
All the evaluated experiments were performed three or more independent times. The latest version of the software GraphPad Prism was used for statistical analysis of all independent unbiased experiments. The results obtained were presented as the mean ± SEM. Entire results were calculated using Student’s unpaired t-test, wherein a p-value not more than 0.05 was considered significant (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001).
Results
AKBA exhibits a promising antiproliferative effect on BC cells
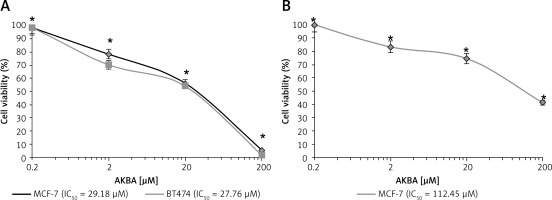
Previous reports demonstrated that AKBA exhibits a antiproliferative effect on various tumor cell models. Hence, we wanted to inspect the in vitro inhibitory activity of AKBA on the growth of luminal A and B subtype cells. AKBA inhibits BC cells in a concentration-dependent manner. The MTT assay was performed to evaluate the inhibitory effect on cell viability. Our results revealed that AKBA initiated an antiproliferative effect on both the types of BC cells (MCF-7 and BT-474) at a concentration of 10 µM. However, when the IC50 concentration values of AKBA was calculated by GraphPad Prism software, we found that the IC50 value was 29.18 µM and 27.76 µM for MCF-7 and BT-474 BC cells respectively (Figure 1 A). Interestingly, when the antiproliferative effect was evaluated for transformed normal MCF-10A cells, we found that 50% of the population of cells were killed at 112.45 µM of AKBA (Figure 1 B), which is quite a high concentration compared to the IC50 value of BC cells, indicating that AKBA specifically inhibits the growth of cancer cells and displays a safe toxicity profile on normal cells. Collectively, these results revealed that AKBA exhibits a promising antiproliferative effect on BC cells and is less toxic to normal cells.
Figure 1
AKBA exhibits an antiproliferative effect on BC cells. A – Effect of AKBA on proliferation of BC cells (MCF-7, BT-474) was determined by MTT assay. B – Effect of AKBA on proliferation of normal breast cells (MCF-10A) determined by MTT assay
The data represent the mean value ± SE of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05.
AKBA abrogates cell migration and invasion of BC cells
To examine whether AKBA could also impact tumor cell motility, migration, and invasion in vitro we intended to perform a wound healing assay and Transwell Boyden chamber cell migration assay in vitro to evaluate the anti-migration or anti-invasive potential of AKBA by treating cells with subtoxic concentrations of AKBA in BC cells. Due to the significant induction of cell death at higher concentrations of AKBA, subtoxic concentrations (10, 20 and 30 µM) of AKBA for 24 h were carefully selected to study the anti-motility and anti-invasive effect on BC cells. Our results revealed that a significant reduction in motility of cells was witnessed once BC cells (MCF-7, BT-474) were exposed to 20 and 30 µM of AKBA, which is as good as positive control staurosporine (25 nM) (Figures 2 A, B), after creating a wound by making a scratch with a 100 µl sterile tip when compared to a control DMSO that was almost filled with migrated cells.
Figure 2
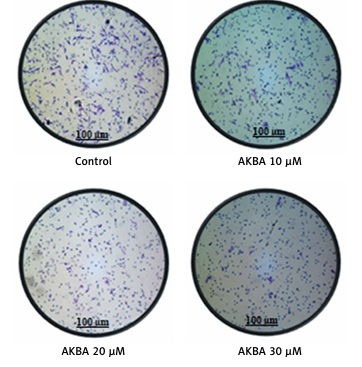
AKBA abrogates cell migration and invasion of BC cells (A) and (B) BC cells (MCF-7, BT-474) were exposed to indicated concentrations of AKBA (10, 20, 30 μM) along with staurosporine (25 nM) as a positive control and DMSO as a control) for 24 h to evaluate the anti-motility effect of AKBA on BC cells. Scale bar: 200 μm; 10×. C – Cell invasion was determined by the Transwell Boyden chamber assay. Briefly, 2 × 105 cells/well were seeded in the top chamber in the presence of AKBA along with control DMSO. Cells were allowed to migrate for 24 h; cells able to cross the porous membrane from the bottom half of the insert membrane were stained with 0.1% crystal violet and counted under phase contrast microscope. Five fields were counted in triplicate from each insert of three independent experiments. Scale bar: 100 μm; 20×. D – Bar diagram showing quantification of invasive cells after exposure with varying concentrations of AKBA
The data represent the mean value ± SE of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01.
