Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is a unique human plasma lipoprotein. It consists of an LDL-like core and covalently bound apolipoprotein(a) [1]. Apolipoprotein(a) [Apo(a)] is encoded by the LPA gene and is highly homologous to plasminogen in its protein sequence [1]. Lp(a) has a highly variable concentration between individuals, which is in large part defined by single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and copy number variants (CNVs) found in the LPA gene locus [1, 2].
Despite over 60 years of research, key functions of Lp(a) still remain enigmatic. On the other hand, Lp(a) has a clearly detrimental role in human disease since high Lp(a) levels are correlated with coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction [2]. These are thought to occur due to the prothrombotic action of Lp(a) and especially through promotion of atherosclerosis [3].
Although high levels of Lp(a) are known to cause cardiovascular disease2, low Lp(a) has been epidemiologically shown to correlate with the incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2D) [4]. In the case of T2D, the mechanism behind this association appears to be much less well elucidated [5].
Because Lp(a) levels are largely determined by genetics, they seem particularly amenable to Mendelian randomization (MR). To further elucidate the connection between T2D and Lp(a) levels, we performed an MR analysis to analyze the impact of genetically predicted Lp(a) concentration on the incidence of T2D.
Methods
Study design
In this research, we conducted a two-sample MR investigation, utilizing genome-wide association study (GWAS) data sourced from publicly accessible repositories. MR is an epidemiological approach that relies on instrumental variable analysis. It involves the use of genetic variants, commonly single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), linked to a modifiable risk factor such as high blood pressure to make inferences about causality. By leveraging these genetic markers as proxy indicators, MR helps minimize bias arising from confounding factors since alleles are randomly inherited at conception. Moreover, it also avoids bias due to reverse causation, as the occurrence of a disease cannot influence an individual’s genotype [6].
Data sources
Exposure: We extracted SNPs as instrumental variables (IVs) associated with Lp(a) concentration from GWAS data downloaded from Neale lab (UK Biobank). Because the measured Lp(a) concentration was positively skewed, inverse rank-normalized data were used. European ancestry female and male individuals were included in this research (N = 361,194) [4].
Outcome
Summary-level data for T2D were obtained from the Finnish FinnGen consortium [7, 8]. We used data from the eighth version of the database, which included 17,268 cases and 184,778 controls, with an analysis covering 16,380,418 variants.
MR analyses
P < 5 × 10–8 was accepted as a genome-wide significance threshold. To reduce the risk of any potential weak instrument bias, F-statistics were calculated based on the formula F = (β/SE)2 [6], where ‘β’ and ‘SE’ refer to the genetic association of SNPs with the exposure and its standard error, respectively. Only the SNPs with F-statistics > 10 were considered potential IVs. To ensure the independence of IVs, SNP in the linkage of disequilibrium (LD) were excluded. The TwoSampleMR R package was used to clamp data with a threshold r2 < 0.001 [9]. If selected SNPs were unavailable in the outcome dataset, they were replaced with proxies in LD of r2 > 0.8 or excluded from further MR analysis. Later, for selected SNPs, the potential association with confounding or risk factors for T2D were evaluated using PhenoScanner V2 [10]. Next, variant harmonization was conducted using the TwoSampleMR package between datasets to confirm that the association between SNPs and exposure and between SNPs and the outcome reflected the same allele. To further validate our results, aside from the aforementioned method of SNP selection, we also analyzed variants listed by ESC guidelines concerning Lp(a) including a subset of loss of function variants [11].
As the main analysis for evaluating the causal effect estimates in our study, we used the inverse variance weighted (IVW) method [12]. Sensitivity analyses were performed using MR-Egger, weighted median, and weighted mode approaches [13–15].
Additionally, to detect the existence of heterogeneity, horizontal pleiotropy, and outlier SNPs we performed several statistical tests. Cochran’s Q test was used to measure the heterogeneity between variant-specific causal estimates (IVW and MR-Egger regression) [16]. The MR-Egger intercept was calculated to measure the presence of horizontal pleiotropy [17]. To detect the potential presence of pleiotropic outlier SNPs, the MR-pleiotropy residual sum and outlier (MR-PRESSO) tests were applied [17]. Finally, leave-one-out analyses were performed to check whether any of the analyzed SNPs were strongly associated with the exposure, which may dominate the estimate of the causal effect.
Results
According to the accepted criteria and after searching in PhenoScanner, we finally identified as IVs for Lp(a) 23 SNPs which were used in MR analysis. Summary characteristics of the final IVs for Lp(a) and T2D are listed in Supplementary Table SI.
