Introduction
Obesity has reached epidemic proportions worldwide and is now recognized as a major risk factor for a wide spectrum of non-communicable diseases. Among these, chronic kidney disease (CKD) has emerged as a significant complication directly associated with obesity. Although diabetes and hypertension have traditionally been considered the principal causes of CKD, mounting evidence suggests that obesity per se – independent of these comorbidities – contributes substantially to the development and progression of renal dysfunction [1–4].
The pathophysiological mechanisms underlying this association are multifactorial and complex, involving hemodynamic changes, metabolic dysregulation, inflammation, oxidative stress, and lipotoxicity [5–8]. Furthermore, recent advances in molecular biology have revealed the involvement of genetic variants [9] in obesity-related renal damage. In addition to host-derived mechanisms, gut microbiota have emerged as important contributors to renal dysfunction through both metabolic and epigenetic pathways. Microbial metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) can modulate gene expression by inhibiting histone deacetylases or altering DNA methylation patterns. Notably, trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), a gut-derived metabolite elevated in diet-induced obesity, has been shown to exacerbate renal injury and may also participate in the regulation of epigenetic responses [10]. These findings emphasize the contribution of epigenetic modifications [11], microRNAs [12], and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) [13], highlighting the need for integrative approaches in both research and therapy.
This review synthesizes current literature on the molecular mechanisms linking obesity and CKD, emphasizing gene polymorphisms, regulatory microRNAs (miRNAs), epigenetic modifications, and emerging therapeutic strategies targeting these pathways. A systematic search of PubMed and Scopus was performed to identify original studies and reviews published between 2003 and 2025. Search terms included combinations of “obesity”, “chronic kidney disease”, “renal dysfunction”, “gene polymorphism”, “epigenetics”, “microRNAs”, “lncRNAs”, and “biomarkers”, using Boolean operators (AND, OR) to refine the strategy.
Studies were included if they met the following criteria: 1) involved human or animal models of obesity-related CKD; 2) addressed molecular mechanisms related to gene variants, epigenetic regulation, or non-coding RNAs; 3) were published in English in peer-reviewed journals; and 4) provided full-text availability. Exclusion criteria comprised studies not addressing kidney-related outcomes, case reports, editorials, and non-English articles.
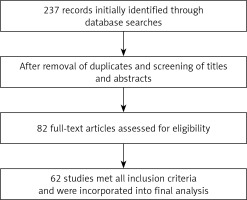
After removing duplicates and screening titles and abstracts, 82 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility, and 62 met the inclusion criteria and were incorporated into the final synthesis. The selection process is illustrated in Figure 1. For each included article, the following data were extracted: study design, population characteristics, molecular pathways evaluated, target genes or RNAs involved, and clinical or experimental findings related to CKD.
Early-onset obesity and lifelong risk of renal and metabolic disease
Childhood obesity has become a growing global health concern and is now widely recognized as a strong predictor of adult obesity and related metabolic comorbidities, including CKD [14]. Longitudinal cohort studies have consistently demonstrated that elevated body mass index (BMI) during childhood persists into adulthood and significantly increases the risk of hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and kidney dysfunction later in life [15–17]. For instance, children with obesity have been shown to have a several-fold increased risk of developing CKD in adulthood [18, 19].
Moreover, early-onset obesity has been associated with glomerular hyperfiltration during childhood, a compensatory mechanism that can lead to progressive glomerular damage and nephron loss over time. This pathophysiological trajectory underscores the importance of early interventions as even subclinical renal alterations during youth may predispose individuals to chronic renal impairment in adulthood [20, 21].
Defining accurate thresholds for childhood obesity remains critical for early identification of individuals at risk for lifelong metabolic and renal complications. Several large-scale studies have shown that BMI percentiles and growth trajectories during childhood are strong predictors of adult obesity and its sequelae, including chronic kidney disease. Notably, thresholds such as the 85th or 95th percentile for age- and sex-specific BMI have been validated as indicators of increased cardiometabolic risk later in life [22–26]. These findings reinforce the importance of early detection and sustained monitoring of pediatric adiposity patterns to guide timely interventions.
Recent studies have also identified genetic and epigenetic markers associated with early-onset obesity and its long-term impact on renal and metabolic health. Polymorphisms in genes such as FTO, LEP, MC4R, and LEPR have been linked to increased adiposity in childhood and progression to hypertension, insulin resistance, and chronic kidney disease in adulthood [27–30]. In parallel, epigenetic modifications – including altered promoter methylation in FTO and LEP, and differential expression of renal-associated microRNAs such as miR-21, miR-155, and miR-29 – have been observed in obese children at risk of subclinical nephropathy [31–33]. These findings support the integration of genetic and epigenetic screening in early preventive strategies.
