Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is defined as a clinical syndrome with current or prior symptoms or signs caused by a structural or functional cardiac abnormality, corroborated by at least elevated natriuretic peptide levels or objective evidence of cardiogenic pulmonary or systemic congestion, confirmed by diagnostic modalities, according to the recent universal definition [1]. HF affects approximately 64.3 million people globally, making it a significant health crisis. Its prevalence is expected to increase by 25% by 2030 due to advancements in treatments and longer life expectancies. In the United States, the healthcare costs for heart failure are projected to rise significantly, from $30.7 to $69.8 billion by 2030 [2–4]. HF is associated with a poor prognosis, similar to that of advanced cancer, highlighting the risk faced by HF patients and the need for optimal prevention and effective treatment [5].
Atherosclerosis is a chronic condition characterized by the buildup of plaque (the formation of fibrofatty lesions) in the arterial walls, resulting in substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular (CV) disease is the most common comorbid condition in patients with HF across left ventricular ejection fraction. These conditions are associated with increased mortality, linked to a higher risk of both CV and non-CV mortality [6, 7]. Well-established risk factors for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease include age, sex, smoking, hypertension, obesity, family history, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia, and all these are ultimately associated with HF, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral arterial disease, myocardial infarction, and sudden death [8–10].
The Global Burden of Disease also estimates the prevalence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, ischemic heart disease and stroke as 315 million and 86 million in the 2023 report respectively [11]. Ischemic heart disease as a cause of HF is the leading cause of CV mortality across males and females in all regions including the USA and Europe, except for females in the Sub-Saharan Africa region and both males and females in South Asia, where stroke is the leading cause of CV mortality. Ischemic heart disease is the top-ranking global cause of age-standardized disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) at 2,275.9 per 100,000, with intracerebral hemorrhage and ischemic stroke as the next leading contributors to CVD-related age-standardized DALYs [11, 12].
HF risk factors are diverse and likely to vary among world regions. Coronary artery disease and hypertension are the most common causes of HF in western countries, while rheumatic heart disease and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy are considered to be causes in other parts of the region, despite a recent epidemiological shift in pattern [13, 14]. Atherosclerosis and HF are interrelated, with HF risk being associated with the severity of modifiable atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk factors, and the presence of multiple uncontrolled risk factors being linked to markedly increased HF risk [15].
Optimizing Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy for HF involves the use of medications such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNI), β-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), and sodium glucose co transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i). This should be complemented by appropriate use of antihypertensive drugs to maintain target blood pressure levels, along with statins and other lipid-lowering medications, antidiabetic drugs, smoking cessation, weight reduction, and applying appropriate primary and secondary preventive strategies. These comprehensive measures are crucial for effectively addressing the significant burden of HF and atherosclerosis-related morbidity and mortality. There is often overlap in treatment approaches for both atherosclerosis and HF. Managing atherosclerosis and its complications with medications or interventions can help in controlling HF progression and can result in significant enhancements in HF symptoms, underscoring the interconnected relationship between these two conditions [16–18].
This narrative review aims to explore the pathophysiological mechanisms linking HF and atherosclerosis, and understand the relationship between HF and ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular ischemic diseases, peripheral arterial disease, dyslipidemia, and obesity. By compiling and analyzing relevant research findings regarding these interconnected aspects, the review aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the complex relationship between HF and atherosclerosis, ultimately contributing to enhancing our understanding of the complex interplay between these two prevalent cardiovascular diseases and offering insights that may guide future research and clinical practice in managing patients with comorbid HF and atherosclerosis.
Physiopathological mechanisms linking HF and atherosclerosis
Heart failure is a medical condition where the heart has no capacity to deliver sufficient amounts of blood to meet the body’s needs. This condition is caused by deviations in either the structure or the functioning of the heart, which result in an impairment in the amount of blood pumped out or an increase in pressure within the heart, both at rest and during physical activity [19]. On the other hand, atherosclerosis is a condition marked by the buildup of lipids, fibrous components, and calcification in the main arteries of the body. The process begins with the activation of the endothelium, which triggers a series of events resulting in the narrowing of blood vessels and the activation of inflammation-related pathways that subsequently lead to the formation of atheroma plaques. Together, these processes give the opportunity for cardiovascular complications, which persist as the primary cause of mortality on a global scale [20]. Although atherosclerosis itself can reduce blood flow by narrowing the arteries, leading to CVD, the primary cause seems to be atherothrombosis. This occurs when plaques are damaged due to the impact of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines on the fibrous cap. When plaques are harmed and burst, compounds which stimulate blood clotting are exposed to the process of blood coagulation, resulting in the obstruction of blood flow and the subsequent development of CVD [21].
Multiple hypotheses have been proposed in an attempt to establish a connection between heart failure and atherosclerosis. Possible connections between these two entities could be explained by factors such as genetic causes, endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation, based on currently available data [22].
The vascular endothelium, composed of endothelial cells (ECs) that line the luminal surface of all blood vessels, is a heterogeneous monolayer that acts as the initial barrier against molecules, cells, or pathogens that may be circulating in the bloodstream. The vessel wall of major arteries is enveloped by an individual EC layer. This layer, in conjunction with collagen and elastic fibers, constitutes the intima or luminal vessel layer. ECs are in close proximity to the tunica media, which comprises elastic and collagenous tissue as well as vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). In conclusion, the tunica adventitia encircles this layer and consists primarily of a dense connective tissue matrix. Conversely, venules and arterioles have the same three-layered walls as the aforementioned larger vessels, with the exception that the adventitia and media are considerably thinner and less conspicuous. In conclusion, post-capillary venules are devoid of any adventitia or media, comprising solely ECs and a basement membrane [20]. By virtue of its advantageous location between circulating blood and tissues, endothelium functions as both a transducer and sensor of signals through the synthesis of biologically active substances. The endothelium is responsible for perceiving all alterations in the bloodstream and subsequently transmitting these signals to the other segments of the vascular wall [23].
Endocrine and paracrine activities, which regulate vascular structure and function, differentiate the endothelium. ECs in optimal condition generate an assortment of vasoconstrictor and vasodilator substances, with endothelin and nitric oxide (NO) constituting the majority. These substances have a significant vasoregulatory impact. The endothelium exerts a vasodilatory effect via the ongoing synthesis and NO release. The development of endothelial dysfunction is primarily caused by a decrease in the production or an increase in the deactivation of bioactive endothelial NO [24].
Patients with HF, regardless of whether they have reduced or preserved ejection fraction (EF), exhibit impaired vasodilation that is dependent on the endothelium. These modifications can be illustrated in various vascular systems. It is anticipated that variables can disrupt the equilibrium between the production of NO and superoxide in the vascular bed will hinder vasodilation dependent on the endothelium. This phenomenon is not limited to overt coronary artery atherosclerosis. It is also observed in diabetes, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease, among others. This highlights the significance of impaired endothelial vasodilation in HF development. It is important to note that patients with both ischemic and non-ischemic causes can experience impaired vasodilation, even in non-coronary vascular beds [19]. Endothelial dysfunction has the potential to cause skeletal muscle maladaptation in both HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), leading to a decrease in the supply of oxygen during periods of heightened oxygen requirements. This can result in fatigue and a decline in cardiorespiratory fitness [25].
Conclusively, the presence of endothelial dysfunction in patients with HF is primarily caused by elevated production of superoxide radicals and other oxidant species within the blood vessels. Any conditions that lead to “oxidative stress” disrupt the equilibrium between the production of oxygen free radicals (OFR) and their neutralization by internal antioxidant systems. This results in direct NO deactivation, leading to a decline in endothelial function [24].
Conversely, oxidative stress is a widely recognized factor in atherosclerosis development, occurring at the same time as the activation of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways and the production of cytokines/chemokines. Oxidative stress is a significant factor in the development of atherosclerotic lesions because of the excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells have the ability to generate oxidants by means of various enzymes. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidases, a group of enzymes commonly found in mesodermal cells, are responsible for the majority of ROS production in the vascular wall [25].