A crucial step of metastatic cells is the capability of these cells to migrate across the various barriers including the extracellular matrix and disseminate the migrated cells away from the primary tumor site. To study the influence of AKBA on the invasive property of cancer cells, we intended to perform a Transwell Boyden chamber assay to determine the inhibitory capability of AKBA on BC cell migration and invasion through the porous biological membrane inserts in vitro. Our results demonstrated that a significant number of invaded cells lost the ability to penetrate through the Matrigel-coated membrane in a dose-dependent manner, when compared to control DMSO (Figure 2 C). The bar diagram (Figure 2 D) shows that the number of invaded cells is 42, 32, and 13 at a concentration of 10, 20, and 30 µM of AKBA respectively, as compared to 145 invaded cells in control DMSO. Collectively, these results indicate that subtoxic doses of AKBA attenuate the growth kinetics of BC cells.
AKBA induces apoptosis in BC cells
In the previous section, the antiproliferative effect of AKBA on BC cells was discussed. Next, to determine whether the AKBA-mediated anti-proliferative effect induces apoptosis in BC cells, we performed the annexin V FITC detection assay after treating BC cells with AKBA in a concentration-dependent manner. Our results demonstrated that AKBA pushes a significant population of cells towards apoptosis as evidenced by 14.5% and 25.3% at 30 and 40 µM of AKBA respectively in BC cells as compared to 35.9% apoptotic population of staurosporine (positive control) and 2.1% of control DMSO (Figures 3 A, B). Moreover, to confirm the mechanism associated with AKBA-induced apoptosis, the immunoblotting analysis revealed that the initiation of caspase-3, as well as PARP1 activation, takes place as evidenced by increased caspase-3 and PARP1 cleavage activity after exposing BC cells to dose-dependent concentrations (20, 30, 40 µM) of AKBA (Figures 3 C, D). Furthermore, phase contrast microscopy revealed that a significant number of apoptotic dead and floated cells were seen after BC cells were treated with 30 and 40 µM of AKBA concentration for 24 h, as compared to control DMSO cells (Figure 3 E). Together, our results demonstrate that the anti-proliferative effect exerted by AKBA is due to the induction of apoptosis as evidenced by prominent caspase-3 and PARP1 cleavage.
Figure 3
AKBA induces apoptosis in BC cells. A – BC cells (MCF-7) were treated with varying (20, 30, 40 μM) concentrations of AKBA along with staurosporine (25 nM) as positive control and DMSO as a control for 24 h and then exposed to staining solution of Annexin V FITC and propidium iodide and analyzed by FACS. B – Bar diagram showing quantification of Annexin V FITC positive cells analyzed by FACS. C – Immunoblotting analysis showing prominent PARP1 and caspase-3 cleavage in lanes 4 and 5 where cells were exposed to AKBA and staurosporine treatment and internal control β-actin. D – Densitometry analysis represented by histogram shows the fold change in protein expression after normalization with β-actin. E – Representative micrograph images by phase-contrast microscopy of BC cells exposed to indicate doses of AKBA and positive control staurosporine. Scale bar: 100 μm; 20×
The data denote the mean value ±SE of three independent unbiased experiments. *P < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
AKBA inhibits matrix MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity and expression in BC cells
Besides cell motility, invasion and migration, a metastatic cell needs proteolytic cleavage of the matrix to disseminate the cells to distant sites. Increased expression, as well as activity of MMPs, has been associated with cancer cell metastasis. As AKBA exerts an anti-migration effect on BC cells, we intended to investigate whether AKBA could display anti-gelatinase activity on BC cells. As shown in Figures 4 A, B, gelatin zymography demonstrated that significant abrogation of gelatinase activity of MMP-9 and MMP-2 in conditional medium samples was seen, after collection of conditional medium from BC cells exposed to AKBA in concentration-dependent fashion for 24 h. Further, we investigated whether AKBA could modulate the MMP-9 and MMP-2 expression. As shown in Figure 3, immunoblotting results revealed that AKBA displays a significant decrease in both MMP-9 and MMP-2 expression in a concentration-dependent manner (Figures 4 C, D). Collectively, these results suggest that AKBA effectively abrogates both the expression as well as the activity of MMP-9 and MMP-2 in a dose-dependent manner.