Genetic and epigenetic factors in obesity and CKD
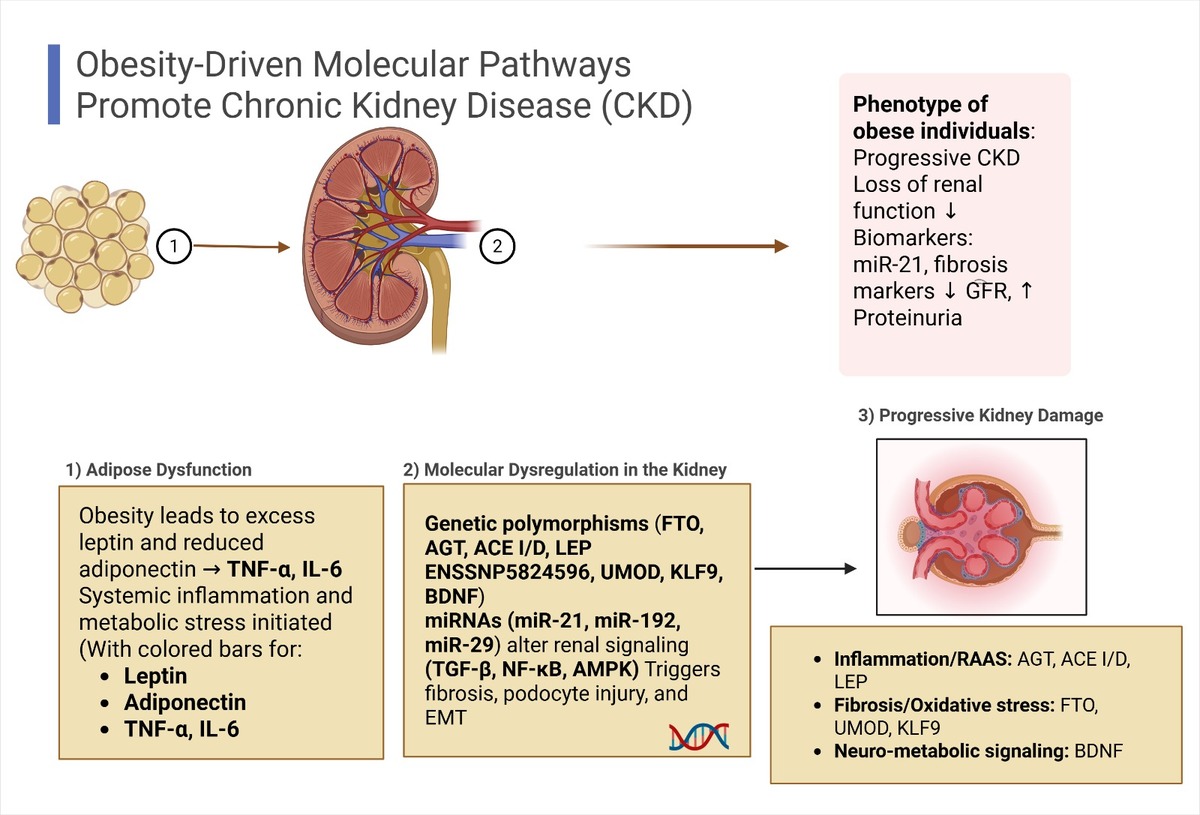
The molecular mechanisms linking obesity and CKD are multifaceted and complex. Obesity-induced metabolic alterations – such as elevated blood pressure and glucose levels – directly impact renal cells by modulating the expression of genes involved in key signaling pathways [5, 9]. Genetic susceptibility – particularly through specific polymorphisms in genes such as AGT, ACE, and FTO – and epigenetic regulation further influence individual risk for CKD [27], while genes like LEP and ADIPOQ have been widely studied for their roles in obesity and metabolic regulation [28, 29]. Additionally, epigenetic mechanisms – including microRNA dysregulation, DNA methylation, and other post-transcriptional modifications – have been implicated in kidney dysfunction by altering gene expression and potentially promoting fibrotic remodeling [5, 15]. Collectively, obesity initiates a cascade of molecular events that culminate in renal injury, with both genetic and epigenetic pathways playing critical roles in the development and progression of chronic kidney disease (Figure 2).