Excessive cell stress, caused by neurohormonal stimulation and/or a systemic pro-inflammatory state, leads to an imbalance in the redox intracellular equilibrium. This imbalance results in increased production of oxidant species and impairs antioxidant defenses. This leads to adverse impacts on the cellular processes that could potentially contribute to HF development. HF has consistently shown mitochondrial dysfunction, which is crucial in the production of reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species. The mitochondria can excessively release ROS into the cytosol, which can further stimulate ROS production through various mechanisms. These mechanisms include the uncoupling of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) or the conversion of xanthine dehydrogenase to its ROS-producing form, xanthine oxidase [26]. These factors can potentially cause an increase in the heart muscle cell size, cell death initiation, activation or inhibition of the body’s immune response, calcium level disrupted regulation, and fibrous tissue development. The aforementioned variables are acknowledged as crucial components in HF progression [22]. Deviation in ryanodine receptor 2 (RyR2) functioning is also implicated in HF progression. The diastolic calcium leakage from the malfunctioning RyR2 results in the depletion of calcium stores in the sarcoplasmic reticulum and decreases cytoplasmic calcium transients, which hampers the generation of contractile strength. In addition, the disturbance of cellular ion balance caused by ROS can potentially lead to ventricular arrhythmias, either through localized triggered activity or the formation of re-entrant pathways. Oxidative stress can also impact the electrical conduction of the heart by modifying the expression of connexin 43 (Cx43), which is the primary constituent of the gap junctions connecting cardiomyocytes [26]. In addition to calcium metabolism, there are various other pathophysiological mechanisms through which ROS can contribute to HF progression. Multiple signaling pathways implicated in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy can be modulated by ROS. Ventricular cardiomyocyte hypertrophy is induced by angiotensin II, endothelin-1, and phenylephrine, among other inducers, via redox-dependent activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 [27].
Additionally, cardiomyocyte apoptosis can be induced by oxidative stress, which contributes to the progression from cardiac hypertrophy to contractile dysfunction and heart failure. Apoptosis initiation occurs via two distinct pathways: extrinsic, regulated by death receptor superfamily ligands such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and intrinsic. The latter is overseen by B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) family proteins and is contingent upon the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) or outer membrane permeabilization. By means of ROS, both signaling pathways may be modulated [28]. Multiple investigations using transgenic mice have substantiated the correlation between oxidative stress and cardiac fibrosis. Excessive collagen deposition under conditions of oxidative stress modifies the structure of the extracellular myocardial environment, which significantly accelerates HF development [29].
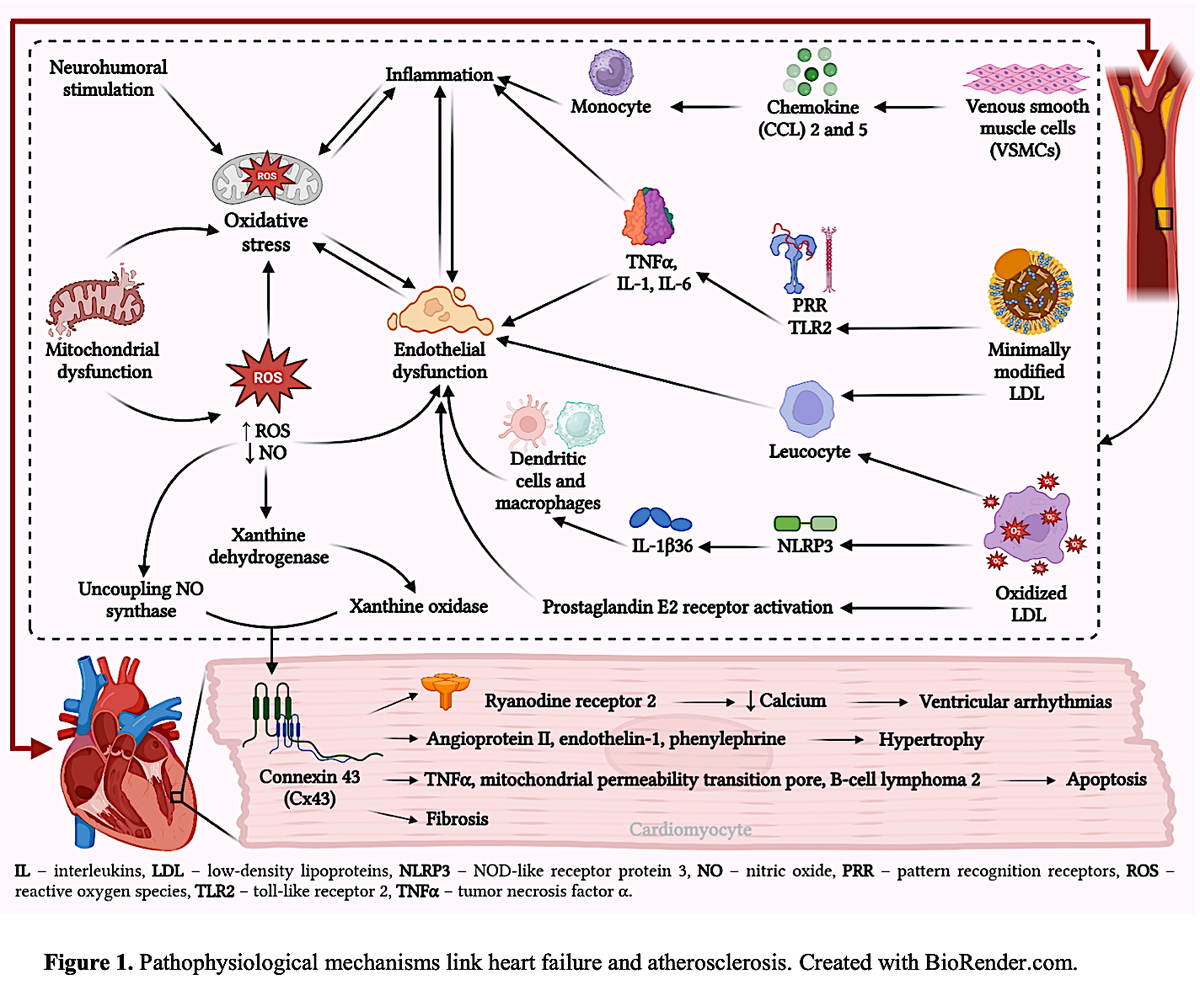
Oxidative stress and inflammation are intricately linked. They interact with each other, both in the early stage after a heart attack and during long-term changes in the heart’s structure. Ischemia-reperfusion injury leads to an increase in ROS production, which subsequently triggers the inflammatory response [30] (Figure 1).
Figure 1
Pathophysiological mechanisms linking heart failure and atherosclerosis. Created with BioRender.com
Nevertheless, it is critical to underscore the involvement of various inflammatory mechanisms in every atherosclerosis stage. Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) amass in the subendothelial region during the initial phases of atherosclerosis, where they undergo modification. VSMCs subjected to modified LDL release chemoattractants, such as chemokine 2 (CCL2) and CCL5, which stimulate monocyte recruitment. Moreover, oxidized LDL (ox-LDL) and minimally modified LDLs (mm-LDLs) can recruit leukocytes, increase endothelial damage, and stimulate a pro-inflammatory response in endothelial cells and macrophages. Moreover, in an NF-κB-dependent manner, mmLDLs can bind to the TLR2 and class 4 PRRs and stimulate secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, and TNF-α. The NLRP3 inflammasomes are activated by CD36-mediated ox-LDL uptake, leading to secretion of the proliferative cytokine IL-1β36. Furthermore, ox-LDL has the ability to form immune complexes with particular antibodies, which stimulate inflammatory reactions in dendritic cells and macrophages [20]. The lipid mediator known as prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is an essential component that plays a role in the pathophysiological processes that are responsible for functions such as inflammation, pain sensation, and pyrexia. Following the participation of the enzymes cyclooxygenase (COX) and PGE2 synthase (PGES), the formation of PGE2 is accomplished by using arachidonic acid as the starting material. Furthermore, prostaglandin receptors, commonly referred to as EP receptors, have been correlated with the early stages of atherosclerosis as well as the inflammatory process, both of which are responsible for plaque erosion and rupture [31].
Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)], a low-density lipoprotein-like particle bound to apolipoprotein(a), is recognized for its pro-inflammatory and pro-atherosclerotic properties, which may be partly attributed to the oxidized phospholipids (OxPLs) it carries. These features are linked to the promotion of vulnerable plaque phenotypes, offering a potential mechanistic explanation for the association between elevated Lp(a) levels and clinical atherothrombotic events independent of baseline disease severity, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and overall plaque burden [32, 33]. Although the Lp(a) molecule shares a high degree of structural homology (75–99%) with plasminogen, it lacks protease activity. This similarity has led to speculation about its potential pro-thrombotic and antifibrinolytic effects [34]. However, these roles remain unproven in vivo and have yet to be conclusively demonstrated in clinical settings [35, 36]. Elevated Lp(a) levels have also been shown to induce the expression of genes involved in inflammation and calcification, particularly under the influence of OxPLs. This effect is evident in both vascular and valvular cells, with a notable impact on the aortic valve. It is thought that Lp(a), through its apolipoprotein(a) [apo(a)] component, facilitates the delivery of OxPLs into the aortic valve. Additionally, enzymes such as lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) and autotaxin, both associated with Lp(a), are believed to contribute to the pathogenesis and progression of aortic valve stenosis. This condition is strongly linked to an increased risk of progression to heart failure [35, 37, 38].
HF is distinguished by a widespread state of inflammation, as indicated by the elevated levels of inflammatory substances circulating in the body, such as TNF-α and IL-6. TNF-α overexpression causes harm to mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), hinders the function of antioxidant factors, and disrupts the mitochondrial complex III activity, resulting in elevated ROS production. Ischemic injury and pressure overload in the heart trigger the activation of both innate and adaptive immunity. The subsequent cardiac inflammatory response offers immediate adaptation to stress during the acute phase. The inflammatory response can be viewed as the myocardial tissue’s effort to counteract an acute stressor with the aim of restoring homeostasis. Nevertheless, if inflammation continues beyond the initial phase of repair following an injury, it becomes maladaptive, resulting in additional damage to the heart muscle and progression towards HF. Indeed, inflammation, in conjunction with the sympathetic nervous system and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, is regarded as having a pivotal role in HF pathophysiology [39].
Multiple factors interact to induce oxidative stress in HF, thereby stimulating a subclinical inflammatory response within the cardiac tissue. Subsequently, tissue damage ensues from inflammation, a process that further intensifies oxidative stress. Furthermore, various inflammatory mechanisms are involved in every atherosclerosis stage. Considering these factors and the aforementioned facts, it is logical for one to conclude that the primary connection between atherosclerosis and heart failure lies within the realm of chronic inflammation and oxidative stress. By focusing on either oxidative stress or inflammation, we may be able to disrupt the harmful cycle that contributes to the progression of both atherosclerosis and HF.
Heart failure and ischemic heart disease
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) frequently accompanies HF, often stemming from coronary artery disease (CAD), a complex condition influenced by various factors, including genetics and the environment. CAD can manifest with periods of stability but also sudden instability, typically triggered by plaque rupture or erosion [40]. In some cases, CAD precedes HF as the primary ailment, while in others, it develops within an existing HF condition. Hence, patients with HF should undergo regular screening for CAD [41]. Prognosis is often poorer in HF cases linked to IHD compared to other causes. Vigilant monitoring, especially after myocardial infarction, aids in early detection of heart failure. Heightened suspicion is crucial in individuals with new-onset HF symptoms (such as breathlessness, fatigue, or ankle swelling) and a history of CAD, facilitating early intervention [42].
Initially, the link between CAD and HF was believed to hinge mainly on the presence of significant myocardial infarctions (MI), which resulted in extensive ventricular scarring and remodeling, precursors to clinically apparent HF. Nevertheless, in recent years, there has been a decrease in the severity of MI and the occurrence of extensive infarct territories [43].
The role of IHD in the development of HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is well established. However, the significance of IHD in HF with mid-range (HFmrEF) and preserved EF (HFpEF) has not been extensively studied [44]. Existing data are derived from small cohorts where patients with HFrEF were not highly susceptible to MI. Nevertheless, findings from certain randomized controlled trials have indicated a linear increase in MI risk with EF decreasing below 45% [45]. This suggests the importance of IHD presence in assessing the risk of new IHD events even in HFpEF and HFmrEF, a factor that may have been underestimated previously [46]. Despite changes in MI epidemiology, the incidence of HF following MI has not declined proportionally, indicating the involvement of other mechanisms in post-MI HF development [47]. Clinical trials have identified IHD as the primary cause of HF in approximately 50–70% of patients, with 95% showing some evidence of IHD, although only 50% have a history of MI [44]. Hypertension is a very important risk factor for MI. Therefore, it is sometimes difficult to separate the etiological factors, as the results may indicate that HF was caused by MI, while the epidemiologist observes that hypertension was an important predisposing factor for both infarction and HF. Also, hypertensive patients are perhaps more likely to develop HF after an MI, as chronic hypertension may lead to hypertrophy, fibrosis and dysfunction, reducing the ventricular reserve in the post-MI setting [48].
Pathophysiology and progression of heart failure caused by ischemic heart disease
During exercise, ischemia can lead to dyspnea instead of angina, attributed to increased left ventricular (LV) filling pressures during ischemic episodes. A considerable number of patients, even those with preserved LV systolic function at rest, experience both exertional angina and breathlessness simultaneously [49].
Silent myocardial ischemia refers to the detection of ischemia without the presence of angina or its equivalents. In patients with HF, ischemia can occur without noticeable symptoms, possibly due to conditions such as diabetic neuropathy. Additionally, previous MI may lead to myocardial denervation, diminishing sensory inputs and potentially masking ischemic symptoms [50].
Myocardial ischemia and infarction can precipitate arrhythmias, with atrial fibrillation being the most prevalent and concerning, affecting roughly 20% of patients with HF. Ventricular arrhythmias, on the other hand, are linked to a grim prognosis in HF [51].
Persistent hypoperfusion or recurrent stunning episodes can lead to the phenomenon known as myocardial “hibernation”. Approximately 50% of patients with IHD may exhibit a significant amount of hibernating myocardium. Ongoing research endeavors are crucial to ascertain whether revascularization is necessary, in addition to medical therapy, for managing patients with HF and hibernating myocardium.
Myocardial infarction is a key factor in the progression of ventricular dysfunction.
In the acute phase, sudden ventricle dysfunction can precipitate rapid deterioration in patients already experiencing ventricular impairment, although in many instances, this progression occurs swiftly without a confirmed or reported diagnosis. Contributing factors include myocardial necrosis, myocardial stunning, and mechanical complications such as papillary muscle rupture, septal defects, and free wall rupture. Additionally, the inflammatory response plays a role in HF development. Reperfusion interventions are associated with increased salvage of myocardial cells, potentially contributing to the rise in the HFpEF incidence. Alternatively, the observed increase in HF incidence after MI might be explained by contemporary trends in MI diagnosis, which now rely on troponin levels, enabling the detection of less severe MIs associated with a lower risk of developing HF [52].
In the chronic phase, MI typically induces LV remodeling, characterized by scar tissue formation, ventricular wall thinning, affected area stretching, and adaptation of the surrounding non-infarcted myocardium, which largely relies on the unaffected tissue adaptive capacity. However, preexisting conditions such as diabetes or hypertrophy may impede this compensatory ability, leading to reduced functional compensation. Additionally, chronic hemodynamic effects, such as resultant mitral regurgitation, may arise. When assessing coronary artery disease, it is crucial to evaluate the extent of ischemia, potentially through coronary angiography and revascularization. In cases where revascularization is not feasible, antianginal drug therapy is a suitable alternative [52].
Patients with HF due to IHD may also benefit from treatments designed to relieve ischemia and prevent coronary occlusion and from revascularization as well.
The pharmacotherapy regimen for patients with HFrEF should encompass several medications: β-blockers, ACEi, MRAs, SGLT2i, and diuretics. If there is intolerance to ACEi, ARBs can be considered [51]. If there is an inadequate response to ACEi or ARBs, they may be substituted with ARNI. Short-acting nitrates are suitable for relieving angina attacks. In symptomatic patients with sinus rhythm and an LV EF below 35% and a systolic frequency above 70/min, ivabradine can be included. Antianginal treatment such as trimetazidine, nitrates, or calcium channel blockers may be administered for symptom relief, although their impact on mortality has not been definitively established [53].
According to the recommendations of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) from 2019, the following procedure is recommended for myocardial revascularization: 1) administer a β-blocker; 2) administer a β-blocker and long-acting nitrates, or a β-blocker and ivabradine; 3) antianginal drugs of second choice [54].