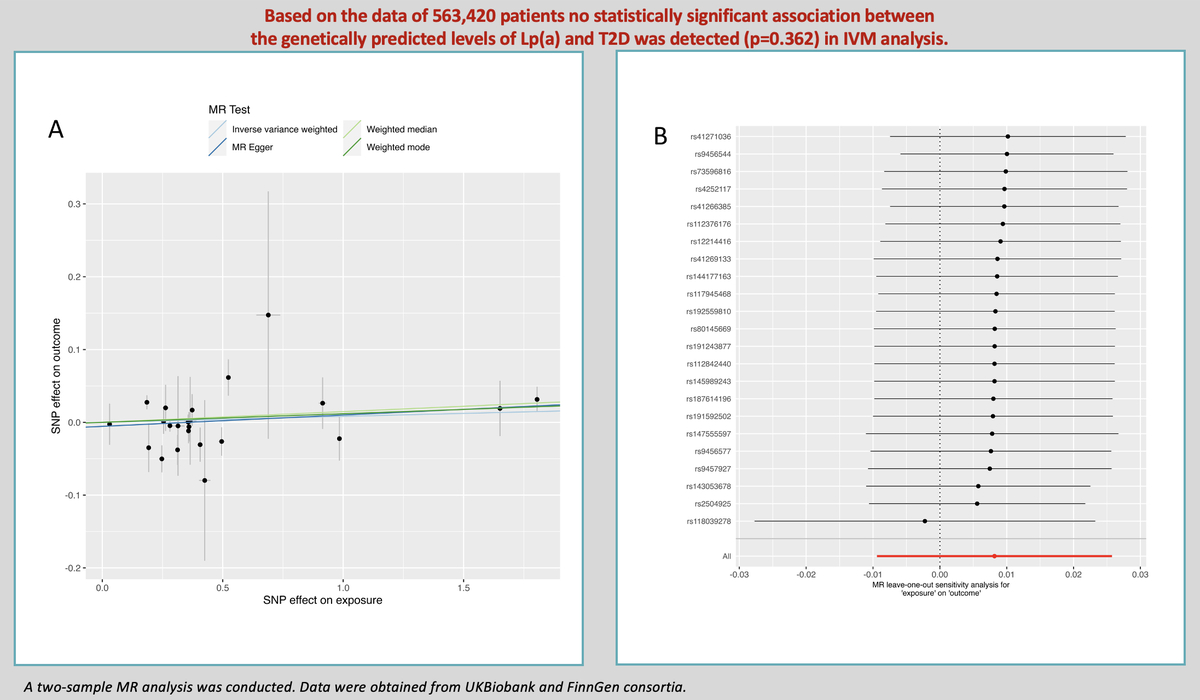
The results of estimating the causal effect between Lp(a) and T2D are presented in Figure 1 A. The main MR analysis showed that the concentrations of genetically predicted Lp(a) (OR = 1.008; 95% CI: 0.991–1.026; p = 0.362) were not associated with T2D. This lack of association was supported by the MR-Egger (OR = 1.016; 95% CI: 0.989–1.043; p = 0.256), weighted median (OR = 1.015; 95% CI: 0.998–1.03; p = 0.098), and weighted mode (OR = 1.012; 95% CI: 0.995–1.029; p = 0.189) approaches in sensitivity analysis.
Figure 1
A – Genetic associations between effect alleles of SNPs, exposure, and outcome. X axis – effect of SNP on exposure (type 2 diabetes). Y axis – effect of SNP on outcome (lipoprotein(a)). Each dot represents SNP + standard error. Lines represent Mendelian randomization estimates of different tests. B – Leave-one-out analysis. Each dot represents a single inverse-variance-weighted mean estimate computed by leaving out the variant specified on the right. Lines represent 95% confidence intervals
As far as other analyses are concerned, we detected weak heterogeneity between Lp(a) and T2D SNPs using Cochran’s Q test (PIVW = 0.03). There was no evidence of horizontal pleiotropy across the analyses in the MR-Egger regression (Pintercept = 0.46). No outlier SNPs were observed in the MR-PRESSO analysis (p = 0.06).
In the leave-one-out analysis, there was no significant change in the risk estimations for genetically predicted Lp(a) levels and preeclampsia risk after removing 1 SNP at a time, demonstrating that the causal association was not driven by any specific SNPs. Only 1 SNP (rs118039278) relatively affected the robustness of the results (Figure 1 B). The analysis of variants included in European Atherosclerosis Society recommendations [11] did not yield a statistically significant result (OR = 1.003; 95% CI: 0.977–1.031; p = 0.781 for IVM). No statistically significant impact of Lp(a) levels on T2D as determined by loss-of-function variants was noted (OR = 0.913; 95% CI: 0.807–1.032; p = 0.145 for IVM).
Discussion
MR has not broadly supported the causal role of Lp(a) in T2D [5]. This two-sample MR analysis utilizing data of a total of 563,420 patients is another such instance. There are several possible reasons behind this.
There is some evidence that insulin reduces apo(a) expression in hepatocytes in vitro, which further complicates the issue of an Lp(a)-T2D relationship, hinting at possible reverse causation [18]. Nevertheless, it does not influence our MR analysis. So far, only one single-sample MR study examining the relationship between serum insulin and Lp(a) has been published, and it did not demonstrate significant reverse causation [19].
The molecular mass of apo(a) is highly variable between individuals due to CNVs of Kringle-IV Type 2 (KIV-2) domains in the LPA gene [1]. This complicates the potential role of Lp(a) in T2D, since some reports emphasize the role of apo(a) KIV-2 CNVs as the potential cause of T2D rather than merely low Lp(a) concentration [5].
Moreover, some have suggested that the relationship between Lp(a) and T2D is non-linear and only the lowest Lp(a) concentrations increase the risks appreciably [5]. This means that standard MR approaches like the one used here may not yield reliable results, as a linear relationship between exposure and outcome is assumed [6]. Nevertheless, even the analysis of loss-of-function variants did not show Lp(a) to causally influence T2D risk, partially mitigating this concern.
In conclusion, this MR study did not show the correlation between Lp(a) and T2D to be causal. Further studies, including those utilizing animals, in vitro models and human patients, and epidemiological data are needed to elucidate the mechanism behind the observed Lp(a)-T2D correlation. This is of particular importance due to the ongoing research on specific Lp(a)-targeting therapies and the already known Lp(a)-lowering effect of PCSK9 inhibitors [20, 21]. Until that time, it is strongly recommended to use available methods to reduce levels of Lp(a), which is a significant residual CVD risk factor [2].