Figure 2
Molecular mechanisms linking obesity to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Obesity-associated adipose tissue dysfunction results in elevated leptin, reduced adiponectin, RAAS activation, and systemic inflammation. These alterations, combined with specific genetic variants (e.g., FTO, ACE, LEP) and miRNA dysregulation (e.g., miR-21, miR-192), disrupt renal homeostasis by affecting signaling pathways such as TGF-β/Smad3, NF-κB, MAPK, and AMPK
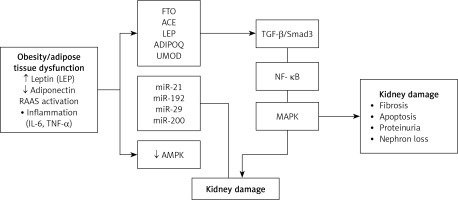
The cumulative effect drives renal fibrosis, apoptosis, and progressive nephron loss
Epigenetic alterations – particularly the dysregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) – have emerged as key contributors to the progression of obesity-related CKD. miRNAs such as miR-21 and miR-130b have been shown to promote renal inflammation and fibrosis, while others like miR-29 exert protective roles by inhibiting extracellular matrix accumulation [31, 33, 34]. These miRNA-based regulatory shifts, together with gene variations in LEP and ADIPOQ, intensify chronic inflammation and metabolic imbalance in renal tissues [9, 35].
Moreover, differential DNA methylation at specific CpG sites has been identified in both obesity and CKD models, suggesting potential biomarkers for early detection and progression monitoring [31, 36]. The interplay between these epigenetic changes and environmental influences – such as urbanization, poor diet, and physical inactivity – further exacerbates disease risk.
Importantly, several of these miRNAs and methylation patterns are emerging as therapeutic targets, with a growing interest in the use of miRNA inhibitors or mimics, and epigenetic modulators to reverse fibrosis and inflammation in the kidneys [31–33]. For instance, miR-130b has been shown to promote renal fibrosis through activation of the TGF-β1/Smad pathway and repression of PPAR-γ in diabetic nephropathy, further supporting the therapeutic relevance of targeting specific miRNAs in chronic kidney disease [34]. These advances hold promise for the development of precision medicine approaches tailored to the molecular profile of individuals with obesity-related CKD.
Direct effects of obesity on CKD – adipose tissue dysfunction and hormonal mediators
Obesity promotes CKD through profound metabolic disturbances originating in dysfunctional adipose tissue. This dysfunction leads to an imbalance in adipokine secretion – characterized by increased levels of proinflammatory mediators such as leptin, TNF-α, and IL-6, and reduced production of the anti-inflammatory adipokine adiponectin [35, 37]. Elevated leptin activates TGF-β1 signaling in renal tissues, promoting glomerulosclerosis and fibrosis. In parallel, leptin resistance exacerbates insulin resistance and fosters a pro-oxidative, pro-inflammatory environment [28, 37].
Low adiponectin levels impair AMPK activation, aggravating albuminuria, podocyte injury, and insulin signaling defects [35, 38]. Additionally, adipokines like resistin amplify renal inflammation and fibrogenesis. These adipose-derived molecular signals – compounded by obesity-related hypertension and glomerular hyperfiltration – accelerate CKD progression through overlapping metabolic and inflammatory pathways [3, 34].
Cytokines and inflammatory mediators
Chronic low-grade inflammation is a hallmark of obesity and plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of CKD. Proinflammatory cytokines, notably TNF-α and IL-6, are secreted by dysfunctional adipose tissue and initiate both systemic and renal inflammatory responses [37]. These cytokines exacerbate oxidative stress and suppress protective mechanisms such as AMPK signaling, thereby amplifying tissue injury [38, 39].
Elevated circulating levels of TNF-α and IL-6 are consistently linked to glomerular damage, podocyte dysfunction, and renal fibrosis, establishing a direct molecular connection between inflammation and CKD progression in obesity [37, 39].
Other inflammatory mediators, such as resistin and visfatin, contribute to endothelial dysfunction and promote further oxidative stress, compounding renal injury [6, 39].
This chronic inflammatory milieu activates profibrotic pathways, particularly TGF-β, leading to progressive scarring and nephron loss [34].
Lipotoxicity
Dysregulated lipid metabolism is a central mechanism in obesity-induced renal damage. The excessive accumulation of free fatty acids (FFAs) and triglycerides in renal cells – especially podocytes and proximal tubular epithelial cells – triggers oxidative stress, apoptosis, and structural injury. This lipotoxic overload stems in part from reduced activity of key enzymes in fatty acid oxidation, such as carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) and PGC1α, which impairs mitochondrial lipid processing and energy balance [40].