If it is HFpEF, it is recommended to administer: a β-blocker, long-acting nitrate calcium blockers, ivabradine, ranolazine, trimetazidine, and nicorandil. Although they can bring relief from anginal difficulties, their effect on mortality and morbidity has not been proven. In patients with a moderate degree of HFrEF, sinus rhythm, a high risk of an ischemic event, and a low risk of bleeding, administration of small doses of rivaroxaban (2 × 2.5 mg) can be considered. The COMPASS trial demonstrated that combining rivaroxaban with aspirin led to a reduction in adverse cardiovascular events but an increase in major bleeding events compared to aspirin alone [55]. In patients with HFmrEF, sinus rhythm, and a high risk of ischemic events but low bleeding risk, the use of small doses of rivaroxaban (2 × 2.5 mg) may be considered [56].
Revascularization (percutaneous coronary intervention [PCI] or coronary artery bypass grafting [CABG]) therapy should be considered in patients with angina, indicated in patients with stenosis of the left coronary artery (LCA) trunk or equivalent (stenosis of proximal left anterior descending artery [LAD] and/or left circumflex [LCx] branch), or 2–3-vessel disease in proximal segments (including the LAD) [53]. In all cases, it is necessary to evaluate the presence of viable myocardium (presence of chest angina, dobutamine echocardiography or SPECT). If less than 10% viable tissue is found, revascularization is generally not recommended [57]. According to some reports, PCI may yield a 20–41% reduction in post-MI HF [58].
Despite the recognized contribution of CAD to HF development, the efficacy of coronary revascularization in mitigating HF-related morbidity and mortality remains a subject of debate. Some studies suggest that patients whose HF stems from IHD typically exhibit a poorer prognosis. However, findings from the Revascularization for Ischemic Ventricular Dysfunction (REVIVED) trial indicate that myocardial revascularization in individuals with ischemic left ventricular dysfunction does not significantly impact mortality or hospitalization rates. This suggests that factors beyond ischemia may wield greater influence over HF prognosis. IHD often coexists with other comorbidities such as anemia or diabetes, which could play pivotal roles in determining the prognosis of HF patients [58].
The STICH (Surgical Treatment for Ischemic Heart Failure) study demonstrated that combining appropriate guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) with CABG (a durable form of revascularization) led to a 16% reduction in mortality compared to GDMT alone. Revascularization was associated with a median survival improvement of 1.4 years. Similar benefits were observed in patients undergoing PCI. Hence, there is a compelling case for directing HF patients toward CAD testing and intervention whenever feasible [59]. Patients with ischemic HF often have a longer duration of HF since diagnosis, allowing them more time to address risk factors such as lifestyle choices or smoking, which could influence whether IHD exacerbates the prognosis of HF.
HF and cerebrovascular ischemic diseases
Atherosclerosis is a multifaceted condition involving various biochemical, immunological, and inflammatory mechanisms that damage the blood vessel walls, leading to the buildup of cholesterol crystals and inflammatory cells. In the context of cerebral arteries, this process triggers gradual compensatory and adaptive changes in vascular structure and disrupts the neurovascular unit, potentially resulting in cognitive decline. Several studies have connected the presence of cerebral atherosclerosis with cognitive impairment in later stages [60]. Among the elderly, intracranial atherosclerotic disease has been linked to higher rates of mild cognitive impairment and dementia [61], while cerebral atherosclerosis and arteriolosclerosis have been associated with poorer cognitive performance across various domains and an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in very old individuals [62]. This correlation between atherosclerosis and cognitive decline also extends to extracranial vessels, with carotid and femoral atherosclerosis being linked to vascular dementia and AD in older populations [63]. Common risk factors for both atherosclerosis and dementia include hypertension, diabetes, cholesterol levels, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and HF [61].
Atherosclerosis plays a crucial role in the development of conditions leading to HF. Furthermore, there are shared pathogenic risk factors identified in the development of both coronary microvascular dysfunction and cerebral small vessel disease. Even without a prior myocardial infarction or significant macrovascular coronary disease, atherosclerosis, inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and microvascular remodeling are believed to be pivotal elements in HF pathophysiology, especially in cases involving HFpEF [64].
There are some mechanisms that explain the relationship between HF and cerebrovascular atherosclerosis (CA). First, HF and CA share common risk factors (e.g., age, ApoE polymorphisms, homocysteine, smoking, obesity, chronic inflammation). In addition, both HF and CA are strongly associated with several underlying conditions – hypertension, diabetes mellitus and hypercholesterolemia [60, 65, 66].
Biomarkers play a crucial role in identifying the presence of HF, CA, and associated cerebrovascular complications. Several biomarkers reflect the underlying pathophysiological processes common to both conditions: natriuretic peptides (BNP, NT-proBNP) are primarily markers of cardiac wall stress and are elevated in HF due to pressure overload and volume expansion. Elevated natriuretic peptide levels have also been associated with increased risk of ischemic stroke and cognitive decline, as they indicate systemic vascular dysfunction and cerebral hypoperfusion. Troponins (cTnI, cTnT) are markers of myocardial injury and are commonly elevated in HF due to ongoing cardiomyocyte damage. Increased troponin levels have also been linked to a higher risk of stroke, reflecting the systemic impact of cardiovascular disease on cerebral circulation. Inflammatory markers (CRP, IL-6, TNF-α) indicate systemic inflammation, which is involved in both HF and atherosclerosis. CRP is predictive for stroke risk and correlates with plaque instability in cerebral atherosclerosis. IL-6 and TNF-α are elevated in both HF and atherosclerosis. In HF, they contribute to adverse cardiac remodeling, while in atherosclerosis, they promote plaque formation and rupture, increasing the risk of cerebral ischemia. Vascular and endothelial dysfunction markers: Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) – an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis – is elevated in HF and atherosclerosis, reflecting endothelial dysfunction. Increased ADMA levels are associated with impaired cerebral perfusion and a higher risk of stroke. Von Willebrand factor (vWF) is a marker of endothelial damage and platelet activation; vWF is often elevated in both HF and atherosclerosis, indicating a pro-thrombotic state that raises the risk of ischemic stroke. Oxidative stress markers: myeloperoxidase (MPO) and malondialdehyde (MDA). MPO is released during inflammation and contributes to oxidative stress, which accelerates atherosclerosis and worsens endothelial dysfunction. Elevated MPO levels are seen in both HF and cerebral atherosclerosis, linking these conditions through vascular damage and increased stroke risk. A marker of lipid peroxidation, MDA is elevated in HF and is linked to the oxidative damage seen in both coronary and cerebral atherosclerosis [67, 68].
D-dimer and fibrinogen are elevated in conditions of increased thrombosis risk. In HF, when blood flow is compromised, elevated D-dimer levels indicate a higher risk of thromboembolism. This is especially relevant in patients with cerebral atherosclerosis, where increased stroke risk due to embolic events is common. Elevated fibrinogen levels are seen in HF and atherosclerosis, reflecting an ongoing pro-coagulant state that raises the risk of cerebral ischemic events [69].
Neurofilament light chain (NfL) is a marker of neuroaxonal damage and is elevated in conditions of cerebral hypoperfusion, such as in HF and cerebral atherosclerosis. Higher levels are associated with cognitive decline and neurodegeneration in HF patients. S100B is a marker of blood-brain barrier disruption; S100B is elevated in conditions involving cerebrovascular injury, such as ischemic stroke and chronic cerebral hypoperfusion [70].
HF and CA are pathophysiologically linked through systemic inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, chronic hypoperfusion, and a pro-thrombotic state. Biomarkers such as BNP, NT-proBNP, troponins, CRP, IL-6, ADMA, and MPO provide critical insight into these processes and help in monitoring the progression of disease, risk of stroke, and cognitive decline in patients with HF and cerebral atherosclerosis. These biomarkers serve not only as diagnostic tools, but also as predictors of adverse outcomes in these interrelated conditions. Moreover, new biomarkers (e.g., galectin-3, interleukin-6, miR-182, endotelin-1, transforming growth factor-β1), which play an important role in pathogenesis of both HF and CA, are being identified and studied [71–74].
The relationship between HF and CA remains largely unclear, but it is known that in HF and CA, all Virchow’s triad components comprising endothelial dysfunction, hypercoagulability, and impaired blood flow are negatively affected. Thus, we can explain how HF contributes to CA development, and vice versa, focusing mainly on reduced cerebral blood flow and neurovascular unit dysfunction (Figure 2) [75].
