Introduction
Respiratory diseases have long been a focus of research in the field of public health, posing a serious threat to the health of the global population [1]. Among them, asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are two highly prevalent diseases, posing significant challenges to patients’ quality of life and the consumption of social medical resources. Although asthma and COPD have distinct pathological and physiological differences, with the former mainly characterized by chronic airway inflammation and the latter encompassing pathological changes such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema, their relationship and mutual influence remain a scientific puzzle of great concern [2, 3].
Asthma manifests as a complex chronic inflammatory condition, featuring airway hyperresponsiveness and reversible airway obstruction. Hundreds of millions of people worldwide suffer from asthma, affecting both adults and children [4]. COPD mainly includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, is a progressive disease commonly found in smokers, and is also influenced by environmental factors such as air pollution. Both diseases are primarily characterized by symptoms such as dyspnea, cough, and chest tightness, causing significant inconvenience to patients’ lives and work [5].
Although asthma and COPD differ in presentation and progression, they share important common features. Studies have shown that in some patients, asthma and COPD may coexist, referred to as “asthma-COPD overlap syndrome” (ACOS) [6]. This situation complicates the management and treatment of the disease, making it even more necessary to investigate the relationship between asthma and COPD to better understand their shared pathophysiological mechanisms and provide more precise bases for treatment strategies [7].
Previous studies have mainly examined the pathogenesis and causative factors of asthma and COPD separately. Whether asthma may causally contribute to the development of COPD, however, remains unclear. Some observational studies have provided some clues, but due to the presence of numerous confounding factors, the research findings are contentious. Therefore, we need a more precise method to control for confounding variables.
By adopting a Mendelian randomization approach, which enables exploration of the causal relationship between asthma and COPD without being influenced by confounding factors, this study evaluated the possible association between the two conditions. Integrating publicly available genome-wide association study (GWAS) datasets and employing careful selection of genetic instrumental variables, alongside various Mendelian randomization analysis methods, the study sought to elucidate the genetic mechanisms underlying asthma and COPD, thereby providing a clearer understanding of their interrelation.
Material and methods
Guidelines for reporting and study design
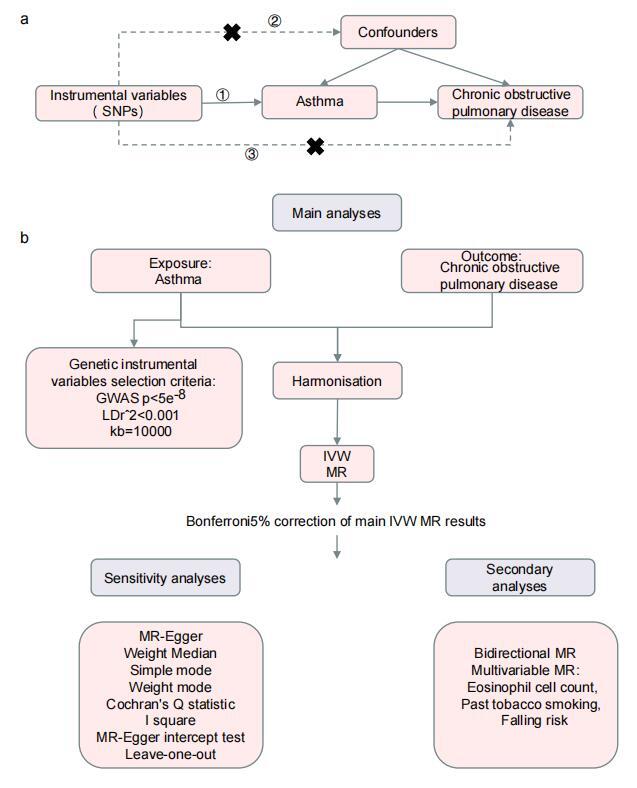
This study used a two-sample MR approach and publicly available datasets to investigate the impact of asthma on COPD. The study report adheres to the STROBE-MR Statement, which enhances the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using Mendelian randomization [8]. Figure 1 illustrates the study design schematically.
