Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
GASTROENTEROLOGY / CLINICAL RESEARCH
Is the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio a useful index in the differential diagnosis of malignancy and tuberculosis-related ascites?
1
Department of Gastroenterology, Dicle University, Diyarbakir, Turkey
Submission date: 2024-11-10
Final revision date: 2025-04-14
Acceptance date: 2025-04-23
Online publication date: 2025-05-22
Corresponding author
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Distinguishing between malignant ascites (MA) and ascites secondary to tuberculous peritonitis (TBpA) can sometimes be challenging for the clinician. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been shown to be a useful index of advanced disease and poor prognosis in patients with cancer. We investigated the suitability of the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, an inflammatory biomarker, in differentiating MA and TBpA.
Material and methods:
Demographic and laboratory characteristics of 100 patients with confirmed diagnoses of malignant ascites and ascites secondary to tuberculous peritonitis between January 2015 and December 2020 were analyzed retrospectively. The diagnostic ability of NLR in differential diagnosis was evaluated.
Results:
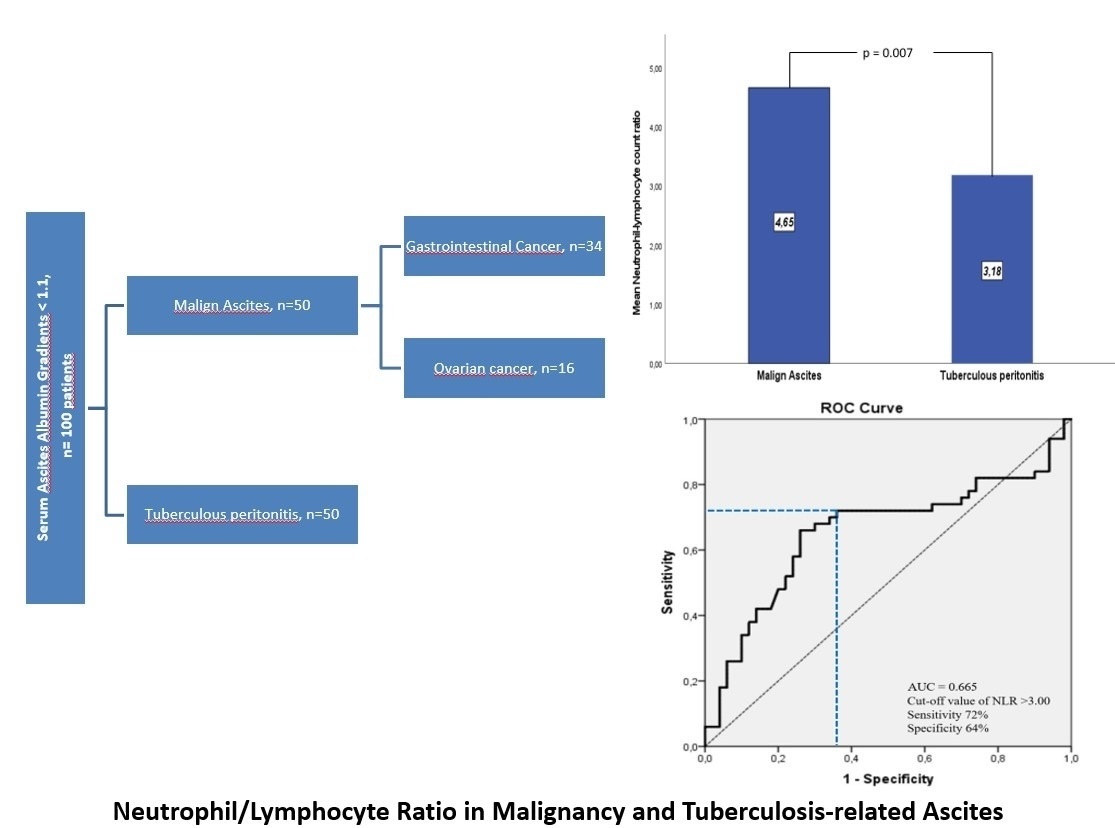
Serum neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio was significantly higher in patients with MA than in patients with TBpA (4.65 ±3.17 vs. 3.17 ±1.74, p = 0.007). The area under the curve value was 0.655 (95% confidence interval = 0.544–0.767, p = 0.007). The optimal threshold value for distinguishing malignant ascites from TBpA was determined to be NLR > 3.00 (sensitivity 72.0%, specificity 64.0%, positive predictive value 66.7%, negative predictive value 69.6%, accuracy 68%). This threshold value was found to have better discrimination rates in the patient group over 40 years of age (sensitivity 70.0%, specificity 88.0%, positive predictive value 85.4%, negative predictive value 74.6%, accuracy 79.0%).
