Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
Editor's Choice
OBESITY / STATE OF THE ART PAPER
A review of the literature on obesity-related chronic kidney disease: a molecular description of gene susceptibility to polymorphisms, noncoding RNAs, and pathophysiology
1
Seccion de estudios de Posgrado e Investigacion, Escuela Superior de Medicina, Instituto Politecnico Nacional, Mexico
2
Laboratorio de biología molecular, Escuela Superior de Medicina, Instituto Politécnico Nacional., Escuela Superior de Medicina, Instituto Politecnico Nacional, Mexico
Submission date: 2025-01-22
Final revision date: 2025-06-03
Acceptance date: 2025-07-12
Online publication date: 2025-07-28
Corresponding author
Gustavo Guevara-Balcazar
Seccion de Estudios de Posgrado e Investigacion Escuela Superior de Medicina Instituto Politecnico Nacional, Mexico
Seccion de Estudios de Posgrado e Investigacion Escuela Superior de Medicina Instituto Politecnico Nacional, Mexico
Arch Med Sci 2025;21(4):1130-1140
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
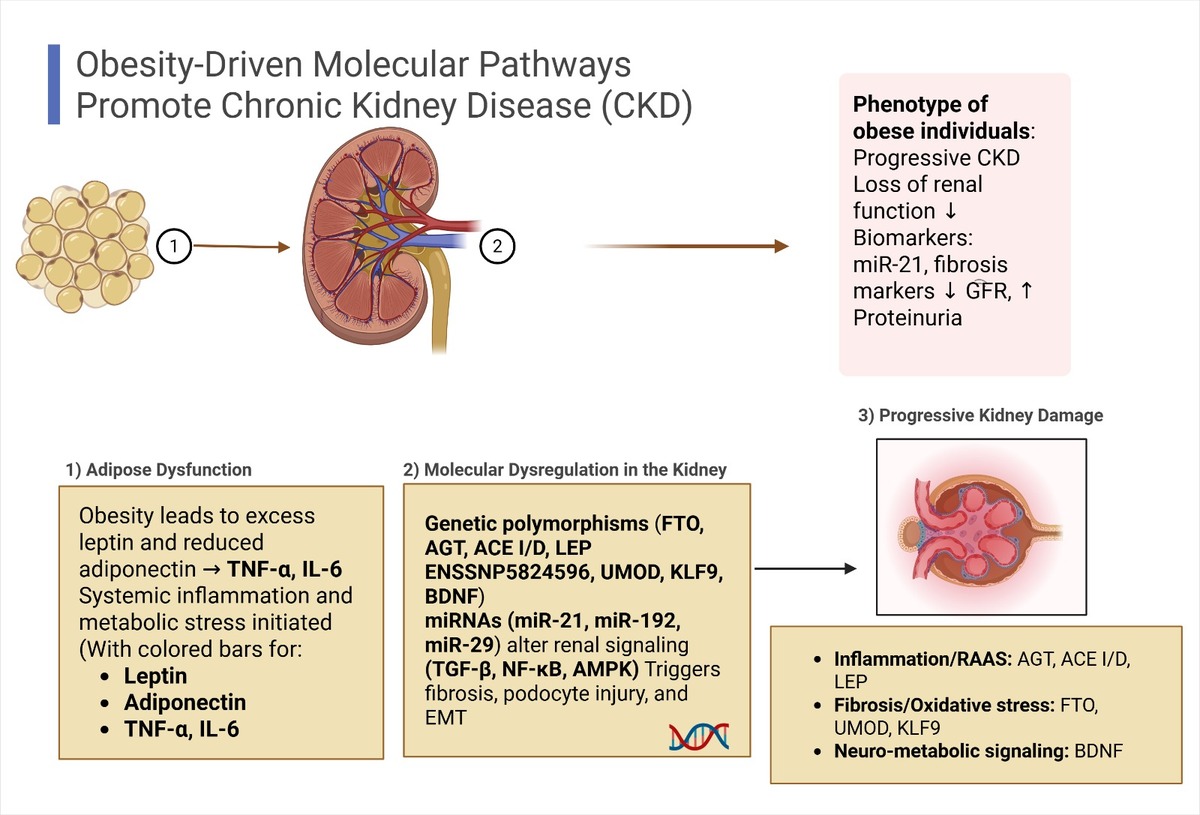
Obesity significantly contributes to the development and progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) by inducing metabolic and hemodynamic disturbances that drive gene dysregulation, inflammation, fibrosis, and renal structural injury. Key molecular mediators include genetic polymorphisms – such as AGT rs699, ACE I/D, LEP ENSSNP5824596, and FTO rs17817449 – and epigenetic regulators like microRNAs (e.g., miR-21, miR-192) and long non-coding RNAs (e.g., ANRIL, HOTAIR). These alterations affect signaling cascades such as TGF-/Smad3, NF-B, and AMPK, accelerating renal damage in obese individuals. Despite advances, reliable biomarkers and therapeutic targets remain scarce. This review integrates current evidence on the genetic and epigenetic basis of obesity-related CKD, offering a framework for early detection and precision medicine.
