Introduction
Human liver cancer ranks fifth among cancers in terms of prevalence across the globe [1]. The malignancy is believed to mainly result from the epithelial cells of the liver where the control over their division and proliferation is lost, as is true for other human cancers [2]. Liver cancer is one of the aggressive human cancers and exhibits very high mortality rates [3, 4]. The presently used anticancer strategies against liver cancer include surgery, chemo- and radiotherapies. However, the results of these existing therapies are still far from satisfactory [5]. As such, there is a pressing need to explore more efficient treatment measures against liver cancer. Over the years, studies have shown the involvement of a small non-coding RNA group, the micro RNAs (miRs), in the development of several cancers [6]. The miRs are a relatively heterogeneous class of non-coding RNAs which are about 22 nucleotides long [6]. They are important for the post-transcriptional gene repression in eukaryotes and have been shown to regulate the growth, differentiation and apoptosis of eukaryotic cells, at the post-transcriptional level [7, 8]. Defects in the miR expression levels have been found to be associated with the development of a number of human diseases including cancer [9]. Studies have proved that miRs regulate the crucial molecular events of cancer development and influence the proliferation of human cancers [10]. Involvement of a number of miRs has been shown to regulate the growth and proliferation of liver cancer [11]. miR-939 is an important molecular regulator and its deregulation is associated with many human cancers [12, 13]. However, little is known about the regulatory role of miR-939 in human liver cancer.
Hence, our aim was to examine the expression profile and investigate the molecular role of miR-939 in liver cancer. The results suggested that miR-939 is downregulated in liver cancer. The overexpression of miR-939 induced apoptosis of liver cancer cells and thus decreased their proliferation. The CRKL gene was found to be targeted by miR-939 and it was shown to modulate the regulatory role of miR-939 in liver cancer. To sum up, the current study provides insights into the therapeutic potential of miR-939 in the treatment of liver cancer.
Material and methods
Tissue samples, cell lines and cell culture
The clinical specimens consisting of cancerous liver tissues and the surrounding normal part were excised from cancer patients, being treated at Harrison International Peace Hospital, Hengshui, Hebei, China, with written consent and under the standard ethical guidelines. The normal liver epithelial cell line (THLE-2) and the cancerous cell lines (HepG2, SNU-182 and SNU-423) were purchased from the American Type Collection Center (ATCC, USA). The culture of cell lines was carried out using RPMI-1640 medium (Thermo Scientific) supplemented with 10% FBS (Sigma-Aldrich). A CO2 incubator was used for maintenance of liver cell lines at 37oC with 5% concentration of CO2. The study protocol was approved by the research ethics committee of the institute under approval number HIPH-234-HS73 of 2019.
Transfection
Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Scientific) was used for the transfection of liver cancer cells. The miR-939 mimics, miR-NC, si-CRKL and si-CRKL constructs were purchased from RiboBio (Guangzhou, China).
qRT-PCR expression studies
For performing the gene expression studies, the human tissues and cell lines were processed for RNA isolation. Total RNA isolation was carried out by the Trizol method and RNA isolated was first treated with DNase I (Thermo Scientific), then cDNA was synthesized using 2 µg of RNA as a template. The qRT-PCR was performed using the SYBR Green mix (Thermo Scientific). The cycling conditions were as follows: 95°C for 20 s, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 s, and 58°C for 1 min. The 2–ddCt method was used to do the required calculations for estimating the expression level of miR-939 using the Ct values of the actin gene for normalization. The primer sequences were as follows: miR-939 forward, TGG GGA GCT GAG GCT CTG and reverse, AGT GCA GGG TCC GAG GTA TT; GAPDH forward, AAC TTT GGC ATT GTG GAA GG and reverse, CAC ATT GGG GGT AGG AAC AC; CRKL forward, 5′-CCTTTGCCATCCACACAGAAT-3′, and reverse, 5′-TTTCACGATGTCACCAACCTCTA-3′.
Cell proliferation assay
The liver cancer cells were transfected with 100 nM of miR-NC or miR-939 mimics or 50 nM si-NC or si-CRKL and cultured for 24 h at 37°C. About 24 h after transfection the cells were seeded in 96-well plates at the density of 2 × 105 cells/well and incubated at 37°C. Thereafter 15 µl of reagent was added to the cultures at 0, 12, 24, 48 and 96 h. The OD570 was determined for each well using the micro-plate reader and these values were taken as the measure of cell proliferation.
