Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS / CLINICAL RESEARCH
Exploring the association between gut microbiota and venous thromboembolism using a Mendelian randomization analysis
1
Department of Peripheral Vascular Surgery, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
Submission date: 2024-11-23
Final revision date: 2025-02-08
Acceptance date: 2025-04-01
Online publication date: 2025-05-18
Corresponding author
Hongshuo Shi
Department of Peripheral Vascular Surgery Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine No. 528 Zhangheng Road Pudong District Shanghai 201203, China
Department of Peripheral Vascular Surgery Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine No. 528 Zhangheng Road Pudong District Shanghai 201203, China
Guobin Liu
Department of Peripheral Vascular Surgery Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine No. 528 Zhangheng Road Pudong District Shanghai 201203, China
Department of Peripheral Vascular Surgery Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine No. 528 Zhangheng Road Pudong District Shanghai 201203, China
Article (PDF)
Supplementary files
References (51)
Exploring the association between - Supplementary Table SI.XLS
Exploring the association between - Supplementary Table SII.XLS
Exploring the association between - Supplementary Table SIII.XLS
Exploring the association between - Supplementary Table SIV.XLSX
Exploring the association between - Supplementary Table SV.XLSX
Exploring the association between - Supplementary Table SVI.XLSX
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Previous observational studies have suggested a potential association between gut microbiota (GM) and venous thromboembolism (VTE), including pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). However, the causal nature of this association remains uncertain due to potential confounding factors.
Material and methods:
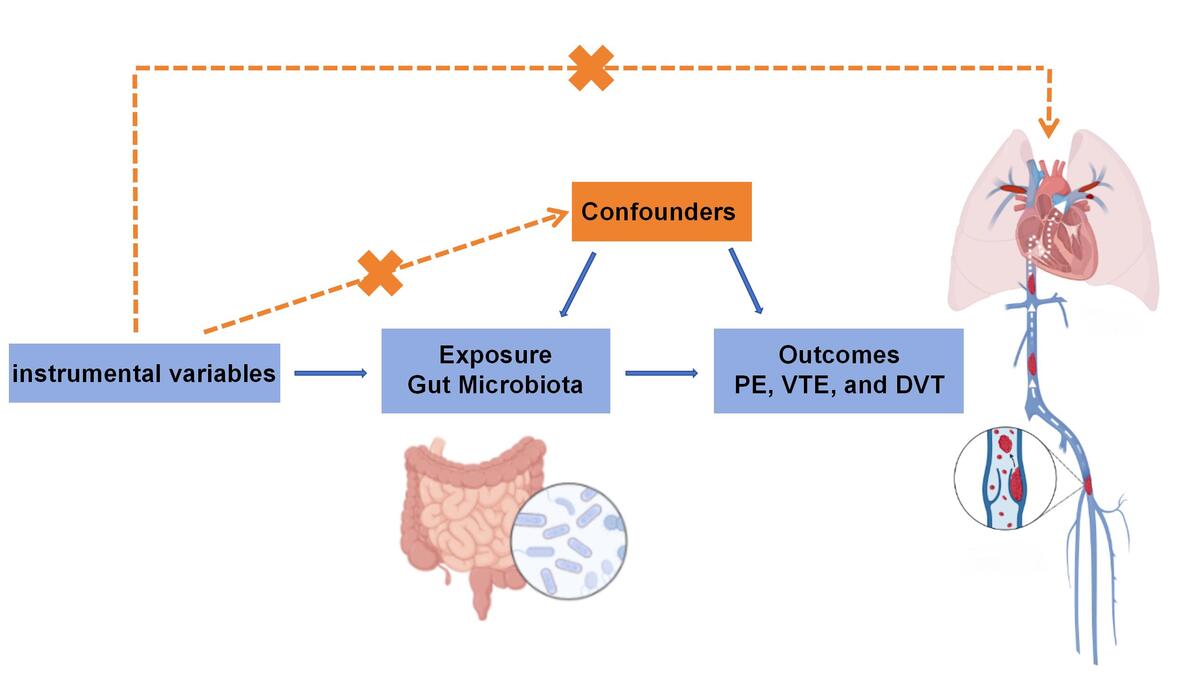
The summary statistics for VTE, PE, and DVT were obtained from the meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) conducted by the FinnGen consortium R9. The genetic data for relevant GM single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were extracted from the meta-analysis of GWAS performed by the global MiBioGen consortium. Using SNPs as instrumental variables, the inverse variance weighting (IVW) method was primarily employed to assess the bidirectional causal relationship between GM and VTE, PE, and DVT.