REFERENCES (65)
1.
García-Carro C, Vergara A, Bermejo S, Azancot MA, Sellarés J, Soler MJ. A nephrologist’s perspective on obesity: from kidney injury to clinical management. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021; 8: 655871.
2.
Luo K, Bian J, Wang Q, et al. Association of obesity with chronic kidney disease in elderly patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Turk J Gastroenterol 2019; 30: 611-5.
3.
Valizadeh M, Ahmadi AR, Abbaspour F, et al. The risk of kidney dysfunction in metabolically healthy/unhealthy population with normal weight or overweight/obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eat Weight Disord 2024; 29: 69.
4.
Kovesdy CP, Furth SL, Zoccali C; World Kidney Day Steering Committee. Obesity and kidney disease: hidden consequences of the epidemic. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2017; 32: 203-10.
5.
Stasi A, Cosola C, Caggiano G, et al. Obesity-related chronic kidney disease: main mechanisms and new approaches in nutritional management. Front Nutr 2022; 9: 925619.
6.
Sarafidis PA, Ruilope LM. Insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and renal injury: mechanisms and implications. Am J Nephrol 2006; 26: 232-44.
7.
He S, Li J, Yao L. Role of MCP-1/CCR2 axis in renal fibrosis: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Medicine (Baltimore) 2023; 102: e35613.
8.
Hall ME, do Carmo JM, da Silva AA, Juncos LA, Wang Z, Hall JE. Obesity, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis 2014; 7: 75-88.
9.
Ye C, Kong L, Zhao Z, et al. Causal associations of obesity with chronic kidney disease and arterial stiffness: a Mendelian randomization study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2022; 107: e825-35.
10.
Tang WH, Wang Z, Kennedy DJ, et al. Gut microbiota-dependent trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) pathway contributes to both development of renal insufficiency and mortality risk in chronic kidney disease. Circ Res 2015; 116: 448-55.
11.
Jang JW, Capaldi E, Smith T, Verma P, Varga J, Ho KJ. Trimethylamine N-oxide: a meta-organismal axis linking the gut and fibrosis. Mol Med 2024; 30: 128.
12.
Sun IO, Lerman LO. Urinary microRNA in kidney disease: utility and roles. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2019; 316: F785-93.
13.
Bravo-Vázquez LA, Paul S, Colín-Jurado MG, et al. Exploring the therapeutic significance of microRNAs and lncRNAs in kidney diseases. Genes (Basel) 2024; 15: 123.
14.
Carullo N, Zicarelli M, Michael A, et al. Childhood obesity: insight into kidney involvement. Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24: 17400.
15.
Forcina G, Luciano M, Frattolillo V, et al. Kidney damage in pediatric obesity: insights from an emerging perspective. J Clin Med 2024; 13: 7025.
16.
Juonala M, Magnussen CG, Berenson GS, et al. Childhood adiposity, adult adiposity, and cardiovascular risk factors. N Engl J Med 2011; 365: 1876-85.
17.
Yajnik CS, Joglekar CV, Lubree HG, et al. Adiposity and hyperinsulinemia in Indian children: relationship to birth size and parental phenotype. Am J Clin Nutr 2003; 77: 932-6.
18.
Vivante A, Golan E, Tzur D, et al. Childhood body mass index and the risk of end-stage renal disease in a cohort of 1.2 million adolescents. J Am Soc Nephrol 2012; 23: 1001-7.
19.
Yim HE, Yoo KH. Obesity and chronic kidney disease: prevalence, mechanism, and management. Clin Exp Pediatr 2021; 64: 511-8.