Figure 4
AKBA inhibits matrix MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity and expression in BC cells. A – BC cells (MCF-7, BT-474) were exposed to varying concentrations of AKBA for 24 h along with control DMSO; conditioned medium was analyzed for MMP-2 and MMP-9 gelatinase activity. B – Representative histogram, shows the fold change in gelatinase activity. C – Immunoblotting analysis of BC cells (MCF-7, BT-474) exposed to different concentrations of AKBA along with control DMSO shows the steady decrease in expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 proteins along with β-actin as an internal control. D – Densitometry analysis represented by histogram shows the fold change in protein expression after normalization with β-actin
The data denote the mean value ± SE of three independent unbiased experiments. *P < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
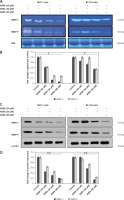
AKBA inhibits EGFR mediated PI3K/Akt pathway and showed a strong synergistic effect with BC inhibitors
Previous reports suggest that the strong correlation of EGFR mutation and post-EGFR signaling pathway activation in BC cells plays a critical role in invasion and metastasis of tumor cells. Therefore, we intended to explore whether AKBA could inhibit EGFR and its post-EGFR signaling in BC cells. As shown in Figures 5 A and B, the immunoblotting results of BC cell lysates treated with dose-dependent concentration (20, 30, 40 µM) of AKBA inhibits protein expression of EGFR as well as phosphorylation status of p-EGFR-Tyr1173. The post-signaling PI3K/Akt pathway modulated by EGFR plays a major role in transmitting extracellular signal transduction to cellular responses of BC cells to regulate tumor cell invasion. To determine whether AKBA could also affect the PI3K/Akt signaling, our immunoblotting results revealed a significant reduction in phosphorylation of PI3K-P110α and p-AKT-Ser473. However, no change was observed in the expression pattern of total Akt when BC cells were exposed to dose-dependent concentrations (20, 30, 40 µM) of AKBA for 24 h. Could downregulation of PI3K/Akt signaling proteins by AKBA also attenuate the expression of MMPs which play a critical role in tumor cell invasion? Our results revealed that upon treatment with dose-dependent concentrations (20, 30, 40 µM) of AKBA for 24 h, we observed a drastic reduction in the MMP-2 and MMP-9 with concomitant induction in the expression of E-cadherin and TIMP1. Collectively these results demonstrate that AKBA attenuates EGFR activation, which in turn abrogates post-EGFR PI3K/Akt and downstream associated proteins MMP-2 and MMP-9 that regulate tumor cell invasion in BC cells.
Figure 5
AKBA inhibits EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway and showed a significant inhibitory effect and strong synergistic effect with gefitinib and erlotinib in BC cells. A – Immunoblotting analysis of BC cells (MCF-7, BT-474) exposed to varying concentrations of AKBA (20, 30, 40 μM) shows the expression pattern of EGFR and post-EGFR signaling associated proteins (p-EGFR-Tyr1173, P110α, Akt, p-Akt-Ser473, MMP-9, MMP-2, TIMP1, E-cadherin) along with β-actin as an internal control. B – Densitometry analysis represented by histogram shows the fold change in protein expression after normalization with β-actin. C – Immunoblotting analysis of BC cells (MCF-7) exposed to concentrations of AKBA (40 μM), gefitinib (5 μM), erlotinib (5 μM) along with untreated control and combination (AKBA 40 μM + gefitinib 5 μM + erlotinib 5 μM) shows the expression pattern of EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling associated proteins along with β-actin as an internal control. D – Densitometry analysis represented by histogram shows the fold change in protein expression after normalization with β-actin
The data denote the mean value ± SE of three independent unbiased experiments. *P < 0.05.