Figure 1
Mendelian randomization analysis flowchart. A – Basic assumptions of Mendelian randomization analysis, including (1) the relevance assumption, which states that selected instrumental variables must be significantly associated with the exposure factor; (2) the exclusion restriction assumption, which states that instrumental variables could only affect the outcome through the pathway “instrumental variable → exposure → outcome”; (3) the independence assumption, which states that instrumental variables must not be significantly correlated with potential confounding factors that might affect exposure or outcome. B – Flowchart of the analysis methods used in this study
SNP – single nucleotide polymorphism. IVW – inverse variance weighted. MR-Egger – Mendelian randomization-Egger. GWAS – genome-wide association study.

Data sources
Genome-wide association study (GWAS) data for preliminary analysis of asthma indicators were obtained from two studies: by Demenais et al. on 127,669 individuals of European ancestry, including 107,715 controls and 19,954 asthma cases [9]; and by Valette et al. on 408,442 individuals of European ancestry, including 352,255 controls and 56,167 asthma cases [10].
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) GWAS data (ebi-a-GCST90018807) were obtained from a study by Sakaue et al. on 468,475 individuals of European ancestry, including 13,530 COPD cases and 454,945 controls [11].
Other GWAS data: eosinophil cell count (ieu-b-33) from Vuckovic et al., including 563,946 samples [12, 13]; past tobacco smoking (ukb-b-2134) [14] from approximately 500,000 UK Biobank samples [15]; falling risk (ebi-a-GCST90012857) from GWAS data analysis including 451,179 samples [16, 17].
Instrumental variable selection
Effective genetic instrumental variables must meet three core assumptions: (1) the relevance assumption, i.e., the chosen instrumental variables must exhibit a significant association with the exposure factor; (2) the independence assumption, i.e., instrumental variables must not be significantly correlated with potential confounding factors that might affect exposure or outcome; (3) the exclusion restriction assumption, i.e., instrumental variables must exclusively influence the outcome through the pathway “instrumental variable → exposure → outcome”.
In this study, the selection criteria for exposure instrumental variables were as follows: single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with p < 5 × 10–8 in GWAS were used as the primary screening condition; SNPs in linkage disequilibrium (r2 < 0.001) and with a physical distance > 10,000 kb between every two genes were excluded. Then, outcome data were extracted from GWAS based on the selected SNPs.
MR causal effect estimation
Various two-sample MR methods were used to assess the causal effects between exposure and outcome, including: inverse-variance weighted (IVW), MR-Egger, weighted median, simple mode, and weighted mode. Studies have shown [18] that the IVW method is slightly stronger under certain conditions than other methods. Its characteristic is that it does not consider the presence of intercept terms during regression and uses the reciprocal of the outcome variance as weights for fitting. Therefore, in the absence of pleiotropy, regardless of the presence or absence of heterogeneity, the IVW method was used as the main MR analysis approach in this study, with the other four methods used as supplementary analyses (an IVW random effects model was used when heterogeneity was present). When pleiotropy was present, the MR-Egger method was used to calculate the results. The reverse causal effect was assessed using the same methods to examine the potential causal effect of the outcome on the exposure.
Sensitivity analysis
Various methods, including heterogeneity testing, pleiotropy testing, and leave-one-out testing, were used to perform sensitivity analysis on the analysis results, as follows:
(1) Heterogeneity testing: Cochran’s Q test was used to assess heterogeneity among estimated values of each SNP. If Cochran’s Q test was statistically significant, it indicated significant heterogeneity in the results, and the effect size of the causal effect was evaluated using the IVW random effects model. Since Cochran’s Q test could only determine the presence or absence of heterogeneity and cannot determine its distribution, the I2 statistic was used to reflect the proportion of heterogeneity in the total variation of instrumental variables: I2 ≤ 0 indicates no observed heterogeneity; I2 = 0–25% indicates mild heterogeneity; I2 = 25–50% indicates moderate heterogeneity; I2 > 50% indicates high heterogeneity.
(2) Pleiotropy assessment: The MR-Egger method was employed to examine pleiotropy in instrumental variables. A MR-Egger’s intercept p-value < 0.05 was considered evidence of substantial horizontal pleiotropy in genetic variation.
