Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
PULMONOLOGY / BASIC RESEARCH
Causal analysis of plasma fatty acids and pneumonia: identifying diagnostic biomarkers through transcriptome-wide association study
1
Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Lishui Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, The First Affiliated Hospital of Lishui University, Lishui People’s Hospital, Lishui, Zhejiang 323000, China
2
Department of Neurosurgery, Lishui Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, The First Affiliated Hospital of Lishui University, Lishui People’s Hospital, Lishui, Zhejiang 323000, China
3
Department of Hepatology and Infectious Diseases, Lishui Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, The First Affiliated Hospital of Lishui University, Lishui People’s Hospital, Lishui, Zhejiang 323000, China
Submission date: 2025-03-14
Final revision date: 2025-05-19
Acceptance date: 2025-07-18
Online publication date: 2025-09-06
Corresponding author
Xiaomei Wang
Department of Hepatology and Infectious Diseases Lishui Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, The First Affiliated Hospital of Lishui University, Lishui People’s Hospital, No. 15 Dazhong Street Liandu District, Lishui 323000, Zhejiang, China Phone: +86-18957092292
Department of Hepatology and Infectious Diseases Lishui Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, The First Affiliated Hospital of Lishui University, Lishui People’s Hospital, No. 15 Dazhong Street Liandu District, Lishui 323000, Zhejiang, China Phone: +86-18957092292
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
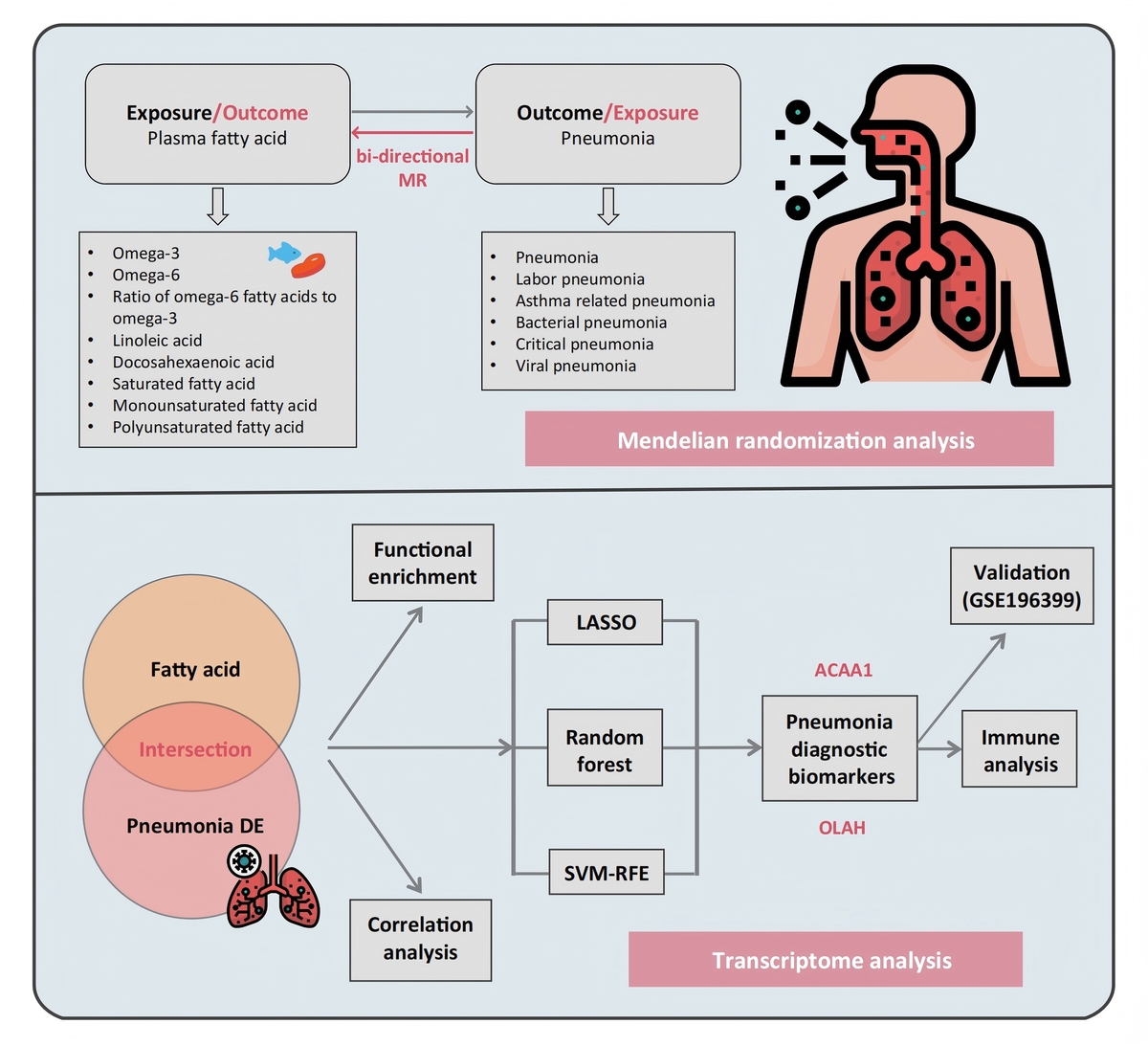
Fatty acids mediate pulmonary inflammation through cytokine regulation, interactions with the tryptophan-kynurenine pathway, and mediators such as 18-HEPE that boost interferon-λ. To systematically dissect these mechanisms and their translational implications, we pioneered a novel framework integrating bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) with multi-algorithm machine learning. This approach not only quantifies causal relationships between fatty acids and inflammatory outcomes but also identifies clinically actionable diagnostic biomarkers.