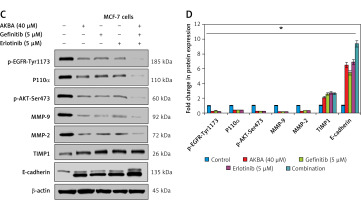
Next, we sought to evaluate the comparative inhibitory and synergistic effect of AKBA on EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt proteins with known inhibitors (gefitinib and erlotinib) in MCF-7 cells. We designed an experiment to expose cells with the highest concentration of AKBA (40 µM), gefitinib (5 µM), erlotinib (5 µM), and combination (AKBA 40 µM + gefitinib 5 µM, erlotinib 5 µM) along with untreated cells as a control for 24 h. Our immunoblotting results demonstrate that AKBA (40 µM) significantly inhibits protein expression of EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling associated proteins (p-EGFR-Tyr1173, PI3K-P110α, p-AKT-Ser473, MMP-9 and MMP-2) and increases the expression of TIMP1 and E-cadherin; however, when compared to known inhibitors, the effect is as good as that of gefitinib (5 µM) and erlotinib (5 µM) at their respective concentrations (Figures 5 C, D). Interestingly, the combination (AKBA 40 µM + gefitinib 5 µM, erlotinib 5 µM) shows a strong synergistic effect on EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling proteins by drastically downregulating the expression of p-EGFR-Tyr1173, PI3K-P110 α, p-AKT-Ser473, MMP-9, and MMP-2 and concomitantly upregulating the expression of TIMP1 and E-cadherin proteins significantly when compared to cells exposed to AKBA 40 µM, gefitinib 5 µM, and erlotinib 5 µM alone. Collectively, these results demonstrated that AKBA effectively targets and inhibits the EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling proteins and the effect is significant as compared to known inhibitors (gefitinib and erlotinib). However, the combination of AKBA, gefitinib and erlotinib has a strong synergistic effect and almost abolishes the expression of EGFR and downstream associated PI3K/Akt signaling associated proteins.
EGF reverses the AKBA inhibitory effect on EGFR and post-signaling PI3K/Akt pathway
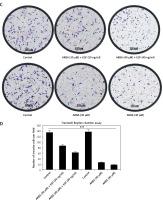
To investigate whether the EGF could restore the activation of EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt activation and neutralize any inhibitory effect of AKBA on tumor cell invasion, a two-set experiment was designed to confirm whether EGF could restore the stimulation of the EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. In the first set BC cells were pre-treated with EGF (30, 40, 50 ng/ml) and in the second set without EGF, followed by dose-dependent (20, 30, 40 µM) treatment with AKBA for 24 h in both the sets. As shown in Figures 6 A and B, interestingly, the immunoblotting results demonstrated that the BC cells pre-treated with EGF followed by AKBA treatment have upregulated EGFR, MMP-9 and MMP-2, expression as well as a significant increase in phosphorylation of EGFR (p-EGFR-Tyr1173), and p-Akt with a concomitant decrease in E-cadherin and TIMP1 protein expression. However, BC cells exposed to AKBA only had a significant reduction in EGFR, MMP-2, and MMP-9 protein expression as well as phosphorylation of EGFR (p-EGFR-Tyr1173) and p-Akt with simultaneous induction of E-cadherin and TIMP1 expression. Additionally, Transwell Boyden chamber invasion assay results reveal that the BC cells pre-treated with EGF (40, 50 ng/ml) followed by dose-dependent (30, 40 µM) treatment of AKBA for 24 h have a number of invasive cells similar to as that of control DMSO (Figures 6 C, D). However, cells treated with AKBA (20, 30, 40 µM) only have significantly fewer invasive cells than control DMSO cells. Collectively, these results indicate that AKBA inhibits EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling and its downstream targets which regulate cell invasion and metastasis.
