Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is characterized by its high malignancy, the difficulty in early detection and treatment, and its poor prognosis [1]. Due to the complex etiology and difficulties in prevention, CRC has become the third most common cancer globally [2, 3]. Despite considerable progress in the field of CRC treatment, the incidence and mortality rates remain on an upward trend, with an incidence rate of 10.2% and a mortality rate of 9.2% in 2021 [4]. Due to the unspecific early symptoms of CRC, which can lead to missed diagnosis, or misdiagnosis as alternative gastrointestinal conditions, most CRC patients receive their diagnosis at later stages when cell invasion and distant metastasis have occurred, which greatly hampers the effectiveness of treatment [5–7]. Thus, it is essential to delve into the molecular processes behind metastasis for more effective CRC therapeutic targets.
Emerging research has established a strong link between copper and the occurrence of cancer, with altered copper levels being a new target for cancer therapy [8]. A deeper comprehension of the interplay between copper and CRC paves the way for exploring innovative treatment strategies to improve the prognosis of CRC patients. Copper ionophores or copper-containing compounds elevate the copper levels in cancer cells, inducing oxidative stress and eventually cell death, showing their potential as anti-cancer agents [9]. The class of copper ionophores, which includes disulfiram (DSF), elesclomol (ES), and clioquinol (CQ), is known for its biological effects. Specifically, the DSF-Cu complex has been demonstrated to inhibit NF-κB activity, thus impeding EMT [10]. Experiments applying Es-Cu pulses to CRC cells and cell lines resistant to oxaliplatin showed that Es-Cu markedly reduces the viability of CRC cells [11]. Despite the salient role that cuproptosis plays in cancer progression, the interaction between cuproptosis and metastasis in CRC is not well defined.
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are essential in the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Modulating almost every facet of RNA metabolism, they feed into a broad spectrum of physiological and pathological activities [12]. RBM24, part of the RBP family, can bind to numerous target mRNAs, thus affecting mRNA maturation or translation [13]. Increasing evidence shows that alterations in RBM24 expression and function can disrupt tissue homeostasis and act as a tumor suppressor in a range of cancers [14, 15]. For instance, circsSMARCA5 can upregulate RBM24 expression by negatively modulating miR-670-5p, which suppresses tumor growth, reduces cell proliferation, and encourages apoptosis [16]. However, the upregulation of RBM24 in other types of cancer appears to promote tumor growth [13]. Given the versatile role RBM24 plays in cancer progression, further research into its regulatory mechanisms in CRC metastasis is justified.
Our study detected a sharp decrease in RBM24 levels in CRC, and the overexpression of RBM24 was found to mediate the inhibition of tumor metastasis via the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. Intriguingly, Es-Cu resulted in upregulation of RBM24 in CRC cells. Cuproptosis was found to obstruct the metastasis of CRC cells by modulating the RBM24/MAPK pathway. Overall, these findings contribute to our understanding of the regulatory mechanisms involved in cuproptosis-mediated cancer inhibition and suggest a promising therapeutic strategy for CRC.
Material and methods
Bioinformatics analysis
We obtained and filtered the counts file data for CRC patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. By leveraging the edgeR package, we conducted an analysis for differentially expressed mRNAs (DEmRNAs) to compare the expression profiles between tumor and normal tissues (log2|FC| > 2, FDR < 0.05). This led to the discovery of 647 tumor tissues and 51 normal tissues, totaling 2185 DEmRNAs, with 1262 upregulated and 923 downregulated. To illuminate the potential role of RBM24 in CRC, we categorized the CRC cohort into high and low expression groups based on the median RBM24 expression and performed gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) to determine whether genes in these groups were enriched in biological functions of significance.
Cell culture
The human colon epithelial cell line FHC and CRC cell lines HT-29, SW480, and DLD-1 were sourced from the BFB–Shanghai Cell Bank (China). They were cultured in DMEM-H medium (HyClone, USA) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Invitrogen, USA), 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 µg/ml streptomycin (Invitrogen, USA) under conditions of 5% CO2 at 37°C.
Cell transfection
The RBM24 overexpression (oe-RBM24) and knockdown (si-RBM24) constructs, along with their negative controls (oe-NC, si-NC), were synthesized by Shanghai GeneChem Co., Ltd. The transfection of these vectors into CRC cells was facilitated using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, USA) following the provided instructions. Forty-eight hours after transfection, the cells were collected for further experimental procedures.
The CRC cells were incubated with DMSO or PD0325901 (10 µM), an inhibitor of the MAPK pathway, for 48 h, followed by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), Western blot (WB), and Transwell [17].
Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from cells using TRIzol reagent, and the RNA concentration and purity were assessed with a NanoDrop One UV-Vis spectrophotometer. The reverse transcription of RNA to cDNA was facilitated by SuperScript III Reverse Transcriptase (Invitrogen, USA). The qRT-PCR was performed on the ABI 7500 PCR system (Applied Biosystems, USA) with the Platinum SYBR Green qPCR SuperMix UDG kit (Invitrogen, USA). The relative expression levels of RBM24 were determined using the 2–ΔΔCT method, with GAPDH serving as the internal control. The primer sequences are detailed in the Table I provided.
WB
Cells were collected and then lysed in RIPA lysis buffer (Beyotime, China) containing 1% protease and phosphatase inhibitors (Beyotime, China) at 4°C to extract total proteins. The protein concentration was quantified using the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay kit (Beyotime, China). The BCA protein assay kit (Beyotime, China) was employed to measure protein concentrations. Denatured proteins were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred onto PVDF membranes. The membranes were blocked with 5% BSA for 2 h at 37°C and incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies for MMP2 (abcam, UK), MMP9 (abcam, UK), E-cadherin (CST, USA), fibronectin (CST, USA), p-ERK/ERK (abcam, UK), p-JNK/JNK (abcam, UK), FDX1 (Abclonal, China), DLAT (Abclonal, China), LIAS (abcam, UK), RBM24 (Proteintech Group, USA), and GAPDH (abcam, UK). The membranes were further incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary goat anti-rabbit IgG (abcam, UK) for 2 h at room temperature. Chemiluminescent detection was performed using the ChemiScope 6000 system (Clinx, China) with NcmECL Ultra (NCM Biotech, China) for imaging.
CCK-8 assay
Cell proliferation was determined by the CCK-8 kit (Dojindo, Japan). CRC cells were dispensed into a 96-well plate at a concentration of 2 × 103 cells per well. After cell adherence, 10 µl of CCK-8 reagent was introduced at 0 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. The plate was incubated in a cell culture incubator away from light for 2 h, and the absorbance at 450 nm in each well was measured with a microplate reader.
Transwell assay
CRC cells, 48 h after transfection, were resuspended in serum-free medium and placed into the upper compartment of the Transwell at a density of 2 × 104 cells per well with 200 µl of the medium. The lower compartment received 600 µl of medium supplemented with 10% FBS. After a 24-h incubation, cells that had migrated to the exterior of the Transwell membrane were fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with 0.1% crystal violet. For the invasion assay, cells were seeded in the upper chamber coated with Matrigel, following the same protocol as the migration assay. The number of cells that migrated or invaded was counted under a microscope by selecting three random fields and calculating the mean cell count.
Immunofluorescence (IF)
The cells were fixed in 75% alcohol for 30 min. Subsequently, they were treated with 0.1% Triton X-100 for permeabilization for 10 min. Next, they were blocked with 5% BSA for 1 h. RBM24 antibody (Proteintech Group, USA) was applied, followed by incubation with a Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody (Abclonal, China). After being washed with PBS, they were observed using an inverted fluorescence microscope.
Measurement of intracellular copper content
HT-29 cells were cultured in a 6-well plate overnight. On the following day, 200 nM elesclomol-Cu (Es-Cu) was added to the cells, obtained from MCE (USA), at a 1 : 1 ratio. After incubation for 24 h, the cells were gathered and resuspended in 100 µl of PBS. The Copper (Cu) Content Assay Kit (Solarbio, China) was used to quantify the copper ion concentration inside the cells, according to the supplier’s guidelines [18].
Data analysis
Experiments were conducted in triplicate, and data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 8 software. The results are reported as mean ± SD. Student’s t-test was chosen for contrasting pairs of groups, whereas the one-way ANOVA was the protocol for assessing differences across multiple groups. P < 0.05 was deemed statistically significant.