Simultaneously, upregulation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c) enhances lipid biosynthesis, further exacerbating intracellular lipid accumulation. The combination of increased lipid influx and diminished lipid clearance leads to cellular dysfunction, contributing to glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis, especially under conditions of suppressed AMPK signaling [38, 39, 41].
In parallel, genetic and epigenetic factors modulate lipotoxic susceptibility. Polymorphisms in adipokine-related genes and dysregulation of miRNAs such as miR-21 and miR-130b intensify inflammatory and fibrotic responses to lipid stress, accelerating CKD progression [12, 34] (Tables I and II).
Table I
Genes related to adipose tissue dysfunction, cytokines, inflammation, and lipotoxicity
| Gene | Function | Mechanism affected | Related pathways | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEP | Encodes leptin, regulates energy balance and satiety | Promotes fibrosis and sympathetic activation | TGF-β, sympathetic nervous system (SNS) | [28, 35] |
| ADIPOQ | Encodes adiponectin, anti-inflammatory adipokine | Protects against inflammation and lipotoxicity | AMPK activation, fatty acid oxidation | [35, 38, 39] |
| TNF | Encodes TNF-α, key mediator of systemic inflammation | Induces insulin resistance and cytokine storm | NF-κB activation, insulin resistance | [6, 37, 38] |
| SREBP-1 | Transcription factor regulating lipogenesis | Enhances lipid accumulation and lipotoxicity | SREBP-1c pathway, fatty acid metabolism | [41] |
Table II
miRNAs related to adipose tissue dysfunction, cytokines, inflammation, and lipotoxicity
| miRNA | Function | Mechanism affected | Related pathways | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 | Regulates inflammation and fibrosis | Activates profibrotic signaling | TGF-β, RAAS | [12, 31, 32] |
| miR-27a | Regulates adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity | Alters adipokine secretion, contributes to insulin resistance | Adipogenesis | [42] |
| miR-130b | Modulates adipokine secretion | Inhibits anti-inflammatory responses | Leptin resistance, adipokine balance | [34] |
| miR-192 | Maintains podocyte function | Promotes glomerulosclerosis and fibrosis | AMPK, oxidative stress | [12, 43] |
| miR-802 | Impairs insulin and energy homeostasis | Amplifies insulin resistance and inflammation | PI3K/AKT/mTOR | [33, 37] |
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance, a hallmark of metabolic syndrome, plays a central role in linking obesity to CKD [1, 44]. Resulting hyperinsulinemia enhances renal sodium reabsorption, leading to volume expansion, hypertension, and increased glomerular pressure. These hemodynamic alterations drive hyperfiltration, ultimately contributing to nephron injury and CKD progression. Furthermore, insulin resistance disrupts metabolic homeostasis, particularly by impairing fatty acid oxidation, which promotes lipid accumulation, lipotoxicity, and podocyte damage [39, 40].
At the molecular level, proinflammatory adipokines such as TNF-α and IL-6 further exacerbate insulin resistance and fuel systemic and renal inflammation [5]. These cytokines also inhibit AMPK signaling, a key energy-sensing pathway, thereby amplifying metabolic dysfunction and accelerating glomerular injury. Additionally, genetic variants involved in insulin signaling (e.g., IRS1, IRS2) have been linked to worsened lipid toxicity and CKD progression in obese individuals [44].
Hypertension
Obesity-associated hypertension is a major driver of CKD progression. Adipose tissue secretes elevated levels of angiotensinogen, activating the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS). This promotes sodium retention, fluid overload, and persistent blood pressure elevation [1, 45]. Chronic hypertension exerts mechanical stress on the glomerular filtration barrier, leading to glomerulosclerosis and progressive nephron loss [1].
In parallel, leptin-induced activation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) further amplifies RAAS activity, reinforcing a vicious cycle of vasoconstriction, oxidative stress, and inflammation [28, 45]. These intertwined mechanisms accelerate kidney damage and contribute to CKD severity in individuals with obesity.
Dyslipidemia
In obesity-related dyslipidemia, elevated triglycerides and reduced HDL cholesterol levels contribute to CKD through multiple molecular mechanisms. Excess FFAs accumulate in renal cells due to impaired fatty acid oxidation, driven by the downregulation of PPARα and CPT1 [46]. This lipotoxic environment damages both glomerular and tubular structures, triggering oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrotic remodeling [5]. Additionally, proinflammatory cytokines and altered lipid-regulating pathways, notably through SREBP-1c activation, promote further triglyceride and cholesterol accumulation, worsening renal injury [39, 46].