Figure 2
Neurovascular unit dysfunction in heart failure and atherosclerosis. Created with BioRender.com
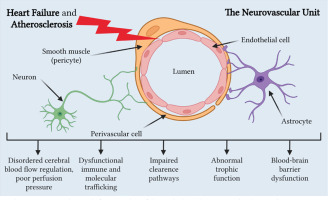
HF is frequently underdiagnosed among older individuals because its symptoms can be confused or obscured by other health issues they may have. The concept of “cardiogenic dementia”, coined in 1977 [76], underscores how HF contributes to cognitive decline, with the severity of cognitive impairment closely tied to the extent of HF [77]. Despite heart disease and cerebral atrophy sharing similar genetic backgrounds and risk factors, such as ApoE polymorphisms, there is growing recognition of their connection through their mutual reliance on sufficient blood supply. Inadequate blood circulation can impact various organs, potentially leading to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Reduced cardiac output in HF is linked to atypical brain aging and cognitive decline [66, 78].
Data from the Framingham Heart Study suggest that lower cardiac index and left ventricular ejection fraction are correlated with cognitive impairment [79], with lower cardiac index values also being associated with diminished brain volumes. Other studies have shown that left ventricular ejection fraction is associated with cognitive decline in HF patients, particularly affecting memory, reasoning, and sequencing abilities. Increasing evidence from neuroimaging studies indicates a connection between HF and structural brain anomalies, further emphasizing the interplay between heart and brain dysfunction. Brain atrophy or demyelination, both total and regional, are frequently observed in HF patients [80].
Cardiac complications are a significant factor in the morbidity experienced after an ischemic stroke. A condition known as stroke-heart syndrome affects about 10–20% of patients following an ischemic stroke and can present as various cardiovascular issues such as electrocardiogram abnormalities, arrhythmias, myocardial damage, acute coronary syndrome, heart failure, Takotsubo (stress) cardiomyopathy, or sudden cardiac death. Stroke-heart syndrome is associated with a 2–3 times higher short-term mortality rate and a 1.5–2 times higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events within a year (Figure 2). Both clinical studies and animal models have shed light on the pathophysiological mechanisms behind this syndrome. These mechanisms include the release of local and systemic mediators from the brain, leading to autonomic dysfunction and an inflammatory response. This cascade ultimately results in coronary microvascular dysfunction, injury to heart muscle cells, malfunction of immune cells called macrophages, and ultimately heart failure [81].
Several studies have revealed the high prevalence of asymptomatic carotid artery disease in the general population, with the number of plaques and the severity of narrowing increasing with age. Increased thickness of the innermost layers of the carotid arteries (intima-media thickness) has been linked to risk factors for coronary heart disease and cerebrovascular diseases, and it has also been associated with asymptomatic reduced blood flow to the heart muscle in older individuals. In middle-aged people, structural changes in the carotid arteries have been tied to hypertension, high cholesterol levels, and smoking. Although the association between risk factors and carotid artery disease is less pronounced in older individuals, studies have shown that high-risk elderly patients with hypertension often have thicker carotid arteries and more plaque build-up in the common carotid arteries [63, 82, 83].
An increased stroke risk in HF patients has been described in several studies [84–86]. Pathophysiologically, a predisposition to thromboembolism is caused by abnormal blood flow, abnormal vessel/chamber lining, and abnormal blood particles, also referred to as Virchow’s triad [87]. Abnormal blood flow is evident in patients with HF because of LV systolic dysfunction associated with LV dilatation and abnormal (slowed) blood flow [88]. Given the fact that HF patients with HFpEF also have an increased stroke risk [65, 89], such patients also exhibit flow abnormalities – apart from vessel wall changes (e.g., endothelial dysfunction) [90, 91] and abnormal blood constituents (e.g., platelet function) [92].
Peripheral arterial disease and heart failure
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and HF are two distinct cardiovascular conditions, yet they share a complex interplay that significantly impacts patients’ health. PAD is characterized by atherosclerotic plaque buildup in the arteries supplying the extremities. However, numerous studies have highlighted a strong association between PAD and HF, indicating that they often coexist and may share common etiological factors [93].
One of the key shared risk factors for PAD and HF is atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a systemic inflammatory condition involving the accumulation of plaques in arterial walls. These plaques can form in both the peripheral arteries and the coronary arteries, contributing to the development of PAD and HF, respectively. Thus, patients with atherosclerosis are at an increased risk of developing both conditions [94].
Moreover, hypertension and diabetes mellitus (DM), recognized risk factors for atherosclerosis, play pivotal roles in the development of both PAD and HF. Hypertension contributes to the increased workload on the heart and arterial walls, promoting the progression of atherosclerosis. DM, on the other hand, induces metabolic changes that accelerate atherosclerotic plaque formation. The convergence of these risk factors emphasizes the intricate web connecting PAD and HF [94].
Beyond shared risk factors, PAD and HF exhibit overlapping pathophysiological mechanisms. Chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction are central players in both conditions. In PAD, inflammation and oxidative stress contribute to the formation and progression of atherosclerotic plaques, narrowing the peripheral arteries and reducing blood flow to the extremities. Similarly, in HF, these processes can lead to myocardial damage and impaired cardiac function [16, 17, 95, 96].
The pathophysiological mechanisms linking PAD and HF are as follows:
Atherosclerosis. Both PAD and HF are primarily caused by atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the build-up of plaque in the arteries. Atherosclerosis reduces blood flow to various organs, including the heart and peripheral limbs.
Endothelial dysfunction. Endothelial dysfunction is a common feature in both PAD and HF. It leads to impaired vasodilation, inflammation, and thrombosis, contributing to the progression of both diseases.
Ischemia-reperfusion injury. In PAD, ischemia-reperfusion injury occurs when blood flow is restored to ischemic tissues, leading to oxidative stress, inflammation, and tissue damage. This process can contribute to systemic inflammation and endothelial dysfunction, worsening heart failure.
Microvascular dysfunction. PAD is associated with microvascular dysfunction, leading to impaired perfusion and oxygen delivery to tissues. In HF, microvascular dysfunction contributes to impaired cardiac function and exacerbates symptoms.
Neurohormonal activation. Both PAD and HF involve neurohormonal activation, including activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and sympathetic nervous system. These pathways contribute to vasoconstriction, sodium retention, and fluid retention, exacerbating both diseases.
Inflammatory markers. Biomarkers of inflammation, such as CRP, IL-6, and tumor necrosis TNF-α, are elevated in both PAD and HF and are associated with disease severity and prognosis.
Endothelial markers. Biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction, such as von Willebrand factor (vWF), endothelin-1, and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), are elevated in both PAD and HF and are associated with vascular damage and adverse outcomes.
Oxidative stress markers. Biomarkers of oxidative stress, such as malondialdehyde (MDA) and ox-LDL, are elevated in both PAD and HF and contribute to endothelial dysfunction and vascular damage.
The bidirectional nature of the PAD-HF relationship further complicates the clinical picture. The impaired blood flow associated with PAD can exacerbate HF by reducing oxygen supply to the heart muscle, worsening its pump function. Conversely, the compromised cardiac output in HF can contribute to the progression of PAD by limiting blood flow to the extremities. This vicious cycle underscores the need for a comprehensive approach in managing patients with both conditions [96].
While numerous studies have explored the link between PAD and HF, providing an exhaustive list is beyond the scope of this response. However, there are several key findings from notable studies that shed light on the intricate relationship between these two cardiovascular conditions (Table I) [97–101].