Results
Overexpression of RBM24 inhibited CRC metastasis
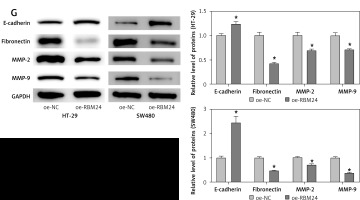
As part of our investigation to identify mRNAs involved in the development of CRC, bioinformatics analysis showed that RBM24 expression was downregulated in CRC tissues (Figure 1 A). qPCR and IF experiments demonstrated significant downregulation of RBM24 expression in CRC cell lines HT-29, SW480, and DLD-1 when compared to the FHC human colon epithelial cell line (Figures 1 B, C). Furthermore, the establishment of oe-NC/oe-RBM24 groups within HT-29 and SW480 cells was executed. qRT-PCR analyses confirmed a significant increase in RBM24 expression in the oe-RBM24 group compared with the oe-NC group (Figure 1 D). The CCK-8 and Transwell assay data showed that the overexpression of RBM24 hindered the proliferative, migratory, and invasive capacities of CRC cells (Figures 1 E, F). Following WB analysis of genes related to migration and invasion (MMP2, MMP9) as well as EMT markers (E-cadherin, fibronectin), the data revealed a marked reduction in the expression levels of MMP2, MMP9, and fibronectin, alongside elevated E-cadherin expression in HT-29 and SW480 cells overexpressing RBM24 (Figure 1 G). In conclusion, the outcomes of this investigation strongly suggest downregulation of RBM24 expression in CRC. Moreover, the overexpression of RBM24 was found to inhibit the metastatic capabilities of CRC cells.
Figure 1
Downregulation of RBM24 in CRC suppresses tumor metastasis. A – Bioinformatics analysis of RBM24 expression levels; B, C – qRT-PCR and IF detection of RBM24 expression in CRC cell lines and colonic epithelial cell lines. D – qRT-PCR confirmation of RBM24 overexpression in HT-29 and SW480 cells; E – CCK-8 assay for cell proliferation assessment; F – Transwell migration and invasion assays for HT-29 cells. G – WB detection of migration and invasion-related (MMP2, MMP9) and EMT-related (E-cadherin, fibronectin) gene expression. All experiments were independently repeated three times, and the mean ± standard deviation was calculated. *P < 0.05
RBM24 inhibited the metastatic potential of CRC via the MAPK signaling cascade
To investigate the mechanisms of RBM24 in controlling the migration of CRC cells, we conducted GSEA analysis and found that RBM24 was associated with the MAPK signaling pathway (Figure 2 A). The MAPK pathway is recognized in cellular function, and its aberrant activation can facilitate the EMT process [19]. Subsequently, we silenced RBM24 and further treated HT-29 cells with the MAPK pathway inhibitor PD0325901. The qRT-PCR results showed that the RBM24 expression was suppressed in both the si-RBM24 + DMSO and si-RBM24 + PD0325901 groups compared to the si-NC + DMSO group (Figure 2 B). WB results revealed that in HT-29 cells with low RBM24 expression, levels of p-ERK and p-JNK were elevated, but no significant change was observed in the levels of ERK and JNK. The application of PD0325901 impaired the stimulatory effect of low RBM24 expression on the MAPK signaling pathway (Figures 2 C, D). We also evaluated the proliferative, migratory, and invasive capabilities of HT-29 cells using CCK-8 and Transwell assays. It was found that low RBM24 expression promoted the proliferation, migration, and invasion of HT-29 cells, and the addition of PD0325901 impaired the influence of low RBM24 expression on the biological behavior of CRC cells (Figures 2 E, F). Another WB analysis revealed that the knockdown of RBM24 led to upregulation of MMP2, MMP9, and fibronectin expression, and a downregulation of E-cadherin expression, and the addition of PD0325901 returned the protein expression levels to control levels (Figure 2 G). Overall, inhibition of the MAPK signaling pathway counteracted the metastatic-promoting effect of low RBM24 expression in CRC.
Figure 2
RBM24 impeded CRC metastatic spread by modulating the MAPK pathway. A – The interaction of RBM24 with the MAPK signaling pathway (NES = 1.55, FDR = 0.347); B – qRT-PCR measurement of RBM24 expression in groups receiving si- NC + DMSO, si-RBM24 + DMSO, and si-RBM24 + PD0325901; C, D – WB evaluation of the expression of proteins in the MAPK signaling pathway (p-ERK/ERK, p-JNK/JNK); E – CCK-8 assessment of cell proliferation in different groups; F – Transwell assays evaluated HT-29 cell migration and invasion; G – WB analysis of E-cadherin, fibronectin, MMP2, and MMP9 expression levels. All experiments were independently repeated three times, and the mean ± standard deviation was calculated. *P < 0.05 when compared to si-NC + DMSO; #p < 0.05 when compared to si-RBM24+DMSO; ns denotes p > 0.05 when compared to si-NC + DMSO
Cuproptosis upregulated RBM24 expression in CRC cells
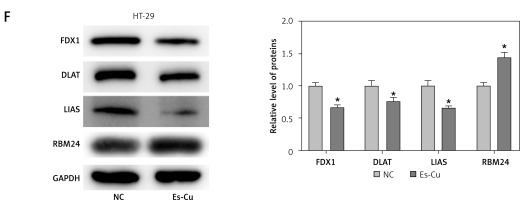