20.
Rodríguez-Segade S, Rodríguez J, Paz JM, et al. Glomerular hyperfiltration in overweight and obese children: a marker of early renal damage. J Pediatr 2021; 229: 127-33.e3.
21.
Muzzio ML, Kabakian ML, Morosán-Allo Y, et al. Association of glomerular hyperfiltration with serum chemokine levels and metabolic features in prepubertal children with overweight/obesity. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2020; 30: 1188-95.
22.
Freedman DS, Khan LK, Serdula MK, Ogden CL, Dietz WH. The relation of childhood BMI to adult adiposity: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics 2005; 115: 22-7.
23.
Aarestrup J, Blond K, Vistisen D, et al. Childhood body mass index trajectories and associations with adult-onset chronic kidney disease in Denmark: a population-based cohort study. PLoS Med 2022; 19: e1004098.
24.
GBD 2021 Adolescent BMI Collaborators. Global, regional, and national prevalence of child and adolescent overweight and obesity, 1990–2021, with forecasts to 2050: a forecasting study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025; 405: 785-812.
25.
Wang Y, Chen HJ. Use of percentiles and Z-scores in anthropometry. In: Handbook of Anthropometry: Physical Measures of Human Form in Health and Disease. Preedy VR, ed. Springer 2012; 29-48.
26.
Jadresic L, Silverwood RJ, Kinra S, Nitsch D. Can childhood obesity influence later chronic kidney disease? Pediatr Nephrol 2019; 34: 2457-77.
27.
Dina C, Meyre D, Gallina S, et al. Variation in FTO contributes to childhood obesity and severe adult obesity. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 724-6.
28.
Farooqi IS, O’Rahilly S. Mutations in ligands and receptors of the leptin–melanocortin pathway that lead to obesity. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2008; 4: 569-77.
29.
Raskiliene A, Smalinskiene A, Kriaucioniene V, Lesauskaite V, Petkeviciene J. Associations of MC4R, LEP, and LEPR polymorphisms with obesity-related parameters in childhood and adulthood. Genes 2021; 12: 949.
30.
López-Rodríguez G, Estrada-Neria A, Suárez-Diéguez T, Tejero ME, Fernández JC, Galván M. Common polymorphisms in MC4R and FTO genes are associated with BMI and metabolic indicators in Mexican children: differences by sex and genetic ancestry. Gene 2020; 754: 144840.
31.
Peters LJF, Floege J, Biessen EAL, Jankowski J, van der Vorst EPC. PTPRO. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 6547.
32.
Glowacki F, Savary G, Gnemmi V, et al. Increased circulating miR-21 levels are associated with kidney fibrosis. PLoS One 2013; 8: e58014.
33.
Hutny M, Hofman J, Zachurzok A, Matusik P. MicroRNAs as the promising markers of comorbidities in childhood obesity: a systematic review. Pediatr Obes 2022; 17: e12880.
34.
Du R, Liu H, Cui H, et al. microRNA-130b promotes renal fibrosis by activating the TGF-1/Smad pathway and suppressing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor- in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Blood Press Res 2018; 43: 1815-30.
35.
Coimbra S, Rocha S, Valente MJ, et al. New insights into adiponectin and leptin roles in chronic kidney disease. Biomedicines 2022; 10: 2642.
36.
Xu W, Zhu Y, Wang S, Liu J, Li H. From adipose to ailing kidneys: the role of lipid metabolism in obesity-related chronic kidney disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 2024; 13: 1540.
37.
Sun D, Chen J, Wu W, et al. miR-802 causes nephropathy by suppressing the NF-B-repressing factor in obese mice and human. J Cell Mol Med 2019; 23: 2863-73.
38.
Tao Y, Tang J, Zhu L, et al. Serum adiponectin and renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022; 13: 837275.
39.
Navarro-González JF, Mora-Fernández C. The role of inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2008; 19: 433-42.
40.
Sharma K, Karl B, Mathew AV, et al. Metabolomics reveals signature of mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2013; 24: 1901-12.
41.
An H, Jang Y, Choi J, Hur J, Kim S, Kwon Y. New insights into AMPK, as a potential therapeutic target in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and hepatic fibrosis. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 2025; 33: 18-38.
42.