Conclusions:
NLR, a simple and rapid inflammatory index, can be among the initial diagnostic tests to distinguish MA and TBpA, especially in those older than 40 years.
Distinguishing between malignant ascites (MA) and ascites secondary to tuberculous peritonitis (TBpA) can sometimes be challenging for the clinician. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been shown to be a useful index of advanced disease and poor prognosis in patients with cancer. We investigated the suitability of the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, an inflammatory biomarker, in differentiating MA and TBpA.
Material and methods:
Demographic and laboratory characteristics of 100 patients with confirmed diagnoses of malignant ascites and ascites secondary to tuberculous peritonitis between January 2015 and December 2020 were analyzed retrospectively. The diagnostic ability of NLR in differential diagnosis was evaluated.
Results:
Serum neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio was significantly higher in patients with MA than in patients with TBpA (4.65 ±3.17 vs. 3.17 ±1.74, p = 0.007). The area under the curve value was 0.655 (95% confidence interval = 0.544–0.767, p = 0.007). The optimal threshold value for distinguishing malignant ascites from TBpA was determined to be NLR > 3.00 (sensitivity 72.0%, specificity 64.0%, positive predictive value 66.7%, negative predictive value 69.6%, accuracy 68%). This threshold value was found to have better discrimination rates in the patient group over 40 years of age (sensitivity 70.0%, specificity 88.0%, positive predictive value 85.4%, negative predictive value 74.6%, accuracy 79.0%).
Conclusions:
NLR, a simple and rapid inflammatory index, can be among the initial diagnostic tests to distinguish MA and TBpA, especially in those older than 40 years.
REFERENCES (38)
1.
Smith E, Jayson GC. The current and future management of malignant ascites. Clin Oncol 2003; 15: 59-72.
3.
Fleming ND, Alvarez-Secord A, Von Gruenigen V, Miller MJ, Abernethy AP. Indwelling catheters for the management of refractory malignant ascites: a systematic literature overview and retrospective chart review. J Pain Sympt Manage 2009; 38: 341-9.
4.
Trends in Tuberculosis, 2021 [Internet]. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Availablefrom:https://www.cdc.gov/tb/publica... [cited 2023 Apr 18].
5.
Donoghue HD, Holton J. Intestinal tuberculosis. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2009; 22: 490-6.
6.
Rasheed S, Zinicola R, Watson D, Bajwa A, McDonald PJ. Intra-abdominal and gastrointestinal tuberculosis. Colorectal Dis 2007; 9: 773-83.
7.
Kaya M, Kaplan MA, Isikdogan A, Celik Y. Differentiation of tuberculous peritonitis from peritonitis carcinomatosa without surgical intervention. Saudi J Gastroenterol 2011; 17: 312-7.
8.
Demir K, Okten A, Kaymakoglu S, et al. Tuberculous peritonitis-report of 26 cases, detailing diagnostic and therapeutic problems. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2001; 13: 581-5.
9.
Chow KM, Chow VC, Hung LC, Wong SM, Szeto CC. Tuberculous peritonitis-associated mortality is high among patients waiting for the results of mycobacterial culture of ascetic fluid samples. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 35: 409-13.
10.
Forget P, Khalifa C, Defour JP, Latinne D, Van Pel MC, De Kock M. What is the normal value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio? BMC Res Notes 2017; 10: 12.
11.
Heshmat-Ghahdarijani K, Sarmadi V, Heidari A, Falahati Marvasti A, Neshat S, Raeisi S. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a new prognostic factor in cancers: a narrative review. Front Oncol 2023; 13: 1228076.
12.
Russell CD, Parajuli A, Gale HJ, et al. The utility of peripheral blood leucocyte ratios as biomarkers in infectious diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Infect 2019; 78: 339-48.
13.
Su X, Li Y, Zhu Y, et al. Development and validation of an ensemble learning risk model for sepsis after abdominal surgery. Arch Med Sci 2024; 21: 138-52.
14.
Nemoto T, Endo S, Isohata N, et al. Change in the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio during chemotherapy may predict prognosis in patients with advanced or metastatic colorectal cancer. Mol Clin Oncol 2021; 14: 107.
15.
Namikawa T, Shimizu S, Yokota K, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio as prognostic factors for unresectable advanced or recurrent gastric cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2022; 407: 609-21.