Material and methods:
We obtained single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) significantly associated with eight plasma fatty acids from genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics and used them as instrumental variables in bidirectional two-sample MR across six pneumonia phenotypes (pneumonia, asthma-related pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, critical pneumonia, viral pneumonia, and lobar pneumonia). Causal estimates were calculated using inverse variance weighting (IVW), which combines SNP-specific Wald ratios weighted by the inverse of their variance, with MR-Egger and weighted median approaches for sensitivity analysis. Transcriptomic data were then analyzed by LASSO regression, support vector machine recursive feature elimination and random forest to identify fatty acid metabolism–related biomarker candidates.
Results:
MR analysis suggested potential causal associations between omega-6 fatty acids and critical pneumonia (OR = 1.28, 95% CI: 1.01–1.61, p = 0.038), linoleic acids (LA) and bacterial pneumonia (OR = 0.85, 95% CI: 0.73–0.99, p = 0.047), and docosahexaenoic fatty acids (DHA) and pneumonia (OR = 0.83, 95% CI: 0.74–0.93, p = 0.002). Moreover, ACAA1 and OLAH, which are genes involved in fatty acid metabolism, were identified as potential candidate biomarkers for pneumonia.
Conclusions:
Our study employed MR analysis to establish a causal association of omega-6, LA, and DHA with pneumonia. Additionally, through transcriptomic analysis, we identified plasma fatty acid metabolism-associated biomarkers that may serve as diagnostic indicators for pneumonia.
Fatty acids mediate pulmonary inflammation through cytokine regulation, interactions with the tryptophan-kynurenine pathway, and mediators such as 18-HEPE that boost interferon-λ. To systematically dissect these mechanisms and their translational implications, we pioneered a novel framework integrating bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) with multi-algorithm machine learning. This approach not only quantifies causal relationships between fatty acids and inflammatory outcomes but also identifies clinically actionable diagnostic biomarkers.
Material and methods:
We obtained single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) significantly associated with eight plasma fatty acids from genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics and used them as instrumental variables in bidirectional two-sample MR across six pneumonia phenotypes (pneumonia, asthma-related pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, critical pneumonia, viral pneumonia, and lobar pneumonia). Causal estimates were calculated using inverse variance weighting (IVW), which combines SNP-specific Wald ratios weighted by the inverse of their variance, with MR-Egger and weighted median approaches for sensitivity analysis. Transcriptomic data were then analyzed by LASSO regression, support vector machine recursive feature elimination and random forest to identify fatty acid metabolism–related biomarker candidates.
Results:
MR analysis suggested potential causal associations between omega-6 fatty acids and critical pneumonia (OR = 1.28, 95% CI: 1.01–1.61, p = 0.038), linoleic acids (LA) and bacterial pneumonia (OR = 0.85, 95% CI: 0.73–0.99, p = 0.047), and docosahexaenoic fatty acids (DHA) and pneumonia (OR = 0.83, 95% CI: 0.74–0.93, p = 0.002). Moreover, ACAA1 and OLAH, which are genes involved in fatty acid metabolism, were identified as potential candidate biomarkers for pneumonia.
Conclusions:
Our study employed MR analysis to establish a causal association of omega-6, LA, and DHA with pneumonia. Additionally, through transcriptomic analysis, we identified plasma fatty acid metabolism-associated biomarkers that may serve as diagnostic indicators for pneumonia.
REFERENCES (52)
1.
Torres A, Cilloniz C, Niederman MS, et al., Pneumonia. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021; 7: 25.
2.
Neill S, Dean N. Aspiration pneumonia and pneumonitis: a spectrum of infectious/noninfectious diseases affecting the lung, Curr Opin Infect Dis 2019; 32: 152-7.