Metabolic and inflammatory changes that lead to nephron loss
Metabolic syndrome, characterized by chronic low-grade inflammation, plays a central role in the progression of CKD. In individuals with obesity, elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines contribute to glomerular injury by disrupting podocyte function and promoting renal fibrosis [5]. These cytokines also induce oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, further impairing nephron integrity [39, 40]. The convergence of insulin resistance, hypertension, and dyslipidemia creates a sustained proinflammatory and profibrotic environment that accelerates glomerulosclerosis and nephron depletion [1, 37, 38]. These pathological mechanisms are further influenced by genetic and epigenetic factors, including overactivation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), suppression of AMPK signaling, and adipokine imbalance, which together form the molecular basis of obesity-related CKD (Table III).
Table III
Genes associated with insulin resistance, hypertension, and metabolic dysfunction in obesity-related CKD
| Gene | Function | Mechanism affected | Related pathways | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRS1 | Insulin receptor substrate 1 | Impairs insulin signaling, promotes lipogenesis | Insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, lipotoxicity | [44] |
| AGT | Encodes angiotensinogen | Promotes vasoconstriction and sodium retention | RAAS activation, hypertension | [45] |
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme | Converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II | Hypertension, glomerular hyperfiltration | [41] |
| ACE2 | Counter-regulator of RAAS | Modulates leptin and insulin signaling | SNS activation, inflammation | [47] |
Mediators of the progression of obesity-induced CKD
Inflammatory mediators. Chronic low-grade inflammation, a hallmark of obesity, plays a central role in the progression of obesity-related CKD. Macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue leads to the sustained release of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and MCP-1 [37, 48]. These mediators disrupt insulin signaling and increase vascular permeability, contributing to glomerular injury. The resulting endothelial dysfunction – marked by tight junction disruption – facilitates proteinuria and worsens kidney damage.
In parallel, MCP-1 promotes the recruitment of additional immune cells, sustaining inflammation and driving renal fibrosis through extracellular matrix accumulation [5, 48]. This proinflammatory environment activates the NF-κB signaling pathway, which upregulates proinflammatory gene expression. The downregulation of tumor-suppressive microRNAs like miR-802 further amplifies NF-κB activity, exacerbating renal injury and accelerating functional decline [37].
Oxidative stress, is a key contributor to renal injury in obesity. The excessive accumulation of free fatty acids in both adipose and renal tissues triggers overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), primarily via activation of NADPH oxidase (NOX-4) [49]. These ROS induce lipid peroxidation and structural damage in renal cells, accelerating glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis [49].
Simultaneously, mitochondrial dysfunction – commonly observed in obesity – further amplifies oxidative stress by increasing ROS output and diminishing antioxidant defenses [39, 50]. This redox imbalance activates NF-κB signaling, which reinforces proinflammatory and profibrotic pathways.
Insulin resistance, another hallmark of obesity, worsens this process by suppressing antioxidant gene expression and enhancing ROS generation [39]. Although sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) normally protects renal tissue by promoting antioxidant enzyme activity and autophagy, its expression and function are impaired in obesity, contributing to progressive kidney damage [11].
Hormonal imbalances act as key mediators in the progression of CKD associated with obesity. One of the main drivers is activation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), which promotes hypertension, sodium retention, and renal fibrosis via elevated levels of angiotensin II and aldosterone. These hormones exacerbate glomerular hyperfiltration and stimulate extracellular matrix deposition, ultimately leading to glomerulosclerosis and nephron loss. This multi-organ involvement has recently been conceptualized as the Cardiac-Kidney-Liver (CKL) syndrome, emphasizing the interconnected impact of obesity and metabolic disease on renal, hepatic, and cardiovascular systems [51].
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), a central mediator of fibrosis in obesity-related CKD, is regulated by microRNAs involved in matrix remodeling, including miR-29 and miR-21. The latter is frequently upregulated in CKD and enhances TGF-β signaling, making it a promising therapeutic target [1, 31] (Table IV).