Clonogenic assay
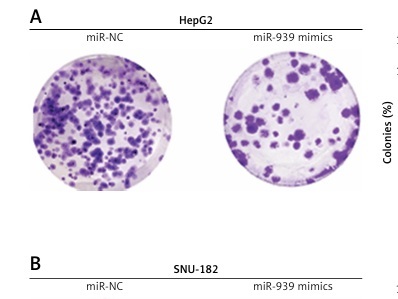
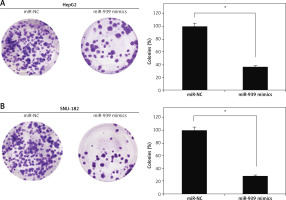
About 24 h after transfection, the liver cancer cells were cultured in 6-well plates for 10 days at 37°C. The cells were then collected, fixed with 70% ethanol and then crystal violet staining was used for analyzing the colony number under the light microscope.
DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) staining
About 24 h after transfection, the liver cancer cells were seeded at the density of 0.6 × 106 cells, in 6-well plates and cultured for 24 h at 37°C. The cells were then harvested, washed, fixed with methanol and stained with DAPI solution. Finally, the liver cancer cells were examined under the fluorescent microscope for assessment of nuclear morphology.
Annexin V-FITC/PI dual staining
The transfected liver cancer cells were also processed for dual annexin V-FITC/PI staining to determine the percentage of apoptotic cells. Briefly, the cells were harvested after being cultured in 6-well plates for 24 h. Fixing of cells was done using methanol. Afterwards, the cells were stained with the dual mix of annexin V-FITC/PI, following which they were analyzed for apoptosis using the flow cytometer.
Target prediction and validation
The scanning through online software, TargetScan (http://www.targetscan.org), was used to identify the post-transcriptional target of miR-939. To validate the identification, dual luciferase assay was used. Briefly, the wild type (WT) or mutated (MUT) UTR fragment of CRKL was cloned into the pCHECK2.0 luciferase reporter vector, which was then co-transduced into liver cancer cells with miR-NC or miR-939 mimics. The luciferase activity was analyzed using the Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega) with the Renilla luciferase gene as activity control.
Western blot analysis
The liver cancer cells were digested by treating them with RIPA lysis buffer and the proteins extracted were quantified by Lowry assay. About 35 µg of total proteins were SDS-PAGE gel separated and transferred to nylon membranes which were then exposed to primary and secondary antibodies. The protein bands were then detected and their intensity was taken as a measure of the expression level. The human actin gene was used as the control of protein expression.
Statistical analysis
To validate the data, three replicates were used for each experiment and the statistical tests, Student’s t-test and one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test, were performed using GraphPad Prism 7.0 software. The final values were presented as mean ± SD. P-values < 0.05 were taken as statistically significant.
Results
Liver cancer is associated with downregulation of miR-939
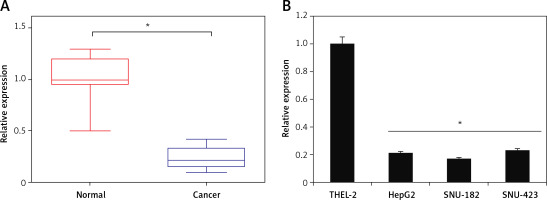
The qRT-PCR analysis of miR-939 revealed miR-939 to be significantly (p < 0.05) downregulated in liver cancerous tissues relative to the normal tissues (Figure 1 A). The expression of miR-939 was also significantly (p < 0.05) lower in liver cancer cell lines (HepG-2, SNU-182 and SNU-423) relative to the normal epithelial cell line, THLE-2 (Figure 1 B). Among the cancer cell lines, HepG2 and SNU-182 exhibited comparatively lower miR-939 expression as against the SNU-423 cell line. Hence, HepG2 and SNU-182 were used for further experimental characterization of the role of miR-939.