To probe into the molecular mechanisms that govern RBM24 expression, we performed bioinformatics analysis, where a connection between RBM24 and copper ion homeostasis pathways was identified (Figure 3 A). Subsequently, we detected the expression of cuproptosis-related proteins in the oe-RBM24/oe-NC group HT-29 cells. The WB experimental results showed that after overexpression of RBM24, the expression levels of FDX1, DLAT, and LIAS were significantly downregulated, and cuproptosis was activated (Figure 3 B). Research has highlighted the pivotal role of cuproptosis in tumor metastasis [20]. Therefore, we hypothesized that the expression of RBM24 might be related to the occurrence of cuproptosis. To test this, we treated HT-29 cells with Es-Cu and measured much higher intracellular copper ion concentrations than in the NC group (Figure 3 C). Additionally, CCK-8 assay results indicated significant inhibition of CRC cell proliferation with Es-Cu treatment (Figure 3 D). The qRT-PCR results supported that Es-Cu treatment significantly increased RBM24 expression (Figure 3 E). Finally, we detected the protein expression levels of cuproptosis-related genes and RBM24 through WB. The results showed that after treatment with Es-Cu, the expression levels of FDX1, DLAT, and LIAS were significantly downregulated, while the expression of RBM24 was significantly upregulated (Figure 3 F). These results collectively indicated that the treatment of CRC cells with copper ionophores and copper ions could upregulate the expression of RBM24.
Figure 3
Cuproptosis upregulated RBM24 expression in CRC cells. A – Enrichment of RBM24 in pathways associated with copper ion homeostasis (NES = 0.81, FDR = 0.822); B – WB detection of cuproptosis- related proteins (FDX1, DLAT, and LIAS); C – HT-29 cells treated with 200 nM Es-Cu (1 : 1 ratio), followed by determination of copper ion level using a detection kit; D – CCK-8 assay to evaluate cell proliferation in both groups; E – qRT-PCR to measure RBM24 mRNA expression levels in both groups; F – WB detection of FDX1, DLAT, LIAS and RBM24 in both groups. All experiments were independently repeated three times, and the mean ± standard deviation was calculated. *P < 0.05
Cuproptosis inhibited metastasis of CRC cells through the RBM24/MAPK axis
To determine whether cuproptosis influences CRC metastasis through the upregulation of RBM24, Es-Cu was introduced to CRC cells with suppressed RBM24 expression, followed by the assessment of RBM24 expression via qRT-PCR. It was observed that the Es-Cu + si-NC group exhibited markedly increased RBM24 expression compared to the DMSO + si-NC group, whereas the Es-Cu + si-RBM24 group exhibited attenuation of the upregulating effect of Es-Cu on RBM24 expression (Figure 4 A). Thereafter, we examined the expression of p-ERK/ERK and p-JNK/JNK by WB and discovered that Es-Cu treatment inhibited the expression of the phosphorylated forms, with the reduction in MAPK signaling pathway gene expression being relieved after RBM24 knockdown (Figure 4 B). In addition, CCK-8 and Transwell assay results showed that after Es-Cu treatment, the proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities of HT-29 cells significantly decreased, while knockdown of RBM24 concurrently led to increased recovery (Figures 4 C–E). WB also demonstrated that Es-Cu treatment downregulated the expression of MMP2, MMP9, and fibronectin, and upregulated E-cadherin expression. Knockdown of RBM24 attenuated the changes in migration, invasion, and EMT-related protein expression levels induced by Es-Cu treatment (Figures 4 F, G). We concluded that elevated levels of cuproptosis disrupted the MAPK signaling cascade, thereby inhibiting CRC cell spread.
Figure 4
Cuproptosis inhibits the metastasis of CRC cells through the RBM24/MAPK axis. A – qRT-PCR determination of RBM24 levels in the DMSO + si-NC, Es-Cu + si-NC, and Es-Cu + si-RBM24 conditions; B – WB analysis quantified the expression of p-ERK/ERK and p-JNK/JNK; C – CCK-8 assay assessing the proliferation rate of HT-29 cells across the groups; D, E – Transwell migration and invasion assays for HT-29 cells; F, G – WB analysis for expression of E-cadherin, fibronectin, and MMP2, MMP9. All experiments were independently repeated three times, and the mean ± standard deviation was calculated. *P < 0.05 compared to the DMSO + si-NC group; *P < 0.05 compared to the DMSO + si-NC group; #p < 0.05 compared to the Es-Cu + si-NC group; ns denotes p > 0.05 when compared to si-NC + DMSO
Discussion
Tumor progression and the ensuing metastasis are always the primary causes of mortality in CRC patients, with no effective treatment strategies currently available [20]. However, the regulation of key targets has shown great potential in preventing and treating CRC [21, 22]. In our research, we identified RBM24, an RNA-binding protein, which was notably underexpressed in CRC and found to inhibit tumor metastasis upon overexpression. Moreover, RBM24 operates by inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway. We also observed that cuproptosis in CRC can lead to an increase in RBM24 expression. These discoveries help elucidate the role of RBM24 in the processes of migration, invasion, and EMT, all of which are instrumental in the metastasis of CRC.