Table I
Relationships between PAD and HF
| 1. | The ARIC Study (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities) | The ARIC study, a large-scale prospective cohort study, has played a pivotal role in understanding the connection between atherosclerosis-related diseases, including PAD and HF. Research from ARIC has consistently demonstrated that individuals with PAD are at a significantly higher risk of developing HF over time. The study has also underscored the role of shared risk factors, such as hypertension and diabetes, in driving the association between these conditions [97]. |
| 2. | The Cardiovascular Health Study | This longitudinal study focused on older adults has provided valuable insights into the relationship between PAD and HF in the elderly population. Findings from the Cardiovascular Health Study emphasize that PAD is an independent predictor of incident HF and contributes to an increased risk of cardiovascular events in this demographic. The study has also highlighted the importance of considering PAD in risk stratification for HF in older adults [98]. |
| 3. | The CHARISMA Trial (Clopidogrel for High Atherothrombotic Risk and Ischemic Stabilization, Management, and Avoidance) | The CHARISMA trial, a randomized controlled trial evaluating antiplatelet therapy in high-risk patients, has offered insights into the interplay between PAD and HF. Subgroup analyses from CHARISMA have demonstrated that individuals with PAD are more likely to experience adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including HF events. This trial underscores the need for targeted interventions to reduce cardiovascular risk in patients with PAD, potentially impacting outcomes in HF [99]. |
| 4. | The CHARM (Candesartan in Heart Failure Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and Morbidity) Program | The CHARM program, comprising several trials, has extensively studied the use of candesartan in patients with HF. Subanalyses from these trials have explored the prevalence of PAD in the HF population and its impact on outcomes. The findings suggest that the presence of PAD in patients with HF is associated with a higher risk of adverse cardiovascular events and mortality, emphasizing the importance of recognizing and addressing PAD in the context of HF management [100]. |
| 5. | The EUROPA Trial (European Trial on Reduction of Cardiac Events with Perindopril in Stable Coronary Artery Disease) | While not specifically focused on PAD, the EUROPA trial has provided insights into the role of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in reducing cardiovascular events. Considering the shared pathophysiological mechanisms between PAD and HF, studies such as EUROPA contribute to our understanding of how interventions targeting common pathways might influence both conditions [101]. |
These studies collectively contribute to the growing body of evidence supporting the association between PAD and HF. They emphasize the need for comprehensive cardiovascular risk assessment, highlighting the bidirectional nature of the relationship and the potential impact on patient outcomes. Ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of the mechanisms underlying this connection and informs the development of targeted interventions for individuals facing the dual challenge of PAD and HF. The coexistence of PAD and HF has significant implications for patient outcomes. Studies have consistently shown that individuals with both conditions face higher morbidity and mortality rates compared to those with either condition alone. The shared risk factors and intertwined pathophysiological mechanisms contribute to a synergistic effect, amplifying the cardiovascular burden on these patients.
The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2022 study reported a comparison of age-standardized DALYs (disability-adjusted life years) per 100,000 population due to lower extremity PAD across global regions, stratified by sex. Eastern Europe demonstrates one of the highest burdens of PAD-related disability globally. Both men and women in Eastern Europe show elevated DALY rates compared to other regions. This reflects a disproportionately high burden of PAD in the region, likely due to high prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors, late diagnosis or underdiagnosis, limited access to early preventive care, and socioeconomic and healthcare disparities. The high PAD burden in Eastern Europe underlines a critical need for early detection and prevention strategies. Regional health systems should prioritize targeted interventions to reduce progression, morbidity, and complications such as limb amputation [11].
Effective management of PAD and HF necessitates a holistic approach that addresses their interconnected nature. Lifestyle modifications, including smoking cessation, regular exercise, and dietary changes, play a crucial role in mitigating shared risk factors. Pharmacological interventions targeting hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia are essential components of the treatment strategy. Additionally, revascularization procedures for PAD, such as angioplasty or bypass surgery, may improve blood flow to the extremities and alleviate symptoms, indirectly benefiting HF outcomes [102].
In conclusion, the link between PAD and HF extends beyond a mere coincidence. Shared risk factors and common pathophysiological mechanisms underscore the need for a comprehensive understanding of their interconnected nature. Managing these conditions requires a multidisciplinary approach that addresses both the peripheral and cardiac aspects of the cardiovascular system. By recognizing and addressing the interplay between PAD and HF, healthcare providers can enhance patient care and improve long-term outcomes for individuals facing this challenging cardiovascular combination.
Obesity and heart failure
The terms overweight and obesity are defined as excessive or abnormal accumulation of adipose tissue. Historically, these conditions were predominantly observed in high-income countries, but their prevalence has risen significantly in low- and middle-income countries, particularly in urban areas [103]. Obesity is especially prevalent in patients with heart failure (HF), notably those with HFpEF [104–106]. Compared to individuals with a normal BMI, those with obesity have a twofold higher risk of developing HF [106].
In the United States the prevalence of HF risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and obesity is notably high, with over 6 million adults affected by HF [107]. Similarly, a high incidence of HF risk factors and comorbidities, including obesity, has been reported in regions such as the Middle East, North Africa, and Turkey, particularly among patients with HFpEF [108].
Abdominal obesity is defined by an increased waist circumference [109]. Obesity exerts direct detrimental effects on the myocardium and indirectly influences HF through its contribution to the development of metabolic risk factors. Several mechanisms link obesity to an elevated HF risk, including hemodynamic changes, neurohormonal activation, endocrine and paracrine effects of adipose tissue, ectopic fat deposition, and lipotoxicity. These processes contribute to concentric left ventricular remodeling and heightened HF risk. Intentional weight loss in patients with HF has been associated with improvements in metabolic risk factors, myocardial function, and quality of life in a dose-dependent manner, while bariatric surgery has also been linked to a reduced risk of HF and improved cardiovascular outcomes [110].
Excessive fat accumulation in the myocardium results in both functional and structural alterations. Adipose tissue secretes hormones and cytokines that promote a proinflammatory and prothrombotic state, thereby contributing to the development and progression of heart failure [111].
In direct cardiac lipotoxicity, lipid accumulation within the heart contributes to cardiac dysfunction that cannot be attributed to other HF risk factors [112].
Obesity contributes to metabolic and inflammatory disorders, which may result in HFpEF [113]. Among younger individuals, the incidence of HF is rising, likely due to increasing rates of obesity and declining cardiorespiratory fitness [114]. Patients hospitalized with heart failure who have either non-obesity or severe obesity exhibit higher mortality rates compared to those with mild to moderate obesity [115]. Clinical and epidemiological studies have revealed a differential risk for HFpEF among postmenopausal women based on the presence of abdominal obesity. Specifically, postmenopausal women with abdominal obesity have a significantly elevated risk of developing HFpEF compared to those without [109].
The obesity paradox refers to the phenomenon in which obese patients with existing heart failure exhibit greater short-term and mid-term life expectancy compared to those with normal weight or underweight. This paradox can be partly attributed to factors such as an excess energy reserve, younger age, better tolerance of heart failure therapies, and improved nutritional status. However, body composition may not be accurately reflected by BMI, especially in HF patients with excess fluid retention. In these individuals, improvements in cardiorespiratory fitness may be more critical than changes in body weight and could serve as a primary therapeutic goal [104].
In patients with HF and left ventricular ejection fraction < 50%, the prescription frequency and dosages of HF medications are more frequently increased in individuals with obesity compared to those without obesity [116]. The management of obesity in HF patients, particularly those with morbid obesity, may yield numerous beneficial effects [117]. Weight reduction through bariatric surgery and caloric restriction represents a promising therapeutic approach for HFpEF related to obesity [118]. A high BMI increases both the incidence and mortality risk of HF [119]. In obese patients with HFpEF, clinically significant weight loss achieved through a 15-week program has been associated with substantial improvements in quality of life and exercise capacity [120]. In cases of HF linked to obesity, weight loss has proven effective in enhancing cardiac function and improving energy metabolism [121]. Preserving metabolic health and maintaining a lean body mass may prevent the progression of HF [122]. Reducing visceral fat through caloric restriction and/or bariatric surgery may offer benefits for obese patients with HFpEF [123]. For patients with heart failure, body mass index > 30 kg/m2 is an independent risk factor for readmission [124]. Younger patients with obesity and diabetes, as well as those with HFpEF, experience the most considerable declines in quality of life [125].
Given the strong association between obesity and HF, effectively managing obesity in HF patients is essential for improving clinical outcomes and quality of life.
Dyslipidemia and heart failure
HF and dyslipidemia are interconnected conditions, with each influencing the development and progression of the other. It is a complex syndrome that can result from various underlying causes and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality [17, 126, 127].