Figure 1
miR-939 is downregulated in human liver cancer. A – qRT-PCR analysis of miR-939 in normal and human liver cancer tissues. B – qRT-PCR analysis of miR-939 in normal and human liver cancer cell lines. The experiments were performed in triplicate and results are expressed as mean ± SD (*p < 0.05)
miR-939 inhibits proliferation of human liver cancer cells
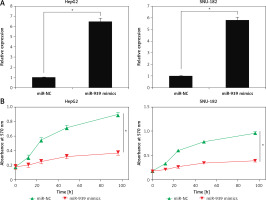
The cell lines (HepG2 and SNU-182) were transfected with miR-939 mimics to achieve the overexpression of miR-939 in cancer cells, which was confirmed by qRT-PCR analysis (Figure 2 A). The CCK-8 assay revealed that overexpression of miR-939 significantly (p < 0.05) reduced the proliferation of HepG2 and SNU-182 cells (Figure 2 B). These results point towards the tumor suppressive role of miR-939 in liver cancer. Additionally, the clonogenic assay showed that miR-939 overexpression significantly (p < 0.05) inhibited the colony formation of the HepG2 and SNU-182 cells (Figure 3).
Figure 2
miR-939 inhibits the proliferation of human liver cancer cells. A – Expression of miR-939 in miR-NC and miR-939 mimics transfected HepG2 and SNU-182 cells. B – Cell viability of miR-NC and miR-939 mimics transfected HepG2 and SNU-182 cells. The experiments were performed in triplicate and results are expressed as mean ± SD (*p < 0.05)
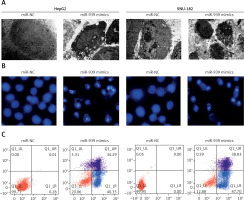
miR-939 induces apoptosis in human liver cancer cells
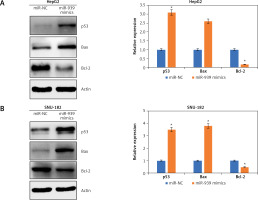
Ultrastructural analysis by electron microscopy showed nuclear fragmentation and membrane blebbing in miR-939 overexpressing HepG-2 and SNU-182 cells suggestive of apoptosis (Figure 4 A). DAPI staining of miR-939 overexpressing HepG-2 and SNU-182 cells showed alterations in the nuclear morphology of these cells, further indicating the induction of apoptosis (Figure 4 B). Annexin V-FITC/PI dual staining showed that the apoptotic cells increased from 0.28 to 40.35% and 0 to 47.40% in HepG2 and SNU-1 cells respectively upon miR-939 overexpression (Figure 4 C). Western blotting of p53, Bax and Bcl-2 proteins showed that transfection of liver cancer cells with miR-939 mimics increased the expression of p53 and Bax proteins. On the other hand, the expression of Bcl-2 protein was decreased under miR-939 overexpression in both HepG2 and SNU-182 cancer cells (Figure 5).
Figure 4
miR-939 induces apoptosis in human liver cancer cells. A – Ultrastructural analysis of miR-NC and miR-939 transfected HepG2 and SNU-182 cells. B – DAPI staining of miR-NC and miR-939 transfected HepG2 and SNU-182 cells. C – Annexin V/PI staining of miR-NC and miR-939 transfected HepG2 and SNU-182 cells. The experiments were performed in triplicate and results are expressed as mean ± SD (*p < 0.05)
CRKL is targeted by miR-939 in liver cancer
Online target identification of miR-939 showed that CRKL is the post-transcriptional target of miR-939 in liver cancer (Figure 6 A). The results were validated by the dual luciferase assay of miR-939 with the 3′ UTR region of the CRKL gene, where the luciferase activity was markedly lower in the SNU-182 cancer cells co-transfected with miR-939 mimics and wild type (WT) 3′ UTR of the CRKL gene (Figure 6 B).