Figure 6
EGF restores EGFR and post-signaling PI3K/Akt pathway activation inhibited by AKBA in BC cells. A – Immunoblotting analysis of BC cells (MCF-7) exposed to different concentrations AKBA, which were initially pre-treated with EGF (30, 40, 50 ng/ml) in one set and another set is exposed to only AKBA, shows the expression pattern of EGFR and post-EGFR signaling proteins (p-EGFR-Tyr1173, P110α, Akt, p-Akt-Ser473, MMP-9, MMP-2, TIMP1, E-cadherin) along with β-actin as an internal control. B – Densitometry analysis represented by histogram shows the fold change in protein expression after normalization with β-actin. C – BC cell invasion was determined by the Transwell Boyden chamber assay. Briefly, 2 × 105 cells/well was seeded in the top chamber in the presence of varying concentrations of AKBA along with control DMSO, which were pre-treated with EGF (40, 50 ng/ml) in one set and in another set only AKBA. Cells were allowed to migrate for 24 h, at which point migratory cells on the bottom half of the insert membrane were stained with 0.1% crystal violet and counted under a phase contrast microscope. Five fields were counted in triplicate from each insert of three independent experiments. Scale bar: 100 μm; 20×. D – Bar diagram showing quantification of invasive cells after exposure with varying concentrations of AKBA and pre-treated with EGF in one set and another set treated with AKBA only
The data represent the mean value ±SE of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01.
Discussion
Boswellic acids are the main components of gum resin obtained from the plant Boswellia serrata. Since ancient times the Indian traditional Ayurveda system of medicine has been using boswellic acid components to treat various inflammatory ailments which include ulcerative colitis, bronchial asthma, chronic colitis, Crohn’s disease and osteoarthritis [20, 26]. Among the boswellic acids, AKBA is one of the active non-redox components and has been reported to inhibit 5-lipooxygenase by acting as a non-competitive inhibitor [28, 29]. Recently AKBA has gained tremendous attention as a promising chemopreventive natural compound. Numerous studies have demonstrated the anti-cancer effect of AKBA against a wide variety of human cancer cells [30]. Moreover, AKBA exerts anti-tumor activity by modulating a plethora of molecules that play a crucial role in the development of tumorigenesis [31]. A growing body of evidence has revealed that AKBA exerts an antiproliferative effect in colorectal cancer cells by influencing miRNAs (let-7 and miR-200 family) [32]. However, AKBA exhibits an antiproliferative effect by triggering G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in glioblastoma cells [33]. Additionally, in pancreatic cancer cells, AKBA suppresses the invasiveness as well as motility of tumor cells by impairing cysteine X chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) expression [22]. Consistent with these results, we note that AKBA exerts an antiproliferative effect by inducing apoptosis in luminal subtype A (MCF-7) and subtype B (BT-474) BC cells. Importantly, the current study found that AKBA inhibits cell migration and invasion by attenuating EGFR-mediated post-PI3K/Akt signaling and downregulates its downstream targets MMP-9 and MMP-2 activity and expression with the simultaneous increase in E-cadherin and TIMP-1 expression in BC cells. These findings demonstrate that AKBA could be a potential chemopreventive agent in the therapeutics of BC patients.
Naturally occurring chemopreventive agents are an important source of drugs against many diseases including cancer. Almost half of the FDA-approved pharmaceutical drugs are derived either from plants directly or from plant derivatives [34]. Still, there is a scope for more drugs with high efficacy towards cancer cells and minimal toxicity towards normal cells. AKBA is a pentacyclic triterpenoid naturally occurring chemopreventive agent that exhibits numerous pharmacological properties such as neuroprotective, anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and antitumor activity by suppressing cell migration and invasion and triggering cell cycle arrest as well as induction of apoptosis in tumor cells [33, 35–37]. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate the antiproliferative potential of AKBA and elucidate the underlying inhibitory mechanism against BC cells. Our results revealed that AKBA displays a strong antiproliferative effect by reducing cell viability of BC cells significantly, but in transformed normal breast cells (MCF-10A), AKBA exerts a cytotoxic effect significantly at high concentration (IC50 = 112.45 µM), indicating that AKBA specifically exhibits an antiproliferative effect on cancer cells and shows minimal toxicity toward normal cells.