16.
Reddy AV, Hill CS, Sehgal S, et al. High neutrophil to-lymphocyte ratio following stereotactic body radiation therapy is associated with poor clinical outcomes in patients with borderline resectable and locally advanced pancreatic cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol 2022; 13: 368-79.
17.
Feng Z, Wen H, Bi R, et al. Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictive and prognostic factor for high-grade serous ovarian cancer. PLoS One 2016; 11: e0156101.
18.
Runyon BA. Ascites. In: Diseases of the Liver. Schiff L, Schiff ER, eds. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia 1993; 990-1015.
19.
Runyon BA, Montano AA, Akriviadis EA, Antillon MR, Irving MA, McHutchison JG. The serum-ascites albumin gradient is superior to the exudate-transudate concept in the differential diagnosis of ascites. Ann Intern Med 1992; 117: 215-20.
21.
Seçkin Büyükkurt E, Yılmaz Ö, Albayrak B, Yerli EB. Tuberculous peritonitis: an analysis of case series of 49 consecutive patients. Eur Res J 2024; 10: 45-50.
22.
Yuksel I, Karaahmet F, Coskun Y, et al. Significance of serum and ascitic fluid C-reactive protein in differential diagnosis of benign and malignant ascites. Dig Dis Sci 2014; 59: 2588-93.
23.
Cheng D, Liang B, Kong H. Clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor and endostatin levels in the differential diagnosis of malignant and benign ascites. Med Oncol 2012; 29: 1397-402.
24.
Li CP, Huang TS, Chao Y, Chang FY, Whang-Peng J, Lee SD. Advantages of assaying telomerase activity in ascites for diagnosis of digestive tract malignancies. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10: 2468-71.
25.
Abdel-Razik A, Eldars W, Elhelaly R, Elzehery R. C-reactive protein and insulin-like growth factor-1 in differential diagnosis of ascites. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016; 31: 1868-73.
26.
Zahorec R. Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts--rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl Lek Listy 2001; 102: 5-14.
27.
Bone G, Lauder I. Cellular immunity, peripheral blood lymphocyte count and pathological staging of tumours in the gastrointestinal tract. Br J Cancer 1974; 30: 215-21.
28.
Dutta A, Bhagat S, Paul S, Katz JP, Sengupta D, Bhargava D. Neutrophils in cancer and potential therapeutic strategies using neutrophil-derived exosomes. Vaccines (Basel) 2023; 11: 1028.
29.
Jaillon S, Ponzetta A, Di Mitri D, Santoni A, Bonecchi R, Mantovani A. Neutrophil diversity and plasticity in tumour progression and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2020; 20: 485-503.
30.
Schmidt H, Bastholt L, Geertsen P, et al. Elevated neutrophil and monocyte counts in peripheral blood are associated with poor survival in patients with metastatic melanoma: a prognostic model. Br J Cancer 2005; 93: 273-8.
31.
Peron J, Cropet C, Tredan O, et al. CD4 lymphopenia to identify end-of-life metastatic cancer patients. Eur. J Cancer 2013; 49: 1080-9.
32.
Ocana A, Nieto-Jimenez C, Pandiella A, Templeton AJ. Neutrophils in cancer:prognostic role and therapeutic strategies. Mol Cancer 2017; 16: 137.
33.
Gentles AJ, Newman AM, Liu CL, et al. The prognostic landscape of genes and infiltrating immune cells across human cancers. Nat Med 2015; 21: 938-45.
34.
You T, Shu L, Chen Y, et al. Diagnosis of malignant versus tuberculous ascites using tumor markers and globulin ratios in serum and ascites: a Fisher discriminant model. Arab J Gastroenterol 2021; 22: 93-8.
35.
Magdy M, Hussein T, Ezzat A, Gaballah A. Pre-treatment peripheral neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker in gastric cancer. J Gastrointest Cancer 2019; 50: 763-8.
36.
Li Z, Hong N, Robertson M, Wang C, Jiang G. Preoperative red cell distribution width and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predict survival in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Sci Rep 2017; 7: 43001.
37.
Ewida E, Abd Elnaby HE, Deraz E, Yousry Z. Diagnostic value of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in exudative pleural effusion. Al-Azhar Int Med J 2022; 3: 119-24.
38.
Yoon NB, Son C, Um SJ. Role of the neutrophil-lymphocyte count ratio in the differential diagnosis between pulmonary tuberculosis and bacterial community-acquired pneumonia. Ann Lab Med 2013; 33: 105-10.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.