(3) Leave-one-out testing: The leave-one-out method was used to evaluate whether a single SNP affects the association between asthma and COPD by sequentially removing individual SNPs and calculating the MR results with the remaining instrumental variables. If there was a large difference between the MR effect estimate after removing a particular instrumental variable and the cumulative effect estimate, it indicated that the MR effect estimate was sensitive to that SNP.
Multivariable MR analysis
MVMR is an extension of MR that uses genetic variations associated with multiple exposures possibly correlated with a single outcome to evaluate the impacts of various exposures on a singular outcome. It could assess the direct effects of individual exposure factors on the outcome. We conducted multivariable MR analysis considering several COPD-related exposure factors – eosinophil cell count (ieu-b-33), past tobacco smoking (ukb-b-2134), falling risk (ebi-a-GCST90012857), and asthma – to estimate the direct effect of asthma on COPD.
Statistical analysis
All data processing and statistical analyses were performed using the R programming language (version 4.2.2). Mendelian randomization analysis primarily relied on the TwoSampleMR package [19]. To ensure the robustness and reliability of the results, Cochran’s Q test and leave-one-out analysis were used. Additionally, genetic pleiotropy was assessed using MR-Egger’s intercept method. Evaluation metrics consisted of odds ratios (OR) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (95% CI). All statistical p-values were two-sided, with SNP loci generated from GWAS studies considered statistically significant at p < 5 × 10–8; statistical significance was determined for other tests at a threshold of p < 0.05.
Results
Instrumental variable selection
Based on the selection criteria for instrumental variables, SNPs with linkage disequilibrium were removed, and SNPs associated with asthma (p < 5 × 10–8, clump=TRUE, r2 < 0.001, kb = 10,000) were included as instrumental variables after matching with COPD GWAS data.
MR causal effect estimation
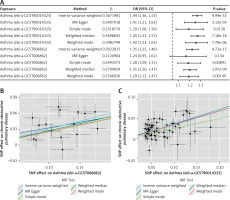
Analysis was conducted using five models: MR Egger, weighted median, inverse variance weighted (IVW), simple mode (SM), and weighted mode. The results of the five models for the causal relationship between asthma and COPD (Figure 2 A, Table I) indicated a significant causal relationship between asthma and COPD, with higher levels of all circulating metabolites associated with an increased risk of COPD occurrence. Different models of MR analysis for asthma (Figures 2 B, C) provided consistent directional estimates, with relatively consistent slopes.
Table I
Estimates of Mendelian randomized causal effects of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Figure 2
Multiple model analysis results of Mendelian randomization analysis for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A – Forest plot showing the causal association analysis results of Mendelian randomization using multiple models for asthma and chronic obstructive COPD. Effect estimates are presented using OR and 95% CI, along with the number of instrumental variables used in each model, as well as the calculated beta values and standard errors. B, C – Scatter plots showing the causal relationship between asthma (id: ebi-a-GCST006862) (B), asthma (id: ebi-a-GCST90014325) (C), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The slope of the line represents the magnitude of the causal relationship predicted by different models
SNPs – single nucleotide polymorphisms, OR – odds ratio, CI – confidence interval.
Sensitivity analysis
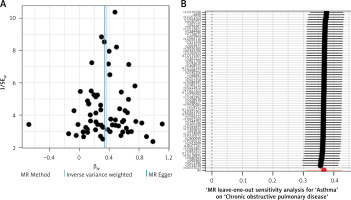
Heterogeneity testing of significant results was conducted using Cochran’s Q test and I2 statistic, as shown in Table II. The results indicated high heterogeneity in the Mendelian randomization (MR) results for asthma (id: ebi-a-GCST006862) with respect to COPD (I2 = 50.65%, Cochran Q p-value < 0.05). However, there was no significant heterogeneity in the MR results for asthma (id: ebi-a-GCST90014325) with respect to COPD (Cochran Q p-value > 0.05, I2 < 50%). The exposure of asthma (id: ebi-a-GCST006862) with high heterogeneity was removed, and the exposure of asthma (id: ebi-a-GCST90014325) was analyzed further. The funnel plot of instrumental variables for asthma (id: ebi-a-GCST90014325) (Figure 3 A) showed a symmetrical distribution of scatter points, indicating no potential bias in the causal association effect.