Park et al. demonstrated that AKBA exhibited an antiproliferative effect in pancreatic cancer cells by downregulating the expression of CXCR4 at the transcriptional level. Interestingly, the reduction of CXCR4 expression leads to the attenuation of cell invasion and migration properties of pancreatic malignant cells [22]. Similarly, Parr et al. showed that Boswellia frereana extract significantly inhibits hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-mediated cell migration and invasion in BC cells by modulating the c-Met signaling pathway [38]. Consistent with previous studies, we observed that AKBA causes significant reduction in motility of BC cells. To discourse any rational discrimination of AKBA in modulating cell migration with apoptosis, we cautiously select subtoxic concentrations and found that 20 µM AKBA did not induce cell killing significantly but altered cell migration significantly even at subtoxic doses when compared to untreated cells which were filled with migrated cells. A crucial step of metastatic cells is the capability of these cells to migrate across various barriers including extracellular matrix and disseminate the migrated cells away from the primary tumor site [39]. Interestingly, the Transwell Boyden chamber invasion assay also supports the notion that subtoxic concentrations of AKBA significantly inhibit the number of invading cells penetrating through a porous biological membrane.
The common mechanism of inducing cell death by natural chemopreventive agents is programmed cell death type I, called apoptosis. The activation of death receptor-mediated apoptosis called the extrinsic apoptosis pathway or the intrinsic apoptosis pathway, which is the mitochondria-dependent pathway, operates when there is depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential and liberation of cytochrome C [40]. Previous reports on colorectal cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma revealed that AKBA induces caspase-3 and PARP1 mediated apoptosis [41]. Consistent with the previous reports, we demonstrated that AKBA also activates caspase-3- and PARP1-mediated apoptosis in BC cells.
Accumulating evidence demonstrates that aberrant EGFR-mediated activation of the post-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and its downstream targets is associated with tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and motility in a wide variety of solid malignancies [42]. Moreover, recent reports suggest the strong correlation between hyperactivation of EGFR with cancer metastasis and drug resistance against neoplastic agents [43]. Upon interaction with its respective receptor, EGF stimulates dimerization of the receptor followed by autophosphorylation, which results in the activation of post-PI3K/Akt signaling and associated downstream targets. In our study, we observed that AKBA downregulates both expressions as well as phosphorylation of EGFR and the post-EGFR downstream PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in both the BC cell lines. However, we also demonstrated that AKBA significantly downregulates the protein expression of MMP-9 and MMP-2, which play a very vital role in malignant cell invasion and migration. Moreover, AKBA treatment simultaneously augments the protein expression of E-cadherin and TIMP1 in BC cells. Further immunoblotting analysis of BC cells exposed to the highest concentration of AKBA (40 µM), along with known inhibitors of EGFR (gefitinib and erlotinib), revealed a significant inhibitory effect on EGFR-mediated downstream PI3K/Akt signaling associated proteins. Interestingly, AKBA showed a strong synergistic effect with gefitinib and erlotinib and almost abolished the expression of EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling proteins and simultaneously upregulated the expression of TIMP1 and E-cadherin in BC cells. Additionally, we observed that pre-treatment with EGF could restore the ability of BC cell to migrate as well as invade even when exposed to AKBA. Taken together, these results demonstrate that AKBA blocks cell migration and invasion of BC cells which are operated by the EGFR-mediated post-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
In conclusion, our results for the first time demonstrate that AKBA exerts an antiproliferative effect by inducing apoptosis and abrogates the metastatic ability of luminal subtype A and subtype B BC cells by downregulating the EGFR-mediated post-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and associated downstream targets MMP-2 and MMP-9 with simultaneous induction of E-cadherin and TIMP1 expression. Additionally, AKBA showed a significant inhibitory and strong synergistic effect on EGFR-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling associated proteins when compared with the known inhibitors gefitinib and erlotinib. Finally, we demonstrate that AKBA is a promising anticancer therapeutic candidate against BC and could be used in future therapeutics for the prevention and therapy of BC.