Results:
For the risk of VTE onset, Candidatus Solea ferrea, Ruminococcaceae UCG002, and Ruminococcaceae UCG004 were negatively correlated, while Eubacterium hallii group, Butyricimonas, and Dorea were positively correlated. For PE, Intestinimonas, an unknown genus, and Firmicutes were negatively correlated, while Veillonella, Erysipelatoclostridium, and Lentisphaerae were positively correlated. For DVT, Mollicutes, Actinobacteria, and Bifidobacteriaceae were negatively correlated, while Adlercreutzia, Collinsella, and Desulfovibrio were positively correlated. After multiple corrections using the Bonferroni method, a significant causal relationship was identified between Ruminococcaceae and VTE. Cochran’s Q test was performed to evaluate instrumental variable heterogeneity (p > 0.05), MR-Egger regression analyses were performed to examine pleiotropy (p > 0.05), and leave-one-out analysis was conducted to assess the impact of each SNP on the outcome.
Conclusions:
Specific GM may have causal effects on VTE, PE, and DVT, potentially contributing to the development of microbiota-centered therapeutic approaches and the identification of novel biomarkers for targeted preventive strategies.
Previous observational studies have suggested a potential association between gut microbiota (GM) and venous thromboembolism (VTE), including pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). However, the causal nature of this association remains uncertain due to potential confounding factors.
Material and methods:
The summary statistics for VTE, PE, and DVT were obtained from the meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) conducted by the FinnGen consortium R9. The genetic data for relevant GM single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were extracted from the meta-analysis of GWAS performed by the global MiBioGen consortium. Using SNPs as instrumental variables, the inverse variance weighting (IVW) method was primarily employed to assess the bidirectional causal relationship between GM and VTE, PE, and DVT.
Results:
For the risk of VTE onset, Candidatus Solea ferrea, Ruminococcaceae UCG002, and Ruminococcaceae UCG004 were negatively correlated, while Eubacterium hallii group, Butyricimonas, and Dorea were positively correlated. For PE, Intestinimonas, an unknown genus, and Firmicutes were negatively correlated, while Veillonella, Erysipelatoclostridium, and Lentisphaerae were positively correlated. For DVT, Mollicutes, Actinobacteria, and Bifidobacteriaceae were negatively correlated, while Adlercreutzia, Collinsella, and Desulfovibrio were positively correlated. After multiple corrections using the Bonferroni method, a significant causal relationship was identified between Ruminococcaceae and VTE. Cochran’s Q test was performed to evaluate instrumental variable heterogeneity (p > 0.05), MR-Egger regression analyses were performed to examine pleiotropy (p > 0.05), and leave-one-out analysis was conducted to assess the impact of each SNP on the outcome.
Conclusions:
Specific GM may have causal effects on VTE, PE, and DVT, potentially contributing to the development of microbiota-centered therapeutic approaches and the identification of novel biomarkers for targeted preventive strategies.
REFERENCES (51)
1.
Al Raizah A, Alrizah M. Artificial intelligence in thrombosis: transformative potential and emerging challenges. Thromb J 2025; 23: 2.
2.
Xia YQ, Tang L, Hu Y. [Advances in the genetics of venous thromboembolic disease]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2024; 45: 1144-7.
3.
Saad M, Batool RM, Waqas SA, et al. Unveiling the trends: growing cancer and venous thromboembolism mortality in older adults in the United States, 1999-2020. Thromb Res 2025; 247: 109259.
4.
Opitz CF, Meyer FJ. Pulmonary embolism: an update based on the revised AWMF-S2k guideline. Hamostaseologie 2024; 44: 111-8.
5.
Navarrete S, Solar C, Tapia R, et al. Pathophysiology of deep vein thrombosis. Clin Exp Med 2023; 23: 645-54.
6.
Szymanski K, Weber C, Daugherty K, et al. A review of venous thromboembolism for the hospitalist. Postgrad Med 2025; 137: 131-8.
7.