Figure 6
miR-939 exerts its effects by targeting CRKL. A – TargetScan analysis showing that miR-939 targets CRKL. B – Dual luciferase assay showing interaction between miR-NC and miR-939. C – Expression of CRKL in normal and liver cancer cell lines. D – Expression of CRKL in normal cancer tissues. E – Expression of CRKL in miR-NC and miR-939 mimics transfected HepG2 cells. F – Expression of CRKL in si-NC and si-CRKL transfected HepG2 cells. G – Cell viability of si-NC and si-CRKL transfected HepG2 cells. H – Cell viability of miRNC, miR-939 mimics, and miR-939 + pcDNA-CRKL transfected HepG2 cells. The experiments were performed in triplicate and results are expressed as mean ± SD (*p < 0.05)
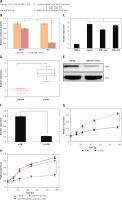
miR-939 exerts its molecular effects via post-transcriptional silencing of CRKL
Next the expression of CRKL was investigated in the human liver cancer cells and it was found that the expression of CRKL was significantly upregulated in human liver cancer tissues and cell lines (Figures 6 C, D). Nonetheless, overexpression of miR-939 could suppress the expression of CRKL in HepG2 cells, as depicted by western blot analysis (Figure 6 E). To assess whether the tumor suppressive effects of miR-939 are exerted through its post-transcriptional regulation of CRKL, CRKL was silenced in the HepG2 cancer cells and silencing was confirmed by RT-PR analysis (Figure 6 E). The assessment of the proliferation rate of liver cancer cells transfected with si-CRKL showed that silencing of CRKL expression led to the decline of proliferation of liver cancer cells and mimicked the anti-proliferative effects of miR-939 in liver cancer (Figure 6 F). However, overexpression of CRKL in HepG2 cells abolished the tumor suppressive effects of miR-939 on HepG2 cells (Figure 6 G).
Discussion
Over the past two decades, the role of miRs in regulation of cancer development and progression has been well established [14]. The miRs exhibit aberrant expression levels in almost all human cancers [15, 16]. As such, they may aid in the prognosis of human cancers at the molecular level [17]. The miRs have been shown to act as suppressors of a number of human cancers such as oral, gastric and colon cancer, to name a few [18–20]. Several miR molecules also act as suppressors of human liver cancer [21]. miR-939 is involved in the growth and progression of different human cancers including ovarian and gastric cancer [12, 13]. However, it has not been studied for its molecular regulatory role in liver cancer. With this background, the present study was conducted to reveal the molecular role of miR-939 in liver cancer. It was found that miR-939 is downregulated in liver cancer. These observations are in agreement with the previous finding of Zhang et al., wherein miR-939 was reported to be downregulated in gastric cancer [13]. In yet another study, miR-32, miR-939, miR-575, miR-765, miR-494, miR-1228, and miR-595 were found to be dysregulated in cirrhotic patients with or without hepatocellular carcinoma [22]. To find out whether the proliferation of liver cancer cells is under the control of miR-939, the cancer cells over-expressing miR-939 were processed for proliferation rate analysis and, interestingly, the results showed the tumor suppressive role of miR-939 in liver cancer cells. In a previous study, miR-939 was shown to induce apoptosis of cancer cells and was responsible for the reduction of their proliferation rate [23]. The results of our study also implicate a similar mechanism behind the tumor-suppressive effect of miR-939 in liver cancer cells. The apoptotic induction of liver cancer cells was mediated through apoptosis-related proteins p53, Bax and Bcl-2. There are reports that Bcl-2 is negatively regulated by p53 [24]. As the liver cancer cells exhibited a higher p53 protein level, it might have resulted in the decline of Bcl-2 protein count. The declining Bcl-2 protein level leads to release of pro-apoptotic Bax protein from binding competition and thus Bax protein increases [25]. Together, these fluctuations are favorable for the induction of apoptotic cell death, which is manifested as the decline of cell proliferation under miR-939 overexpression. As is true for miRs, they regulate the mechanics of eukaryotic cells through the post-transcriptional silencing of specific target genes. A similar mechanism of action was revealed for exertion of the molecular role of miR-939 in liver cancer. CRK-like protein, CRKL, was shown to be the post-transcriptional target of miR-939 in liver cancer. The overexpression of CRKL has a tumor promoting role [26]. The regulatory effect of miR-939 was seen to be exerted through CRKL in human liver cancer. Summing up, the results of this study revealed that downregulation of miR-939 is one of the molecular factors responsible for the development of human liver cancer and also highlighted the therapeutic potential of miR-939 to suppress the growth and proliferation of liver cancer.
In conclusion, the study revealed significant downregulation of miR-939 in human liver cancer. Overexpression of miR-939 in human liver cancer cells inhibits proliferation via induction of apoptosis. The results of this study underlined the possibility of utilizing miR-939 in the management of human liver cancer.