Table II
Mendelian randomization analysis heterogeneity test for the association between asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
| Exposure | Q | Q df | Cochran Q p-value | I2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asthma (ebi-a-GCST006862) | 34.45016675 | 17 | 0.007340785 | 50.65 |
| Asthma (ebi-a-GCST90014325) | 80.35204633 | 64 | 0.081408939 | 20.35 |
Figure 3
Funnel plot for heterogeneity testing and effect estimates of IVW random effects model in Mendelian randomization analysis of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A – Funnel plot displaying the causal effect estimates of each instrumental variable for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The causal effect estimates of the IVW and MR Egger models are indicated by lines on the plot. B – Forest plot showing the sequential effect estimates of asthma and COPD using single SNP locus analysis
Instrumental variable horizontal pleiotropy testing was conducted using MR-Egger regression. The p-value of the intercept term in the statistical hypothesis test for the p-value associated with asthma (id: ebi-a-GCST90014325) exceeded 0.05, and the intercept value approached zero, indicating that the causal inference of this study was not affected by horizontal pleiotropy (Table III).
Table III
Mendelian randomization analysis of horizontal pleiotropy for the association between asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
| Exposure | MR-Egger intercept | Standard error | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asthma (ebi-a-GCST90014325) | 0.001909126 | 0.005021459 | 0.705080595 |
We performed leave-one-out analysis, systematically excluding each instrumental variable locus, to examine the causal impact of asthma on COPD (Figure 3 B). It was found that there was no significant deviation from the total effect of the instrumental variable set. The Steiger directional test result confirmed the causal direction with a p-value less than 0.05, indicating no reverse causal effect (Table IV).
Reverse MR analysis
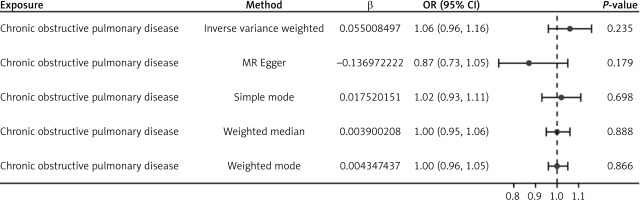
To evaluate reverse causal effects, we used COPD as the exposure and asthma (id: ebi-a-GCST90014325) as the outcome. Following the selection criteria for instrumental variables in this study and removing SNPs with linkage disequilibrium, the reverse causal MR analysis results (Figure 4) indicated that COPD did not have a significant causal effect on asthma (p > 0.05), as shown in Table V.
Table V
Results of reverse causal Mendelian randomization analysis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
Figure 4
Multiple model analysis results of reverse causal Mendelian randomization analysis for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. The forest plot presents the results of reverse causal association analysis between COPD and asthma using multiple Mendelian randomization models. Effect estimates are displayed using OR and 95% CI, along with the number of instrumental variables used in each model, as well as the calculated beta values and standard errors
SNPs – single nucleotide polymorphisms, OR – odds ratio, CI – confidence interval.
Multivariable MR analysis
We conducted multivariable MR analysis by incorporating exposures such as eosinophil cell count (ieu-b-33), past tobacco smoking (ukb-b-2134), falling risk (ebi-a-GCST90012857), etc., to assess the direct effect of asthma (ebi-a-GCST90014325) on COPD (Table VI). In Model 1, correcting for the indirect effect of eosinophil cell count, the results indicated that asthma (ebi-a-GCST90014325) still significantly affects COPD. In Model 2, correcting for the influence of smoking, the results showed that asthma (ebi-a-GCST90014325) still significantly affects COPD. In Model 3, considering the impact of falling risk, the results demonstrated that asthma (ebi-a-GCST90014325) still significantly affects COPD.