Wang X, Zhang C, Pan M, et al. Design and rationale of the multicenter randomized clinical trial (REVERSE): efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban in the early postoperative period for patients with bioprosthetic valve replacement or valve repair. Int J Cardiol 2025; 425: 133023.
8.
Zeng J, Feng J, Luo Y, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers as predictors of symptomatic venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with AECOPD: a multicenter cohort study. J Atheroscler Thromb 2025; 32: 439-57.
9.
Liu Q, Yang F, Kong K, et al. Potential causal relationships between blood metabolites, inflammatory cytokines, and venous thromboembolism. Front Immunol 2024; 15: 1445790.
10.
Dong Y, Zhang K, Wei J, et al. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids regulate gastrointestinal tumor immunity: a novel therapeutic strategy? Front Immunol 2023; 14: 1158200.
11.
Larsson SC, Butterworth AS, Burgess S. Mendelian randomization for cardiovascular diseases: principles and applications. Eur Heart J 2023; 44: 4913-24.
12.
Wu Q, Li J, Sun X, et al. Multi-stage metabolomics and genetic analyses identified metabolite biomarkers of metabolic syndrome and their genetic determinants. EBioMedicine 2021; 74: 103707.
13.
Xu S, Li X, Zhang S, et al. Oxidative stress gene expression, DNA methylation, and gut microbiota interaction trigger Crohn’s disease: a multi-omics Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med 2023; 21: 179.
14.
Pasqualini J, Facchin S, Rinaldo A, et al. Emergent ecological patterns and modelling of gut microbiomes in health and in disease. PLoS Comput Biol 2024; 20: e1012482.
15.
Gong F, Zheng X, Zhao S, et al. Disseminated intravascular coagulation: cause, molecular mechanism, diagnosis, and therapy. MedComm 2025; 6: e70058.
16.
Johnson TA, Mukhopadhyay S, Buzza MS, et al. Regulation of macrophage fibrinolysis during venous thrombus resolution. Thromb Res 2024; 243: 109149.
17.
Birney E. Mendelian randomization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2022; 12: a041302.
18.
Song Q, Huang T, Song J, et al. Causal associations of body mass index and waist-to-hip ratio with cardiometabolic traits among Chinese children: a Mendelian randomization study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2020; 30: 1554-63.
19.
Zhou J, Li Y, Lin Y, et al. The genetic causal association between hip or knee osteoarthritis and frailty: a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 938-46.
20.
Jiang R, Qu Q, Wang Z, et al. Association between air pollution and bone mineral density: a Mendelian randomization study. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 1334-8.
21.
Kurilshikov A, Medina-Gomez C, Bacigalupe R, et al. Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition. Nat Genet 2021; 53: 156-65.
22.
Kamat MA, Blackshaw JA, Young R, et al. PhenoScanner V2: an expanded tool for searching human genotype-phenotype associations. Bioinformatics 2019; 35: 4851-3.
23.
Emdin CA, Khera AV, Kathiresan S. Mendelian randomization. JAMA 2017; 318: 1925-6.
24.
Bowden J, Del Greco MF, Minelli C, et al. A framework for the investigation of pleiotropy in two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization. Stat Med 2017; 36: 1783-802.
25.
Zhang Y, Li D, Zhu Z, et al. Evaluating the impact of metformin targets on the risk of osteoarthritis: a mendelian randomization study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2022; 30: 1506-14.
26.
Zhao JV, Schooling CM. Using Mendelian randomization study to assess the renal effects of antihypertensive drugs. BMC Med 2021; 19: 79.
27.
Liu Z, Zhang H, Sun X, et al. Causal association between metabolites and age-related macular degeneration: a bidirectional two-sample mendelian randomization study. Hereditas 2024; 161: 51.
28.
Wu Y, Shen Z, Chen B, et al. Investigation of bidirectional causal association between temporomandibular disorders and five mental disorders. Arch Oral Biol 2024; 171: 106169.
29.
Zhou C, Zhou Y, Ma W, et al. Revisiting Virchow’s triad: exploring the cellular and molecular alterations in cerebral venous congestion. Cell Biosci 2024; 14: 131.
30.
Lv K, Chen S, Xu X, et al. Protein disulfide isomerase cleaves allosteric disulfides in histidine-rich glycoprotein to regulate thrombosis. Nat Commun 2024; 15: 3129.