3.
Zhang H, Zhan D, Chen D, et al. Next-generation sequencing diagnosis of severe pneumonia from fulminant psittacosis with multiple organ failure: a case report and literature review, Ann Transl Med 2020; 8: 401.
4.
Savla SR, Prabhavalkar KS, Bhatt LK. Cytokine storm associated coagulation complications in COVID-19 patients: pathogenesis and management. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2021; 19: 1397-413.
5.
Kusumawardhani NY, Putra ICS, Kamarullah W, et al. Cardiovascular disease in post-acute COVID-19 syndrome: a comprehensive review of pathophysiology and diagnosis approach. Rev Cardiovasc Med 2023; 24: 28.
6.
Cilloniz C, Dela Cruz CS, Dy-Agra G, Pagcatipunan RS Jr. World Pneumonia Day 2024: fighting pneumonia and antimicrobial resistance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2024; 210: 1283-5.
7.
Garcia C, Andersen CJ, Blesso CN. The role of lipids in the regulation of immune responses. Nutrients 2023; 15: 3899.
8.
Torres RM, Cyster J. Lipid mediators in the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev 2023; 317: 4-7.
9.
Bogie JFJ, Haidar M, Kooij G, Hendriks JJA. Fatty acid metabolism in the progression and resolution of CNS disorders. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2020; 159: 198-213.
10.
Kotlyarov S, Kotlyarova A. Anti-inflammatory function of fatty acids and involvement of their metabolites in the resolution of inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 12803.
11.
Guo B, Xue M, Zhang T, et al. Correlation between immune-related Tryptophan-Kynurenine pathway and severity of severe pneumonia and inflammation-related polyunsaturated fatty acids. Immun Inflamm Dis 2023; 11: e1088.
12.
Krupa A, Kowalska I. The kynurenine pathway-new linkage between innate and adaptive immunity in autoimmune endocrinopathies. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 9879.
13.
Siska PJ, Jiao J, Matos C, et al. Kynurenine induces T cell fat catabolism and has limited suppressive effects in vivo. EBioMedicine 2021; 74: 103734.
14.
Hinojosa CA, Gonzalez-Juarbe N, Rahman MM, Fernandes G, Orihuela CJ, Restrepo MI. Omega-3 fatty acids in contrast to omega-6 protect against pneumococcal pneumonia. Microb Pathog 2020; 141: 103979.
15.
Zhao H, Dennery PA, Yao H. Metabolic reprogramming in the pathogenesis of chronic lung diseases, including BPD, COPD, and pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2018; 314: L544.
16.
Kocherlakota C, Nagaraju B, Arjun N, Srinath A, Kothapalli KSD, Brenna JT. Inhalation of nebulized omega-3 fatty acids mitigate LPS-induced acute lung inflammation in rats: Implications for treatment of COPD and COVID-19. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2022; 179: 102426.
17.
Hagihara M, Yamashita M, Ariyoshi T, et al. Clostridium butyricum-induced ω-3 fatty acid 18-HEPE elicits anti-influenza virus pneumonia effects through interferon- upregulation. Cell Rep 2022; 41: 111755.
18.
Sanderson E, Glymour MM, Holmes MV, et al. Mendelian randomization. Nat Rev Methods Primers 2022; 2: 6.
19.
Burgess S, Small DS, Thompson SG. A review of instrumental variable estimators for Mendelian randomization. Stat Methods Med Res 2017; 26: 2333-55.
20.
Hartwig FP, Davies NM, Hemani G, Davey Smith G. Two-sample Mendelian randomization: avoiding the downsides of a powerful, widely applicable but potentially fallible technique. Int J Epidemiol 2016; 45: 1717-26.
21.
Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, Do R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet 2018; 50: 693-8.
22.
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, et al. Iimma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 2015; 43: e47.
23.
Wu T, Hu E, Xu S, et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation (Camb) 2021; 2: 100141.
24.
Zeng D, Ye Z, Shen R, et al. IOBR: multi-omics immuno-oncology biological research to decode tumor microenvironment and signatures. Front Immunol 2021; 12: 687975.
25.
Radzikowska U, Rinaldi AO, Çelebi Sözener Z, et al. The Influence of dietary fatty acids on immune responses. Nutrients 2019; 11: 2990.
26.
Djuricic I, Calder PC. Beneficial outcomes of omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on human health: an update for 2021. Nutrients 2021; 13: 2421.
27.
Merchant AT, Curhan GC, Rimm EB, Willett WC, Fawzi WW. Intake of n-6 and n-3 fatty acids and fish and risk of community-acquired pneumonia in US men. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 82: 668-74.
28.