Table VI
Results of multivariable Mendelian randomization analysis on the impact of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
[i] Model 1: Multivariable MR analysis of asthma and eosinophil cell count on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Model 2: Multivariable MR analysis of asthma and past tobacco smoking on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Model 3: Multivariable MR analysis of asthma and falling risk on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. MR – Mendelian randomization, SNPs – single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Discussion
This study evaluated into the causal impact of asthma on COPD through a two-sample Mendelian randomization design. Firstly, by rigorously screening publicly available GWAS data, we successfully selected a series of SNPs that meet the criteria for instrumental variables for subsequent causal effect estimation. Through various two-sample MR methods, we concluded that asthma serves as a significant risk factor for COPD, providing solid genetic evidence for further elucidating the relationship between these two diseases.
In sensitivity analysis, we validated the robustness of the results through methods such as heterogeneity testing and pleiotropy testing. Even after excluding SNPs with high heterogeneity, the results remained significant. Through leave-one-out analysis, we further confirmed the robustness of the instrumental variables, eliminating the significant influence of individual SNPs on the overall outcomes. The results of the MR-Egger intercept method also indicate that the causal inference of this study is not significantly affected by horizontal pleiotropy.
To gain a more comprehensive understanding of the impact of asthma on COPD, we conducted reverse MR analysis and found that COPD does not have a significant causal effect on asthma, thereby ruling out the possibility of reverse causality.
Finally, through multivariable MR analysis, we explored the impact of multiple potential confounding factors on the relationship between asthma and COPD. The results indicate that the causal effect of asthma on COPD still exists after considering factors such as eosinophil cell count, smoking, and falling risk.
Previous research in the asthma and COPD field had extensively explored their pathogenesis, pathophysiological processes, and their relationship with environmental, genetic, and other factors. However, the relationship between asthma and COPD has always been a contentious issue. Here are some key points and findings from previous studies: Previous research in the asthma and COPD field had extensively explored their pathogenesis, pathophysiological processes, and their relationship with environmental, genetic, and other factors. For instance, recent studies, such as the one by Kurmi et al. [20], have also investigated the genetic links and shared risk factors between these diseases, further supporting the potential overlap in their etiology. However, the relationship between asthma and COPD remains a contentious issue.
Traditionally, asthma and COPD were considered to be two diseases with distinct biological characteristics [21]. Asthma mainly involves airway inflammation and reversible airway obstruction, while COPD includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, characterized by irreversible airway narrowing [22]. However, recent studies suggest that some patients might have both asthma and COPD, leading to asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS), with symptoms and biomarkers showing overlapping features, thereby increasing attention to the relationship between the two [23].
Early observational studies attempted to reveal the relationship between asthma and COPD but faced challenges due to confounding factors. For example, smoking, air pollution, occupational exposure, etc., are factors that affect respiratory health, making it difficult for observational studies to establish whether asthma directly leads to the development of COPD [24]. In recent years, advances in techniques such as genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have enriched our comprehension of the genetic underpinnings of respiratory disorders. Some genes have been confirmed to be associated with asthma and COPD, but their specific mechanisms and their interrelationship remain uncertain.
In clinical practice, distinguishing between asthma and COPD is sometimes not straightforward, especially in some elderly patients or long-term smokers. The presence of this overlapping pathological state increases the difficulty of disease management [25].
Additionally, the understanding of asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS) remains incomplete, necessitating further research to elucidate the nature of this dual pathological state.
Our study contributes to this discussion by providing evidence that asthma is a risk factor for COPD development. To further understand the mechanisms involved, exploring how asthma-related factors influence COPD onset is crucial. Given the overlap of symptoms in ACOS and the inconclusive findings from previous observational studies, our study stands out by utilizing genetic evidence from GWAS to establish a causal relationship between asthma and COPD. Additionally, our results emphasize the importance of addressing asthma control to potentially prevent COPD progression. Future research directions may involve studying specific asthma-related genetic markers and their impact on COPD development, as well as implementing personalized therapeutic interventions based on genetic susceptibility analysis. Overall, our study highlights the significance of recognizing asthma as a contributing factor to COPD and underscores the necessity for targeted interventions to alleviate disease burden and improve patient outcomes.