Table IV
Inflammatory and oxidative mediators in obesity-induced CKD
| Mediator | Role in CKD | Mechanism of action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | Proinflammatory cytokine | Disrupts insulin signaling, increases endothelial permeability | [10, 37] |
| IL-6 | Proinflammatory cytokines | Enhances oxidative stress and stimulates fibrotic remodeling | [35, 39] |
| MCP-1 | Chemokine for monocyte recruitment | Attracts immune cells and promotes sustained inflammation and fibrosis | [5, 7] |
| NOX-4 | ROS generator | Induces oxidative stress and contributes to podocyte injury | [10, 49, 52] |
| TGF-β | Master regulator of fibrosis | Activates the Smad3 pathway, increasing extracellular matrix deposition and glomerulosclerosis | [31, 34] |
Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in obesity-related CKD
Advances in the understanding of gene–miRNA regulatory networks have uncovered multiple molecular targets for therapeutic intervention in obesity-related CKD. The disease progression is driven by intricate metabolic, inflammatory, and fibrotic pathways, which are modulated by both genetic and epigenetic mechanisms. Notably, interactions between specific genes and miRNAs play a pivotal role in determining susceptibility and disease severity [12, 31, 34].
Several candidate biomarkers have emerged from these regulatory networks. Genes such as FTO, KLF9, PAX6, BDNF, and CDKAL1 are associated with adipose tissue dysfunction and are involved in critical pathways regulating fat storage, energy balance, and systemic inflammation – key contributors to obesity-induced renal injury [9, 27].
Similarly, miRNAs including miR-21, miR-192, miR-34a, and miR-200 have been implicated in the regulation of fibrosis, inflammation, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), underscoring their potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in obesity-related CKD [31, 33, 43].
Table V summarizes selected genes and miRNAs involved in obesity-related CKD, highlighting their biological functions, pathways, therapeutic potential, and supporting references.
Table V
Therapeutic relevance of key genes and miRNAs in obesity-related CKD
| Gen/miRNA | Function | Roads involved | Therapeutic potential | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTO | Regulates energy storage and adipogenesis | mTOR, PI3K–Akt | Modulation of fat metabolism and insulin sensitivity | [9, 30] |
| KLF9 | Controls oxidative stress and apoptosis | Oxidative stress, apoptosis | Target for redox balance restoration | [9, 53] |
| miR-21 | Promotes fibrosis and inflammation | TGF-β, MAPK | Antifibrotic target via miRNA inhibition | [31, 32] |
| miR-192 | Enhances fibrosis | TGF-β, EMT | Antifibrotic strategy through miRNA silencing | [12, 43] |
| LEP | Appetite regulation, sympathetic tone | Leptin signaling | Use of leptin antagonists to reduce renal stress | [2, 14, 35] |
| ADIPOQ | Anti-inflammatory, insulin sensitizer | AMPK, adiponectin pathways | Adiponectin receptor agonists | [2, 14, 35] |
| UMOD | Regulates tubular function | Uromodulin secretion | SNP-based therapeutic targeting | [54] |
| miR-29 | Antifibrotic effect | TGF-β, Wnt/β-catenin | miRNA mimics to block ECM deposition | [55] |
Key genes and miRNAs in obesity-related CKD
Genetic variants and regulatory miRNAs contribute significantly to the molecular landscape of CKD in obese individuals.
Genes related to adipose tissue dysfunction
Polymorphisms in LEP and ADIPOQ, which encode leptin and adiponectin respectively, influence adipokine secretion and have been associated with both obesity and CKD risk [14, 28, 35]. Variants in FTO and MC4R modulate energy balance and fat accumulation, playing a direct role in obesity-associated renal injury [9]. Similarly, polymorphisms in LEPR and POMC, key genes involved in appetite regulation, contribute to metabolic dysregulation and increase susceptibility to CKD through mechanisms involving insulin resistance and hypertension [56, 57]. In this context, LEPR-mediated leptin signaling is often altered in CKD, promoting systemic inflammation, disrupting energy homeostasis, and accelerating renal damage [58].
Beyond these genetic factors, fibrosis-related miRNA networks also play a crucial role in obesity-related CKD. Among antifibrotic regulators, miR-29 exerts a protective effect by repressing extracellular matrix accumulation, whereas miR-192 enhances fibrosis by modulating transcription factors such as ZEB1 and ZEB2, which are involved in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) [43, 55]. These regulatory miRNAs are emerging as attractive therapeutic targets. Moreover, oxidative stress and chronic inflammation – hallmarks of type 2 diabetes – can modulate miRNA expression patterns, further linking metabolic disturbances to renal injury [43, 55].