Dyslipidemia plays a significant role in the development and progression of HF. This impact can be understood through various mechanisms, including atherosclerosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, and myocardial lipotoxicity. Dyslipidemia is the main factor promoting atherosclerosis development [128]. Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, along with low HDL cholesterol (or dysfunctional HDL [129]), contribute to plaque formation and progression [130]. Atherosclerosis can lead to CAD, which is a primary cause of ischemic heart disease and subsequent HF. Plaque rupture and thrombosis can result in myocardial infarction, reducing cardiac output and leading to HF [131]. Dyslipidemia is associated with increased systemic inflammation [132]. Elevated LDL cholesterol can undergo oxidative modification to form oxLDL, which is highly atherogenic and pro-inflammatory [133]. OxLDL triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and recruits inflammatory cells to the vascular endothelium [134]. Dyslipidemia contributes to oxidative stress by generating reactive oxygen species. Oxidative stress damages endothelial cells, promotes vascular dysfunction, and exacerbates myocardial injury [135]. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress contribute to endothelial dysfunction, myocardial remodeling, and progressive HF [136]. Elevated levels of circulating free fatty acids (FFAs) and triglycerides in dyslipidemia can lead to their accumulation in cardiac myocytes. Excessive lipid accumulation within the myocardium is termed myocardial lipotoxicity. FFAs and triglycerides can be metabolized to toxic lipid intermediates, such as ceramides and diacylglycerols, which can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) and impair cardiac myocyte function [137]. Myocardial lipotoxicity contributes to impaired contractility, myocardial stiffness, and overall cardiac dysfunction, leading to HF. In heart failure, there is a shift in myocardial energy metabolism from fatty acid oxidation to glucose utilization. However, dyslipidemia can interfere with this adaptive shift, leading to inefficient energy production. Dyslipidemia is often associated with insulin resistance, which can further impair glucose uptake and metabolism in the myocardium, exacerbating heart failure. Altered lipid metabolism and insulin resistance contribute to the energy deficit in failing hearts, worsening cardiac function. Insulin resistance impairs the ability of insulin to suppress lipolysis (the breakdown of fat) in adipose tissue. This leads to elevated levels of circulating FFAs. High levels of FFAs interfere with insulin signaling in muscle and liver tissues. This impairs glucose uptake by muscles and enhances gluconeogenesis in the liver, contributing to hyperglycemia and insulin resistance [138]. Excess FFAs are taken up by muscle cells, leading to the accumulation of lipid intermediates (e.g., diacylglycerol and ceramides) within the cells. These lipid intermediates activate serine/threonine kinases that phosphorylate and inhibit insulin receptor substrates, impairing insulin signaling and glucose uptake [139]. The lipid abnormalities associated with insulin resistance, particularly elevated triglycerides and small, dense LDL particles, are highly atherogenic and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. The pro-inflammatory state associated with insulin resistance further exacerbates endothelial dysfunction and promotes atherosclerosis. HF activates the sympathetic nervous system and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Increased catecholamines and angiotensin II levels stimulate lipolysis, leading to elevated FFAs and triglycerides. Aldosterone may also affect lipid synthesis and transport. This dysregulation of lipid metabolism contributes to dyslipidemia characterized by increased triglycerides and altered lipoprotein profiles [140]. Catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine) are released from the adrenal glands in response to stress or sympathetic nervous system activation. Catecholamines bind to β-adrenergic receptors on adipocytes (fat cells), activating adenylate cyclase [141]. Adenylate cyclase converts ATP to cyclic AMP (cAMP), which activates hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) and lipolysis. There is increased breakdown of triglycerides stored in adipocytes into FFAs and glycerol, which are released into the circulation [140]. Angiotensin II is produced from angiotensin I through the action of ACE, primarily in the kidneys and lungs. Angiotensin II binds to AT1 receptors on adipocytes, stimulating cAMP production through phospholipase C activation. Increased cAMP levels activate HSL, enhancing lipolysis and release of FFAs. Similar to catecholamines, angiotensin II promotes the breakdown of triglycerides, leading to elevated levels of FFAs and glycerol in the circulation [142]. In HF, chronic inflammation is characterized by elevated levels of cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α, and CRP [143]. Elevated inflammatory markers in HF patients can disrupt lipid metabolism. High levels of IL-6 and TNF-α can increase triglyceride synthesis and reduce lipoprotein lipase activity, contributing to hypertriglyceridemia. Inflammatory cytokines can impair the synthesis and functionality of HDL cholesterol, leading to lower levels of protective HDL particles. Chronic inflammation can modify LDL particles, making them more susceptible to oxidation and promoting atherogenesis [144]. Inflammation contributes to endothelial dysfunction, impairing the regulation of vascular tone and permeability, which further complicates lipid metabolism and cardiovascular health. Inflammatory processes in HF also induce oxidative stress, which can exacerbate lipid peroxidation and contribute to lipid profile abnormalities.
Recent research has increasingly highlighted Lp(a) as a potential contributor to cardiovascular disease, including its involvement in HF. Elevated levels of Lp(a) and oxidized phospholipids are known to promote atherosclerosis, inflammation, and thrombosis – key mechanisms that act as independent risk factors in the development and progression of symptomatic heart failure or cardiovascular death [145, 146]. Moreover, elevated Lp(a) levels have been associated with poorer clinical outcomes in individuals with established HF, including increased rates of cardiovascular mortality and HF-related hospitalizations. Lp(a) concentrations ≥ 30 mg/dl have been shown to independently predict these adverse events, regardless of conventional cardiovascular risk factors [147, 148]. Emerging evidence indicates a significant link between genetically elevated Lp(a) levels and a higher risk of developing HF, particularly HFrEF. This relationship suggests that Lp(a) may contribute to heart failure through mechanisms that extend beyond traditional lipid-related pathways. Notably, the impact of Lp(a) appears to vary across HF phenotypes, with stronger associations seen in HFrEF than in HFpEF. This disparity is likely attributable to the role of Lp(a) in promoting atherosclerosis and ischemic heart disease as key underlying factors more commonly linked to the pathogenesis of HFrEF [145, 149–151].
Lipid-lowering therapies (LLTs) have evolved over the years with the introduction of newer and more effective agents that play a crucial role in reducing lipid levels and preventing atherosclerosis-related complications, including HF. Statins remain the most extensively studied class of LLTs in the context of HF, with multiple clinical trials and real-world studies consistently demonstrating their effectiveness. They are endorsed by major clinical guidelines for use in both primary prevention and ischemic heart disease, and high-dose statin therapy has been shown to offer superior benefits in lowering the risk of HF and reducing related hospitalizations compared to lower doses [127, 152, 153]. The role of LLT may vary depending on left ventricular systolic function, with potentially greater benefits observed in patients with HFpEF, likely due to differences in underlying etiology and pathophysiological mechanisms contributing to heart failure, as well as the pharmacological actions of statins. While statin therapy has not been shown to significantly reduce mortality in patients with HFrEF, a meta-analysis of 12 placebo-controlled randomized trials reported a 12% reduction in the risk of heart failure related hospitalizations, supporting a modest benefit in this population [154–157]. Currently, there is still a lack of strong evidence regarding the efficacy of nonstatin LLTs in patients with heart failure. However, emerging research is beginning to shed light on the potential role of PCSK9 in the development and progression of heart failure through mechanisms that appear to be independent of its effects on lipid metabolism. Despite this growing understanding, the therapeutic potential of targeting PCSK9 either through monoclonal antibodies such as alirocumab and evolocumab, or through small interfering RNA (siRNA) approaches like inclisiran remains insufficiently studied in the context of HF [127, 158, 159].
Clinical trial data have shown that LLT can reduce Lp(a) levels, although the extent of this effect varies across agents. Statins, for instance, are generally associated with a modest increase in Lp(a) concentrations. In contrast, more encouraging results have been observed with PCSK9 inhibitors. In the FOURIER trial, treatment with evolocumab led to a 26% reduction in Lp(a) levels, which was associated with a 23% reduction in cardiovascular events. Similarly, in the subanalysis of the ODYSSEY OUTCOMES study, a 5 mg/dl decrease in Lp(a) with alirocumab correlated with a significant reduction in cardiovascular risk. However, the direct impact of these therapies on heart failure outcomes remains unclear and requires further investigation [160, 161]. A large-scale analysis comparing patients to healthy controls demonstrated that lowering Lp(a) levels is associated with a reduced risk of ischemic heart disease. Specifically, for every 10 mg/dl decrease in Lp(a), the risk of ischemic heart disease declined by approximately 5.8%. Given the close link between ischemic heart disease and the development of ischemic heart failure, this reduction is also believed to contribute to lowering the risk of ischemic heart failure [162].
