Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
PANCREATOLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting ICU mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis: A dual-center retrospective cohort study.
1
Changde Hospital , Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University(The First People's Hospital of Changde City), China
2
The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, China
Submission date: 2025-03-29
Final revision date: 2025-07-15
Acceptance date: 2025-07-16
Online publication date: 2025-07-26
Corresponding author
Yuting Yang
Changde Hospital , Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University(The First People's Hospital of Changde City), China
Changde Hospital , Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University(The First People's Hospital of Changde City), China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Acute pancreatitis(AP) is a severe inflammatory disease causing abdominal pain and organ failures, potentially leading to necrosis and dysfunction. This study aimed to create a nomogram to predict mortality in intensive care unit(ICU) patients with AP.
Material and methods:
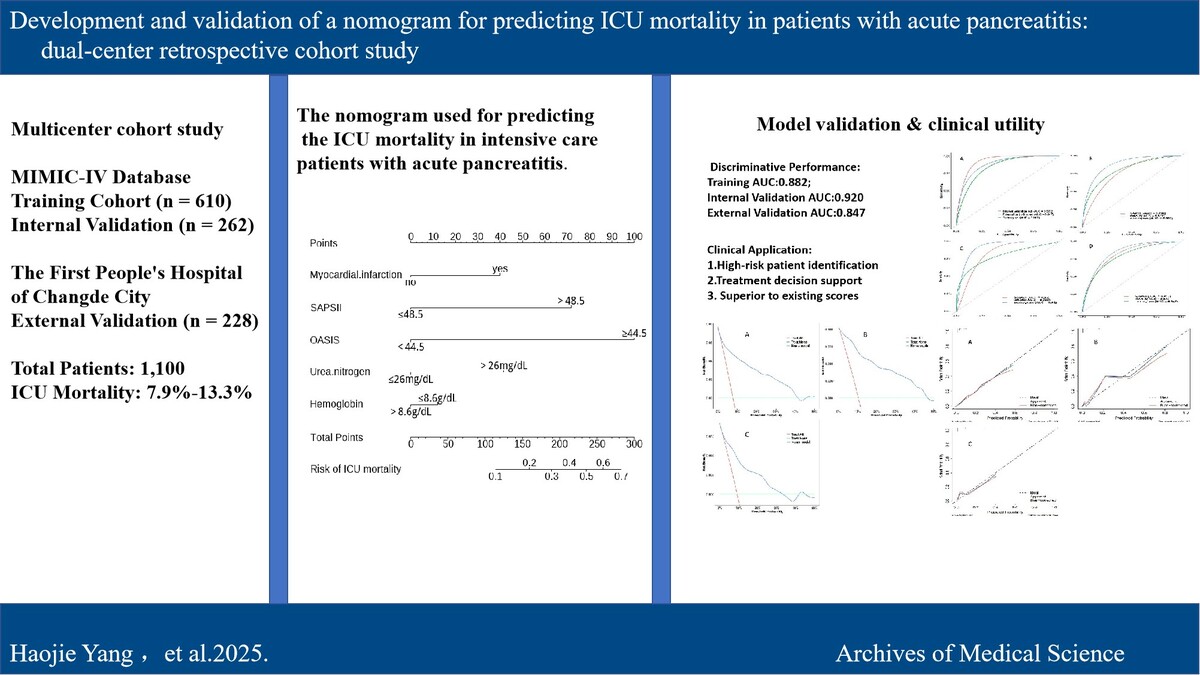
We conducted cohort study using the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV(MIMIC-IV) and data from the first people’s hospital of Changde city, selecting variables via univariate logistic regression and constructing a nomogram with multivariate logistic regression. The nomogram's performance was evaluated with the area under the curve (AUC) calculated from the receiver operating curve (ROC), reclassification improvement (NRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI), while clinical utility was assessed with a calibration curve and decision curve analysis (DCA) validated the predictive model's efficacy.
Results:
A total of 1100 patients were analyzed, with ICU mortality rates of 7.9% in the training set, 9.2% in the internal validation set, and 13.3% in the external validation set. From the 32 extracted variables, five were ultimately selected: hemoglobin, urea nitrogen, SAPSII score, OASIS score, and myocardial infarction. We subsequently developed and validated a nomogram. The AUC, NRI, and IDI of the nomogram were superior to the traditional SAPSII and OASIS scoring systems. Calibration curves and the Hosmer-Lemeshow test revealed satisfactory alignment between predicted and observed outcomes, while DCA substantiated the clinical utility of the model across a wide range of threshold probabilities.
Conclusions:
The nomogram accurately predicted ICU AP patients' mortality and may serve as a valuable tool for clinicians to identify high-risk patients and optimize medical decision-making.
Acute pancreatitis(AP) is a severe inflammatory disease causing abdominal pain and organ failures, potentially leading to necrosis and dysfunction. This study aimed to create a nomogram to predict mortality in intensive care unit(ICU) patients with AP.
Material and methods:
We conducted cohort study using the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV(MIMIC-IV) and data from the first people’s hospital of Changde city, selecting variables via univariate logistic regression and constructing a nomogram with multivariate logistic regression. The nomogram's performance was evaluated with the area under the curve (AUC) calculated from the receiver operating curve (ROC), reclassification improvement (NRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI), while clinical utility was assessed with a calibration curve and decision curve analysis (DCA) validated the predictive model's efficacy.
Results:
A total of 1100 patients were analyzed, with ICU mortality rates of 7.9% in the training set, 9.2% in the internal validation set, and 13.3% in the external validation set. From the 32 extracted variables, five were ultimately selected: hemoglobin, urea nitrogen, SAPSII score, OASIS score, and myocardial infarction. We subsequently developed and validated a nomogram. The AUC, NRI, and IDI of the nomogram were superior to the traditional SAPSII and OASIS scoring systems. Calibration curves and the Hosmer-Lemeshow test revealed satisfactory alignment between predicted and observed outcomes, while DCA substantiated the clinical utility of the model across a wide range of threshold probabilities.
Conclusions:
The nomogram accurately predicted ICU AP patients' mortality and may serve as a valuable tool for clinicians to identify high-risk patients and optimize medical decision-making.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.