Long non-coding RNAs in obesity-related chronic kidney disease
Several long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as important regulators in CKD, particularly in its obesity-associated forms. These transcripts, although non-coding, influence gene expression through interactions with chromatin, transcription factors, and microRNAs, thereby modulating key processes such as inflammation, fibrosis, and oxidative stress involved in renal damage [59].
One of the most recently validated lncRNAs in CKD is ANRIL (antisense non-coding RNA in the INK4 locus). A 2022 study demonstrated that ANRIL mediates endothelial dysfunction by downregulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a mechanism that contributes to vascular complications and disease progression in CKD. In addition, ANRIL has been shown to epigenetically regulate the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in diabetic nephropathy by interacting with chromatin-modifying enzymes such as p300 and enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2), thus promoting vascular injury and fibrotic remodeling associated with CKD [60].
Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) is overexpressed in models of diabetic nephropathy and promotes TGF-β1 signaling and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in renal tubular epithelial cells. This activity leads to extracellular matrix accumulation and tubulointerstitial fibrosis, contributing to CKD progression [61].
Taurine upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) has shown protective roles in renal pathology. It reduces oxidative stress and inflammation in renal injury models by acting as a molecular sponge for miR-29b and by upregulating SIRT1, thereby enhancing antioxidant defenses and limiting tubular injury [62].
Plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1) promotes fibrogenic gene expression and extracellular matrix remodeling through its interaction with miR-1207. It is overexpressed in diabetic nephropathy models and contributes to renal fibrosis and progressive kidney damage [63].
HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) is another lncRNA implicated in renal fibrosis. It promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by repressing miR-124 and activating the EZH2–TGF-β1 axis, leading to chromatin remodeling and profibrotic gene expression. In diabetic kidney disease models, HOTAIR has been shown to exacerbate renal injury and matrix deposition [64].
These lncRNAs form complex networks with microRNAs and transcription factors, acting as scaffolds or sponges within competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) systems. Their convergence in both metabolic and renal pathology suggests that ANRIL, HOTAIR, MALAT1, and TUG1 may serve as key molecular bridges in obesity-related CKD. Further research is needed to validate their clinical utility as biomarkers or therapeutic targets (Table VI).
Table VI
lncRNAs involved in obesity-related CKD
| lncRNA | Main function | Affected mechanism | Relationship with obesity and CKD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANRIL | Inflammation and renal fibrosis | NF-κB, TGF-β/Smad3 | Indirect evidence in both contexts | [60] |
| HOTAIR | Epigenetic remodeling and EMT | PRC2, EMT | Indirect evidence in both contexts | [64] |
| MALAT1 | Inflammation, fibrosis, apoptosis | NF-κB, MAPK, TGF-β | Direct experimental evidence | [61] |
| TUG1 | Mitochondrial homeostasis, fibrosis | miR-29c, oxidative stress | Partial evidence, separate models | [62] |
Summary of genetic variants with quantitative associations
Several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have demonstrated significant associations with both obesity and the progression of CKD. For example, the rs9939609 A allele in the FTO gene has been linked to increased BMI and elevated CKD risk, with an odds ratio (OR) of 1.29 in European populations [9]. Similarly, the ACE insertion/deletion (I/D) polymorphism – particularly the D allele – is associated with hypertension and renal fibrosis, showing an OR of 1.45 in Asian cohorts [13, 29]. These findings underscore the relevance of genetic screening for early identification of individuals at risk for obesity-related renal impairment.
Other variants, such as rs7799039 in LEP and rs12917707 in UMOD, also contribute to the obesity-CKD interface. The LEP rs7799039 polymorphism is associated with dysregulated adipokine secretion and increased CKD susceptibility (OR = 1.25), while the UMOD rs12917707 variant exerts a protective effect against CKD (OR = 0.74) by preserving tubular integrity and reducing sodium reabsorption. Integrating such genetic markers may enhance risk prediction and support personalized preventive strategies.
In addition to the variants already included in Table VII, four specific SNPs highlighted in the abstract merit further discussion due to their functional implications in obesity-related CKD:
Table VII
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with quantitative associations to obesity and chronic kidney disease
| SNP | Gene | Effect in obesity/CKD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| FTO rs9939609 | FTO | Increased BMI and CKD risk (OR = 1.29) | [9] |
| FTO rs17817449 | FTO | Increased adiposity and insulin resistance | [9, 15] |
| ACE I/D | ACE | D allele associated with hypertension and renal fibrosis (OR = 1.45) | [13, 29] |
| AGT rs699 (M235T) | AGT | Tallele increases RAAS activation and glomerular injury | [21, 25] |
| LEP rs7799039 | LEP | Increased CKD susceptibility due to adipokine imbalance (OR = 1.25) | [14] |
| LEP ENSSNP5824596 | LEP | Potential impact on leptin expression and secretion, under investigation | [14] |
| UMOD rs12917707 | UMOD | Protective effect on CKD via tubular sodium handling (OR = 0.74) | [65] |
AGT rs699 (M235T), a missense variant in exon 2 of the AGT gene, is associated with elevated angiotensinogen levels. The T allele enhances renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) activation and promotes hypertension and glomerular injury in obese individuals [21, 25].
