Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
LIPID DISORDERS / CLINICAL RESEARCH
COX7C alleviates lipid accumulation and apoptosis in a hyperlipidemia model via the HIF-1α pathway
1
Department of General Medicine, Minhang Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Submission date: 2025-05-08
Final revision date: 2025-06-17
Acceptance date: 2025-06-22
Online publication date: 2025-09-20
Corresponding author
Dongqing Zhang
Department of General Medicine Minhang Hospital Fudan University 170 Xinsong Road Shanghai, China, 201199
Department of General Medicine Minhang Hospital Fudan University 170 Xinsong Road Shanghai, China, 201199
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
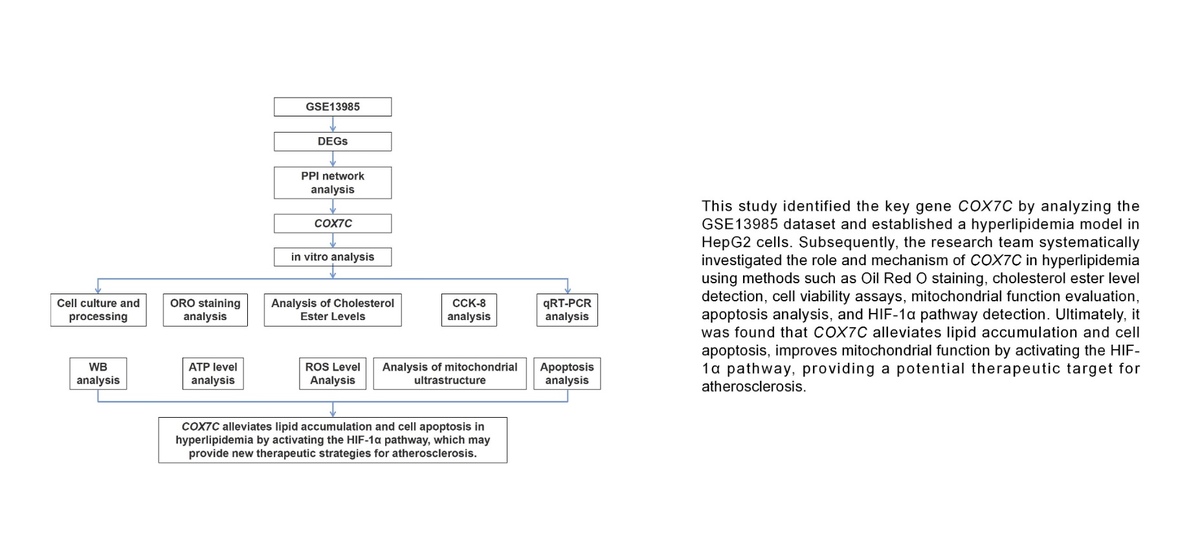
One of the main contributing factors to the growth of atherosclerosis is hyperlipidemia (HLP). COX7C is a mitochondrial protein that is essential to mitochondrial function and cellular homeostasis. However, its role in hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis remains underexplored. The aim of the study was to investigate the function of COX7C in lipid accumulation, mitochondrial function, and apoptosis in a hyperlipidemia model, and explore its mechanism of action through the HIF-1α pathway.
Material and methods:
Bioinformatics analysis of the GSE13985 dataset was performed, and COX7C was selected as a hub gene. Free fatty acids were used to treat HepG2 cells to establish a hyperlipidemia model. Lipid buildup was assessed by oil red O (ORO) staining, and cholesterol ester levels, adenosine triphosphate content, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels were quantified using kit assays. Western blot (WB), flow cytometry, and CCK-8 were employed to assess protein expression levels, cell viability, and apoptosis. The effects of HIF-1α inhibition were investigated using the HIF-1α inhibitor KC7F2.
Results:
Overexpression of COX7C significantly reduced lipid accumulation, improved cell viability, and alleviated mitochondrial damage in a hyperlipidemia model. Flow cytometry and WB research on apoptosis-related proteins demonstrated that COX7C overexpression also reduced ROS production and inhibited apoptosis. In addition, COX7C overexpression activated the HIF-1α pathway, further alleviating mitochondrial damage and apoptosis. KC7F2 reversed the protective effect of COX7C, indicating that COX7C acts through the HIF-1α pathway in the context of hyperlipidemia.
Conclusions:
COX7C reduces lipid accumulation and apoptosis in a hyperlipidemia model by activating the HIF-1 pathway and may provide a therapeutic strategy for atherosclerosis.