When discussing how asthma affects COPD and its implications for disease prevention or treatment, several mechanisms may be relevant. Firstly, the regulation of inflammation has a potential key role. Both asthma and COPD are associated with the inflammatory response, so studying the mechanism of inflammation regulation, such as reducing airway inflammation through medication or biological treatment, may prevent or treat the progression of COPD [26]. Further research may focus on developing novel inflammation-regulating agents and evaluating their effectiveness and safety in clinical practice. Secondly, the airway remodeling mechanism is also an important research direction. Asthma and COPD patients have abnormal airway structure and function; hence, studying the mechanism of airway remodeling and attempting to restore normal airway structure and function through medication or other treatment methods may help prevent or treat COPD [27]. Further research may include the development of novel treatment methods targeting airway remodeling and the evaluation of their long-term effects on COPD patients. Lastly, the immune regulation mechanism may also be a promising treatment approach. The immune system plays an important role in the development of asthma and COPD, so studying the mechanism of immune response regulation, such as the use of immunomodulators, may help prevent or treat COPD [28]. Further research may include the evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of different types of immunomodulators and the determination of the optimal treatment strategy. These potential mechanisms require further research to promote their application in disease prevention or treatment. Such research may encompass basic scientific investigations, including mechanism studies and drug development, as well as clinical research, such as clinical trials and epidemiological studies, to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of these mechanisms and determine the optimal treatment strategies. Additionally, interdisciplinary cooperation is needed to promote joint efforts from different fields of expertise and accelerate the application of these mechanisms in clinical practice.
In addition to genetic factors, immune pathways play a significant role in the development of both asthma and COPD. Recent studies have highlighted the importance of Th17 cells and the IL-31/IL-33 axis in modulating chronic inflammation and immune responses, which are pivotal in the pathogenesis of these diseases. Furthermore, factors such as vitamin D and the microbiome have been shown to influence immune regulation, potentially impacting disease progression. For example, recent work by Murdaca et al. [29] discussed these mechanisms in the context of chronic immune-mediated diseases, offering new insights into their therapeutic potential.
This study is innovative in its genetic approach, using Mendelian randomization methods to minimize confounding factors, and evaluating whether asthma directly affects the risk of COPD. This will help fill the gaps in existing research and provide new directions for future studies. Additionally, through multivariable MR analysis, we will explore the impact of other exposure factors related to COPD, thereby achieving a more comprehensive understanding of this complex disease relationship.
In summary, this study provides new genetic evidence and theoretical support for understanding the relationship between asthma and COPD through comprehensive analysis from multiple perspectives and methods. This has positive implications for the formulation of preventive and therapeutic strategies for related diseases and the selection of future genetic research directions.
In this study, there are limitations that need to be considered. Firstly, despite our efforts to screen publicly available GWAS data rigorously, the limited nature of the data prevents us from conducting detailed analyses on more disease pathological types. Particularly, due to the scarcity of patients and the lack of specific SNP data, we cannot confirm the relationship between asthma and certain specific pathological types of COPD. Additionally, due to the diversity of “exposure” sources and the lack of relevant SNP data, we have yet to investigate whether specific sources of “exposure” exert similar biological effects on diseases and whether “exposure” has a consistent impact across different subgroups. It is worth noting that our data primarily consist of samples of European ancestry, and thus, may not adequately differentiate ethnic variations from various regions, potentially limiting the generalizability of these results to a global scale. Although the data from GWAS or large samples used for diseases are continuously increasing, there remains a problem of data insufficiency. Further exploration of the basic multicenter research mechanisms between “exposure” and “outcome” is needed to better understand how asthma affects the occurrence and development of COPD.
In conclusion, our research findings suggest that there is a significant causal relationship between asthma and COPD, indicating that the occurrence of asthma increases the likelihood of COPD developing in patients. Even when considering potential confounding factors, asthma still exerts a significant causal effect on COPD. These findings deepen our understanding of the association between COPD and asthma, providing an important reference for further research and clinical practice. Future studies should further explore the complex relationship between these two diseases to promote the development of prevention and treatment strategies for respiratory system diseases.