The ACE I/D polymorphism, already discussed above and listed in Table VII, influences circulating ACE activity. The D allele increases angiotensin II levels and contributes to renal fibrosis, particularly under conditions of obesity-induced hypertension [13, 29].
LEP ENSSNP5824596 is a less-characterized variant in the LEP gene that may influence leptin expression and secretion. Although its direct association with CKD remains under investigation, it is functionally related to LEP rs7799039, which has been associated with altered adipokine balance and renal inflammation [14].
FTO rs17817449, located in intron 1 of the FTO gene, is associated with increased adiposity and insulin resistance. While FTO rs9939609 is the most extensively studied variant in this context and is included in Table VII [9], rs17817449 exerts comparable effects on metabolic regulation and renal vulnerability [9, 15].
Therapeutic perspectives
Epigenetic modifications
Reversing epigenetic alterations that contribute to CKD progression represents a promising therapeutic avenue. Modifications such as DNA methylation of genes involved in fibrosis – e.g., RASAL1 – and histone changes affecting profibrotic gene expression have been proposed as potential intervention points. A particularly compelling target is miR-21, a microRNA that amplifies TGF-β/Smad3 signaling, thereby promoting fibrosis and inflammation in the obese kidney [15].
In this context, miRNA-based therapies have gained attention. Antagomirs or inhibitors targeting miR-21 have shown efficacy in preclinical models by attenuating fibrosis and preserving renal function. Conversely, miR-29 mimics may help restore antifibrotic signaling pathways that are often repressed in advanced CKD [15, 17]. Inhibiting miR-192, which drives matrix deposition and glomerular injury, has also been proposed as a strategy to mitigate progressive renal fibrosis, particularly in obese individuals [43].
Gene therapy and pharmacogenomics
The identification of genetic polymorphisms in genes such as FTO, KLF9, and BDNF enables the development of personalized therapies based on an individual’s genetic background. These genes influence metabolic regulation, oxidative stress, and inflammation – key drivers of CKD progression in obesity [15].
Variants in UMOD and MTHFS, identified through Mendelian randomization (MR) studies, are directly associated with CKD risk. These findings open opportunities for targeted therapeutic approaches that modulate tubular function and folate metabolism to prevent renal decline in genetically susceptible individuals [65].
Metabolic regulation
Genes involved in energy homeostasis, such as FTO and MC4R, play critical roles in the regulation of metabolic pathways linked to obesity, insulin resistance, and renal injury. Therapeutic strategies aimed at modulating the activity of these genes may help reduce fat accumulation, improve glucose handling, and alleviate metabolic stress, thereby limiting kidney damage in obese individuals [9].
In parallel, pharmacological agents that enhance insulin sensitivity or modulate leptin signaling – such as leptin mimetics and POMC-targeted therapies – have shown promise in reducing systemic inflammation and protecting renal function [29]. These approaches offer an opportunity to address the metabolic underpinnings of CKD, particularly in genetically susceptible populations.
Altogether, these therapeutic avenues underscore the promise of precision medicine to halt or even reverse the progression of obesity-related CKD by intervening directly on its molecular and metabolic roots.
Final considerations
Investigating gene and miRNA networks in obesity-related CKD has revealed multiple targets for therapeutic development. Genetic variants such as FTO, LEP, UMOD, KLF9, and BDNF, along with regulatory miRNAs like miR-21, miR-192, and miR-29, play key roles in disease progression and represent viable intervention points.
Therapeutic strategies – including miRNA-based approaches, gene modulation, and epigenetic therapies – offer promising opportunities for personalized treatment. Harnessing these molecular insights represents a critical step toward precision nephrology, with the potential to transform how obesity-related CKD is prevented and treated.
Future clinical translation will require integrative studies that combine genomic, transcriptomic, and clinical data to stratify risk and personalize interventions in obesity-related CKD.
Ethical aproval
Not applicable.