One of the main contributing factors to the growth of atherosclerosis is hyperlipidemia (HLP). COX7C is a mitochondrial protein that is essential to mitochondrial function and cellular homeostasis. However, its role in hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis remains underexplored. The aim of the study was to investigate the function of COX7C in lipid accumulation, mitochondrial function, and apoptosis in a hyperlipidemia model, and explore its mechanism of action through the HIF-1α pathway.
Material and methods:
Bioinformatics analysis of the GSE13985 dataset was performed, and COX7C was selected as a hub gene. Free fatty acids were used to treat HepG2 cells to establish a hyperlipidemia model. Lipid buildup was assessed by oil red O (ORO) staining, and cholesterol ester levels, adenosine triphosphate content, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels were quantified using kit assays. Western blot (WB), flow cytometry, and CCK-8 were employed to assess protein expression levels, cell viability, and apoptosis. The effects of HIF-1α inhibition were investigated using the HIF-1α inhibitor KC7F2.
Results:
Overexpression of COX7C significantly reduced lipid accumulation, improved cell viability, and alleviated mitochondrial damage in a hyperlipidemia model. Flow cytometry and WB research on apoptosis-related proteins demonstrated that COX7C overexpression also reduced ROS production and inhibited apoptosis. In addition, COX7C overexpression activated the HIF-1α pathway, further alleviating mitochondrial damage and apoptosis. KC7F2 reversed the protective effect of COX7C, indicating that COX7C acts through the HIF-1α pathway in the context of hyperlipidemia.
Conclusions:
COX7C reduces lipid accumulation and apoptosis in a hyperlipidemia model by activating the HIF-1 pathway and may provide a therapeutic strategy for atherosclerosis.
REFERENCES (41)
1.
Severs NJ, Robenek H. Constituents of the arterial wall and atherosclerotic plaque: an introduction to atherosclerosis. In: Cell Interactions in Atherosclerosis. Severs NJ, Robenek H (eds.). CRC Press; Boca Raton 2024; 1-49.
2.
Li J, Wang H, Dong C, Huang J, Ma W. The underlying mechanisms of FGF2 in carotid atherosclerotic plaque development revealed by bioinformatics analysis. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 1209-19.
3.
Ataei S, Ganjali S, Banach M, Karimi E, Sahebkar A. The effect of PCSK9 immunization on the hepatic level of microRNAs associated with PCSK9/LDLR pathway. Arch Med Sci 2023; 19: 203-8.
4.
Miao J, Zang X, Cui X, Zhang J. Autophagy, hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerosis. Autophagy: biology and diseases. Clin Sci 2020: 237-64.
5.
Da Dalt L, Cabodevilla AG, Goldberg IJ, Norata GD. Cardiac lipid metabolism, mitochondrial function, and heart failure. Cardiovasc Res 2023; 119: 1905-14.
6.
Yao YS, Li TD, Zeng ZH. Mechanisms underlying direct actions of hyperlipidemia on myocardium: an updated review. Lipids Health Dis 2020; 19: 23.
7.
Čunátová K, Reguera DP, Houštěk J, Mráček T, Pecina P. Role of cytochrome c oxidase nuclear-encoded subunits in health and disease. Physiol Res 2020; 69: 947-65.
8.
Wang C, Lv J, Xue C, et al. Novel role of COX6c in the regulation of oxidative phosphorylation and diseases. Cell Death Discov 2022; 8: 336.
9.
Jia J, Deng J, Jin H, et al. Effect of Dl-3-n-butylphthalide on mitochondrial Cox7c in models of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front Pharmacol 2023; 14: 1084564.
10.
Wu B, Chen S, Zhuang L, Zeng J. The expression level of COX7C associates with venous thromboembolism in colon cancer patients. Clin Exp Med 2020; 20: 527-33.
11.
Yin J, Ren Y, Yang K, et al. The role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell Biol Int 2022; 46: 46-51.
12.
Kierans S, Taylor C. Regulation of glycolysis by the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF): implications for cellular physiology. J Physiol 2021; 599: 23-37.
13.
Zheng CM, Hou YC, Liao MT, et al. Potential role of molecular hydrogen therapy on oxidative stress and redox signaling in chronic kidney disease. Biomed Pharmacother 2024; 176: 116802.
14.
Zhao H, Wang Y, Wu Y, et al. Hyperlipidemia does not prevent the cardioprotection by postconditioning against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and the involvement of hypoxia inducible factor-1 upregulation. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 2009; 41: 745-53.
15.
Wang P, Zeng G, Yan Y, et al. Disruption of adipocyte HIF-1 improves atherosclerosis through the inhibition of ceramide generation. Acta Pharm Sin B 2022; 12: 1899-912.