Chen T, Zhang Y, Liu Y, et al. MiR-27a promotes insulin resistance and mediates glucose metabolism by targeting PPAR--mediated PI3K/AKT signaling. Aging (Albany NY) 2019; 11: 7510-24.
43.
Fan Y, Chen H, Huang Z, Zheng H, Zhou J. Emerging role of miRNAs in renal fibrosis. RNA Biol 2020; 17: 1-12.
44.
Li M, Chi X, Wang Y, Setrerrahmane S, Xie W, Xu H. Trends in insulin resistance: insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022; 7: 216.
45.
Thethi T, Kamiyama M, Kobori H. The link between the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and renal injury in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Curr Hypertens Rep 2012; 14: 160-9.
46.
Tain YL, Hsu CN. The renin-angiotensin system and cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome: focus on early-life programming. Int J Mol Sci 2024; 25: 3298.
47.
Chen YY, Hong H, Lei YT, Zou J, Yang YY, He LY. ACE2 deficiency exacerbates obesity-related glomerulopathy through its role in regulating lipid metabolism. Cell Death Discov 2022; 8: 401.
48.
Singh S, Anshita D, Ravichandiran V. MCP-1: function, regulation, and involvement in disease. Int Immunopharmacol 2021; 101: 107598.
49.
Sedeek M, Nasrallah R, Touyz RM, Hébert RL. NADPH oxidases, reactive oxygen species, and the kidney: friend and foe. J Am Soc Nephrol 2013; 24: 1512-8.
50.
Forbes JM, Thorburn DR. Mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 2018; 14: 291-312.
51.
Katsiki N, Kolovou G, Melidonis A, Banach M. The cardiac-kidney-liver (CKL) syndrome: the “real entity” of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 207-15.
52.
Gorin Y, Block K. Nox4 and diabetic nephropathy: with a friend like this, who needs enemies? Free Radic Biol Med 2013; 61: 130-42.
53.
Mallipattu SK, Estrada CC, He JC. The critical role of Krüppel-like factors in kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2017; 312: F259-65.
54.
O’Seaghdha CM, Fox CS. Genome-wide association studies of chronic kidney disease: what have we learned? Nat Rev Nephrol 2011; 8: 89-99.
55.
He Y, Huang C, Lin X, et al. miR-29 inhibits renal fibrosis by targeting TGF-β/Smad pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2019; 316: F786-800.
56.
Shah BP, Sleiman PM, McDonald J, Moeller IH, Kleyn P. Functional characterization of all missense variants in LEPR, PCSK1, and POMC genes arising from single-nucleotide variants. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab 2023; 18: 209-19.
57.
Rahmouni K. Cardiovascular regulation by the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus: neurocircuitry and signaling systems. Hypertension 2016; 67: 1064-71.
58.
Hall JE, do Carmo JM, da Silva AA, Wang Z, Hall ME. Obesity, kidney dysfunction and hypertension: mechanistic links. Nat Rev Nephrol 2019; 15: 367-85.
59.
Su H, Liu B, Chen H, et al. LncRNA ANRIL mediates endothelial dysfunction through BDNF downregulation in chronic kidney disease. Cell Death Dis 2022; 13: 661.
60.
Huang H, Zhang G, Ge Z. lncRNA MALAT1 promotes renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by targeting the miR-2355-3p/IL6ST axis. Front Pharmacol 2021; 12: 647650.
61.
Xu Y, Niu Y, Li H, Pan G. Downregulation of lncRNA TUG1 attenuates inflammation and apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cell induced by ischemia-reperfusion by sponging miR-449b-5p via targeting HMGB1 and MMP2. Inflammation 2020; 43: 1362-74.
62.
Alvarez ML, DiStefano JK. Functional characterization of the plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 gene (PVT1) in diabetic nephropathy. PLoS One 2011; 6: e18671.
63.
Gao J, Chen Q, Zhao Z, et al. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition via modulating miR-124/EZH2 in renal fibrosis. J Cell Physiol 2018; 233: 1-12.
64.
Strauss-Kruger M, Olinger E, Hofmann P, et al. UMOD genotype and determinants of urinary uromodulin in African populations. Kidney Int Rep 2024; 9: 3477-89.
65.
Larkin BP, Glastras SJ, Chen H, Pollock CA, Saad S. DNA methylation and the potential role of demethylating agents in prevention of progressive chronic kidney disease. FASEB J 2018; 32: 5215-26.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.