Poggioli R, Hirani K, Jogani VG, Ricordi C. Modulation of inflammation and immunity by omega-3 fatty acids: a possible role for prevention and to halt disease progression in autoimmune, viral, and age-related disorders. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2023; 27: 7380-400.
29.
Lemoine C, Brigham E, Woo H, et al. Relationship between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acid intake and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease morbidity. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2020; 17: 378-81.
30.
Chen X, Wu S, Chen C, et al. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation attenuates microglial-induced inflammation by inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-B pathway following experimental traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation 2017; 14: 143.
31.
Marton LT, Goulart RA, Carvalho ACA, Barbalho SM. Omega fatty acids and inflammatory bowel diseases: an overview. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 4851.
32.
Reifen R, Karlinsky A, Stark AH, Berkovich Z, Nyska A. -Linolenic acid (ALA) is an anti-inflammatory agent in inflammatory bowel disease. J Nutr Biochem 2015; 26: 1632-40.
33.
Shin Y, Han S, Kwon J, et al. Roles of short-chain fatty acids in inflammatory bowel disease. Nutrients 2023; 15: 4466.
34.
Huang X, Li Y, Zhuang P, et al. Habitual fish oil supplementation and risk of incident inflammatory bowel diseases: a prospective population-based study. Front Nutr 2022; 9: 905162.
35.
Palanki R, Yamagata H, Mitchell MJ. OLAH connects fatty acid metabolism to the severity of respiratory viral disease. Cell 2024; 187: 4549-51.
36.
Sordillo JE, Sharma S, Poon A, et al. Effects of endotoxin exposure on childhood asthma risk are modified by a genetic polymorphism in ACAA1. BMC Med Genet 2011; 12: 158.
37.
Pechous RD. With friends like these: the complex role of neutrophils in the progression of severe pneumonia. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2017; 7: 160.
38.
Zhou A, Chen K, Gao Y, et al. Bioengineered neutrophil extinguisher targets cascade immune pathways of macrophages for alleviating cytokine storm in pneumonia. ACS Nano 2023; 17: 16461-77.
39.
Domon H, Terao Y. The role of neutrophils and neutrophil elastase in pneumococcal pneumonia. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021; 11: 615959.
40.
Palmer CS, Kimmey JM. Neutrophil recruitment in pneumococcal pneumonia. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022; 12: 894644.
41.
Guillon A, Arafa EI, Barker KA, et al. Pneumonia recovery reprograms the alveolar macrophage pool. JCI Insight. 2020; 5: e133042.
42.
Miyagi M, Uchida K, Takano S, et al. Macrophage-derived inflammatory cytokines regulate growth factors and pain-related molecules in mice with intervertebral disc injury. J Orthop Res 2018. DOI: 10.1002/jor.23888.
43.
Turner S, Khan MA, Putrino D, Woodcock A, Kell DB, Pretorius E. Long COVID: pathophysiological factors and abnormalities of coagulation. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2023; 34: 321-44.
44.
Wei H, Zhao H, Li R, Yang F, Wu Y. Rhinovirus impairs the immune response of alveolar macrophages to facilitate Streptococcus pneumonia infection. Pathog Dis 2020; 78: ftaa020.
45.
Hu Y, Hu Q, Li Y, et al. T cells: origin and fate, subsets, diseases and immunotherapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2023; 8: 434.
46.
Güleç T, Yılmaz S, Ak R, Tatlıparmak AC, Karcıoğlu Ö. Can we recognize severe community-acquired pneumonia without pneumonia severity index? Use of modified qSOFA with procalcitonin. Heliyon 2023; 9: e19937.
47.
Saleh NY, Ibrahem RAL, Saleh AAH, Soliman SES, Mahmoud AAS. Surfactant protein D: a predictor for severity of community-acquired pneumonia in children. Pediatr Res 2022; 91: 665-71.
48.
Bhattacharya S, Munshi C. Biological significance of C-reactive protein, the ancient acute phase functionary. Front Immunol 2023; 14: 1238411.
49.
Xu Z, Hou XF, Feng CM, et al. The association between serum complement C3a and severity in patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Front Immunol 2023; 14: 1034233.
50.
Zinellu A, Mangoni AA. Serum complement C3 and C4 and COVID-19 severity and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis with meta-regression. Front Immunol 2021; 12: 696085.
51.
Ozbay S, Ayan M, Ozsoy O, Akman C, Karcioglu O. Diagnostic and prognostic roles of procalcitonin and other tools in community-acquired pneumonia: a narrative review. Diagnostics (Basel) 2023; 13: 1869.
52.
Elmore A, Almuntashiri A, Wang X, Almuntashiri S, Zhang D. Circulating surfactant protein D: a biomarker for acute lung injury? Biomedicines 2023; 11: 2517.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.