16.
Bai G, Ma CG, Chen XW. Effect of unsaturation of free fatty acids and phytosterols on the formation of esterified phytosterols during deodorization of corn oil. J Sci Food Agriculture 2021; 101: 2736-43.
17.
Ma H, Bell KN, Loker RN. qPCR and qRT-PCR analysis: regulatory points to consider when conducting biodistribution and vector shedding studies. Mol Ther Meth Clin Develop 2021; 20: 152-68.
18.
Hou P, Fang J, Liu Z, et al. Macrophage polarization and metabolism in atherosclerosis. Cell Death Dis 2023; 14: 691.
19.
Watson SA, McStay GP. Functions of cytochrome c oxidase assembly factors. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 7254.
20.
Zhu H, Toan S, Mui D, Zhou H. Mitochondrial quality surveillance as a therapeutic target in myocardial infarction. Acta Physiol 2021; 231: e13590.
21.
Tarbell J, Mahmoud M, Corti A, Cardoso L, Caro C. The role of oxygen transport in atherosclerosis and vascular disease. J Royal Soc Interface 2020; 17: 20190732.
22.
Wieder N, Fried JC, Kim C, et al. FALCON systematically interrogates free fatty acid biology and identifies a novel mediator of lipotoxicity. Cell Metabol 2023; 35: 887-905. e11.
23.
Henderson GC. Plasma free fatty acid concentration as a modifiable risk factor for metabolic disease. Nutrients 2021; 13: 2590.
24.
Pei K, Gui T, Kan D, et al. An overview of lipid metabolism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. BioMed Res Int 2020; 2020: 4020249.
25.
Du J, Wu W, Zhu B, et al. Recent advances in regulating lipid metabolism to prevent coronary heart disease. Chem Phys Lipids 2023; 255: 105325.
26.
Čunátová K. Role of cytochrome C oxidase nuclear-encoded subunits in health and disease. Department of Bioenergetics, Institute of Physiology.
27.
Wang H, Zhao Y. Prediction of genetic risk factors of atherosclerosis using various bioinformatic tools. Genet Mol Res 2016; 15: gmr7347.
28.
Kowalczyk P, Sulejczak D, Kleczkowska P, et al. Mitochondrial oxidative stress – a causative factor and therapeutic target in many diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 13384.
29.
Patro S, Ratna S, Yamamoto HA, et al. ATP synthase and mitochondrial bioenergetics dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 11185.
30.
Mailloux RJ. An update on mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production. Antioxidants 2020; 9: 472.
31.
Korotkov SM. Mitochondrial oxidative stress is the general reason for apoptosis induced by different-valence heavy metals in cells and mitochondria. Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24: 14459.
32.
Dubois-Deruy E, Peugnet V, Turkieh A, Pinet F. Oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases. Antioxidants 2020; 9: 864.
33.
Emma P, Bennett MR. The role of mitochondrial DNA damage in the development of atherosclerosis. Free Radical Biol Med 2016; 100: 223-30.
34.
Qu K, Yan F, Qin X, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in vascular endothelial cells and its role in atherosclerosis. Front Physiol 2022; 13: 1084604.
35.
Wolf P, Schoeniger A, Edlich F. Pro-apoptotic complexes of BAX and BAK on the outer mitochondrial membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2022; 1869: 119317.
36.
Shan C, Xia Y, Wu Z, Zhao J. HIF-1 and periodontitis: novel insights linking host-environment interplay to periodontal phenotypes. Progress Biophys Mol Biol 2023; 184: 50-78.
37.
Lestón Pinilla L, Ugun-Klusek A, Rutella S, De Girolamo LA. Hypoxia signaling in Parkinson’s disease: there is use in asking “What HIF?”. Biology 2021; 10: 723.
38.
Lee P, Chandel NS, Simon MC. Cellular adaptation to hypoxia through hypoxia inducible factors and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2020; 21: 268-83.
39.
Akhtar S, Hartmann P, Karshovska E, et al. Endothelial hypoxia-inducible factor-1 promotes atherosclerosis and monocyte recruitment by upregulating microRNA-19a. Hypertension 2015; 66: 1220-6.
40.
Hutter R, Speidl WS, Valdiviezo C, et al. Macrophages transmit potent proangiogenic effects of oxLDL in vitro and in vivo involving HIF-1 activation: a novel aspect of angiogenesis in atherosclerosis. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 2013; 6: 558-69.
41.
Li X, Zhao H, Wu Y, et al. Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 enhanced the cardioprotective effects of ischemic postconditioning in hyperlipidemic rats. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 2014; 46: 112-8.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.