31.
Gong D, Zhang L, Zhang Y, et al. Gut microbial metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide is related to thrombus formation in atrial fibrillation patients. Am J Med Sci 2019; 358: 422-8.
32.
Reiner MF, Muller D, Gobbato S, et al. Gut microbiota-dependent trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) shows a U-shaped association with mortality but not with recurrent venous thromboembolism. Thromb Res 2019; 174: 40-7.
33.
Papa A, Santini P, De Lucia SS, et al. Gut dysbiosis-related thrombosis in inflammatory bowel disease: potential disease mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies. Thromb Res 2023; 232: 77-88.
34.
Jonsson AL, Backhed F. Role of gut microbiota in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol 2017; 14: 79-87.
35.
Huang X, Zhang Y, Yi S, et al. Potential contribution of the gut microbiota to the development of portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis. Front Microbiol 2023; 14: 1217338.
36.
Lee H, An J, Kim J, et al. A novel Bacterium, Butyricimonas virosa, preventing HFD-induced diabetes and metabolic disorders in mice via GLP-1 receptor. Front Microbiol 2022; 13: 858192.
37.
Tsai Y, Tai W, Liang C, et al. Alternations of the gut microbiota and the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio after biologic treatment in inflammatory bowel disease. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2025; 58: 62-9.
38.
Mi HTN, Chaiyasarn S, Kim H, et al. C-glycoside-metabolizing human gut Bacterium, Dorea sp. MRG-IFC3. J Microbiol Biotechnol 2023; 33: 1606-14.
39.
Wu Y, Chen Y, Li Q, et al. Tetrahydrocurcumin alleviates allergic airway inflammation in asthmatic mice by modulating the gut microbiota. Food Funct 2021; 12: 6830-40.
40.
Wang L, Cai Y, Garssen J, et al. The bidirectional gut-lung axis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2023; 207: 1145-60.
41.
Montatore M, Zagaria A, Masino F, et al. A rare case of Lemierre’s syndrome due to Veillonella Parvula: a dangerous and forgotten complication of a septic condition. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2024; 76: 3570-5.
42.
Li J, Liu C, Xu Y, et al. Gut microbiota alterations in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis are associated with aberrant bone homeostasis. Orthop Surg 2024; 16: 965-75.
43.
Li T, Chu Y, Yan K, et al. Simultaneous determination of tanshinol, protocatechuic aldehyde, protocatechuic acid, notoginsenoside R1, ginsenoside Rg1 and Rb1 in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application. Biomed Chromatogr 2017; 31: doi: 10.1002/bmc.3889.
44.
Cao J, An G, Li R, et al. Novel strategy for human deep vein thrombosis diagnosis based on metabolomics and stacking machine learning. Anal Chem 2024; 96: 14560-70.
45.
Barone M, Barone M, Ricci F, et al. A specific host/microbial signature of plasma-derived extracellular vesicles is associated to thrombosis and marrow fibrosis in polycythemia vera. Cancers 2021; 13: 4968.
46.
An J, Kwon H, Kim YJ. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio as a risk factor of breast cancer. J Clin Med 2023; 12: 2216.
47.
Rafie E, Zugman M, Pal SK, et al. What is the role of fecal microbiota transplantation in immunotherapy trials? Current perspectives and future directions. Eur Urol Focus 2024; 10: 882-5.
48.
Tiwari S, Paramanik V. Role of probiotics in depression: connecting dots of gut-brain-axis through hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal axis and tryptophan/kynurenic pathway involving indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase. Mol Neurobiol 2025; 62: 7230-41.
49.
Yu J, Wu Y, Zhu Z, et al. The impact of dietary patterns on gut microbiota for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review. Nutr J 2025; 24: 17.
50.
Almeida-Santos AC, Duarte B, Tedim AP, et al. The healthy human gut can take it all: vancomycin-variable, linezolid-resistant strains and specific bacteriocin-species interplay in Enterococcus spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 2025; 91: e169924.
51.
Abdullah, Ahmad N, Xiao J, et al. Gingerols: preparation, encapsulation, and bioactivities focusing gut microbiome modulation and attenuation of disease symptoms. Phytomedicine 2025; 136: 156352.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.