RBM24, an RNA-binding motif protein, is a versatile regulator that influences cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation through its effects on pre-mRNA splicing and mRNA stability [13]. Furthermore, it acts as a tumor suppressor across various cancer types. In hepatocellular carcinoma cells, RBM24 is believed to inhibit the formation of multicellular three-dimensional tumor spheres. According to Rong et al., RBM24 directly interacts with and stabilizes phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) mRNA, which in turn inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of CRC cells, blocking CRC tumorigenesis [14]. Our research, echoing the results of past studies, revealed that the overexpression of RBM24 in CRC cells strongly inhibited their migration and invasion abilities, with a concurrent decrease in the expression of fibronectin and MMP2/MMP9, and a surge in E-cadherin expression. This illustrated that RBM24 expression negatively modulated the metastatic behavior of CRC cells.
The MAPK signaling pathway is a central regulatory nexus for a host of cellular functions, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and stress responses [23]. The human MAPK family predominantly includes three pathways, known as extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p38, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) [24, 25]. It has been established that activation of the MAPK pathway can enhance the proliferation and metastatic capabilities of cancer cells. Peng et al. reported that the GXYLT1S212* mutation mainly facilitates CRC metastasis through activation of the MAPK pathway [26]. It was recently discovered that mutations and increased expression of MAPK signaling pathway-associated molecules, along with excessive activation of this crucial pathway, are common occurrences in CRC. Targeting the MAPK pathway with specific pharmacological inhibitors has been demonstrated to elicit notable anti-cancer activity [27]. For example, PD-0325901, a specific MAPK inhibitor with oral efficacy, is being tested in early-phase clinical trials for a range of cancers, including CRC. In approximately 16% of late-stage CRC patients, the treatment resulted in a response rate and clinical benefit of approximately 5%, with a progression-free survival of 2.8 months [28]. Bioinformatics analysis in our research has revealed the possible involvement of RBM24 in the modulation of the MAPK signaling pathway. Notably, by downregulating RBM24 and introducing PD0325901, we explored the effects of RBM24 on MAPK signaling in the context of CRC metastasis. We discovered that the inhibition of the MAPK signaling pathway with a specific inhibitor could reduce the increased metastasis observed with low RBM24 expression. Thus, targeting RBM24 to suppress MAPK signaling represents a potential new approach for CRC treatment.
Continuing our investigation into the regulation of RBM24 expression in CRC, bioinformatics analysis suggested a connection between RBM24 and copper ion homeostasis. After adding Es-Cu, the expression of FDX1, DLAT, and LIAS significantly decreased, while the expression level of RBM24 increased. Cuproptosis, a novel copper-mediated form of regulated cell death, is believed to contribute to cancer progression [29]. For example, 4-octyl itaconate (4-OI) inhibits aerobic glycolysis by targeting GAPDH to facilitate cuproptosis in CRC cells, thereby inhibiting tumor growth [11]. The findings of Li et al. have highlighted the role of FDX1 in combating tumor growth via cuproptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-small cell lung cancer cell lines [30]. However, researchers are just beginning to explore the field of cuproptosis. More investigation is needed, especially in relation to CRC. Our results revealed that suppressing RBM24 could mitigate the inhibitory effects of Es-Cu on cell migration and invasion. Therefore, a therapeutic approach that combines copper ionophores with copper ions and MAPK inhibitors may present a viable option for CRC therapy.
The above findings established that cuproptosis resulted in an increase in RBM24 expression, which suppressed MAPK signaling pathway activation and consequently reduced the ability of CRC to metastasize. This research offers a novel perspective for understanding the mechanisms behind CRC development and positions the RBM24 gene as a potential marker for evaluating copper ionophore-based therapies. However, we should not overlook its limitations: the molecular regulatory network involving RBM24 remains to be fully elucidated, and the research was confined to a cellular level and without animal experimental validation. In future, we will explore the precise regulatory mechanisms of RBM24 in CRC across various levels and examine its role in the immune response to CRC tumors, aiming to provide new insights and a strong theoretical foundation for the advancement of CRC clinical practice.