Currently, the only FDA-approved treatment for elevated Lp(a) is lipoprotein apheresis. However, several promising therapies aimed at significantly lowering Lp(a) levels are under investigation. Among them is pelacarsen, an antisense oligonucleotide targeting apolipoprotein(a), which has demonstrated reductions in Lp(a) levels exceeding 80%. Another agent, olpasiran, is a siRNA that blocks the translation of the apo(a) protein, achieving reductions of up to approximately 100% in circulating Lp(a) levels. Despite these impressive results in lowering Lp(a), it remains unclear whether these therapies translate into meaningful reductions in major adverse cardiovascular events or improve outcomes in heart failure. These questions are currently being explored in large-scale cardiovascular outcome trials, such as the ongoing Lp(a) HORIZON study [163].
New pharmacological perspectives for heart failure and atherosclerosis
SGLT2i
In line with the 2021 and 2023 European Society of Cardiology Guidelines for the management of heart failure, SGLT2i are now a cornerstone for the treatment of HF across the full range of ejection fractions [164, 165].
The DAPA-HF trial was the first to establish SGLT2i efficacy in HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), enrolling 4744 patients with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Dapagliflozin significantly reduced HF first and repeat admissions, cardiovascular mortality, and all-cause mortality [166, 167]. A subanalysis confirmed benefits in both ischemic and non-ischemic HF [168]. In DEFINE-HF, 263 HFrEF patients received dapagliflozin or placebo for 12 weeks, with 61.5% of SGLT2i patients showing improvement in NT-pro-BNP (> 20% decrease) or in Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire scores, regardless of diabetic status [169]. The EMPEROR-Reduced trial enrolled 3730 HFrEF patients, indicating that empagliflozin reduced cardiovascular death or HF hospitalizations (HR: 0.72–0.78) and slowed kidney function decline. Benefits were consistent across all glycemic subgroups, reducing loop diuretic use and HF interventions [170]. Finally, the CVD-REAL 2 study, a real-world analysis of HFrEF and HFpEF patients with T2DM, demonstrated a significant reduction in HF hospitalizations and all-cause mortality with dapagliflozin or empagliflozin vs. conventional antidiabetics [171].
The efficacy of SGLT2i in HFpEF and HFmrEF has been well documented. The EMPEROR-Preserved trial, which included 5988 patients with EF > 40%, demonstrated that empagliflozin significantly reduced HF hospitalizations, decreased diuretic use, and enhanced exercise tolerance compared to placebo [170]. Moreover, functional capacity was increased in 44% of patients receiving dapagliflozin vs placebo in the PRESERVED-HF trial, carried out in 289 HFpEF patients [172]. Concerns regarding safety in elderly patients were addressed in the DELIVER trial, which included HFpEF and HFmrEF patients up to 99 years old, with or without T2DM. Dapagliflozin consistently attenuated the risk of cardiovascular death or need for hospitalization across all age groups [173].
In the context of acute HF, the EMPULSE trial evaluated 530 patients randomized to empagliflozin or placebo. At 90 days, those receiving SGLT2i had improved clinical outcomes and reductions in all decongestion-related endpoints [174]. Similarly, the SOLOIST-WHF trial extended these findings to a broader population, enrolling 1222 T2DM patients hospitalized for worsening HF, regardless of EF. Treatment with sotagliflozin led to a more than 40% reduction in cardiovascular death, hospitalizations, and urgent HF visits, reinforcing the role of SGLT2i in acute HF management [175]. Collectively, these trials underline the consistent benefits of SGLT2i across the entire spectrum of HF, reinforcing their essential role in HF management.
Given the extensive glycemic, cardiovascular, and renal benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors, their potential influence on atherosclerosis has garnered significant research interest. A meta-analysis of 60 randomized trials demonstrated that SGLT2i reduce triglyceride levels while increasing total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and HDL cholesterol [176]. However, this lipid profile alteration is hypothesized to be of limited clinical relevance, as these agents are thought to induce lipolysis [177]. Regarding arterial stiffness, Szigeti et al. evaluated 40 T2DM patients receiving SGLT2i, demonstrating a significant reduction in pulse wave velocity (PWV) at both 90 days and 3.3 years of follow-up, despite no observed effect on central systolic blood pressure [178]. Similarly, a study comparing SGLT2i combined with ramipril versus ramipril alone in T2DM patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) found no significant impact on PWV [179]. The beneficial effects of SGLT2i on coronary artery disease were highlighted in the EMPT-ANGINA trial, where 75 T2DM patients with refractory angina were randomized to empagliflozin or placebo. Those receiving SGLT2i experienced significant improvements in functional capacity and prolonged pain-free periods [180]. Similarly, the EMMY trial demonstrated positive outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, with SGLT2i administration within 72 h leading to significant reductions in NT-proBNP and improvements in EF [181]. The impact of SGLT2i on peripheral artery disease (PAD) remains controversial. Some authors have reported an increased risk of amputation, particularly in patients receiving canagliflozin [182]. However, other analyses have found no elevated risk associated with SGLT2i, suggesting that the observed amputations may be attributable to the underlying PAD [183]. Finally, a potential protective effect against hemorrhagic stroke was suggested in the CREDENCE trial, which examined 4401 T2DM patients with CKD [184]. However, a meta-analysis of five major trials found no significant impact on stroke risk [185]. Overall, while SGLT2 inhibitors demonstrate promising effects on atherosclerosis and its counterparts, further large-scale studies to clarify their impact are required.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)
The relationship between obesity and HFpEF has led to the recognition of obesity as a hemodynamic and metabolic stressor, contributing to cardiac remodeling, systemic inflammation, and neurohormonal dysregulation [186, 187]. Anti-obesity pharmacotherapies are gaining attention not only for their efficacy in weight reduction but also for their potential to modulate the pathophysiological mechanisms implicated in HFpEF.
Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, has demonstrated significant benefit in patients with HFpEF. In the STEP-HFpEF trial, which enrolled 529 patients randomized to receive semaglutide or placebo, the semaglutide group showed significant improvements in functional capacity, symptom burden, and quality of life. After 52 weeks of treatment, the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire-Clinical Summary Score (KCCQ-CSS) improved significantly across all LVEF categories (45–49%, 50–59%, ≥ 60%), with no significant heterogeneity between groups (p for interaction = 0.56) [188]. Semaglutide also led to substantial weight loss, particularly among females [189], and improved functional capacity as measured by the 6-minute walking distance test (p for interaction = 0.19) [188]. Additionally, semaglutide was associated with reverse cardiac remodeling, including reductions in left atrial volumes (p = 0.0013) and improvements in echocardiographic indices of diastolic function, such as E/A ratio, E wave velocity, and E/e′ ratio [190]. The cardiovascular benefits of semaglutide were further supported by the FLOW trial, a randomized controlled study of 3533 patients over 3.4 years. Semaglutide led to a remarkable 27% relative risk reduction in the composite endpoint of first heart failure event or cardiovascular death (p = 0.0005). When analyzed separately, consistent reductions were observed in HF events alone (by 27%, p = 0.0068) and CV death (by 29%, p = 0.0036). These benefits occurred irrespective of patient baseline HF status, highlighting semaglutide’s potential role in both primary and secondary HF prevention. Treatment discontinuation due to adverse effects was mostly due to gastrointestinal disorders and was more common in the subgroup without pre-existing HF [191].
Tirzepatide, a dual agonist of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and GLP-1 receptors, has recently garnered attention for its benefits in HFpEF. In the SUMMIT trial, which randomized 731 patients to receive tirzepatide or placebo, the composite endpoint of worsening HF or CV death was reduced by 38% (p = 0.026). HF events alone were reduced by 46%, and while a numerically higher rate of CV death in the tirzepatide group was observed, it was not statistically significant [192]. Functional capacity improved significantly with tirzepatide, as reflected by a marked increase in KCCQ-CSS scores (p < 0.001) that surpassed the threshold for clinical relevance. This was accompanied by gains in 6-minute walk distance and a reduction in NYHA functional class, collectively indicating enhanced exercise tolerance and improved capacity for daily activities [193]. Although generally well tolerated, 6.3% of patients discontinued the use of tirzepatide due to gastrointestinal adverse effects [192].
Conclusions
The intricate interconnection between HF and atherosclerosis is driven by complex pathophysiological mechanisms. Addressing both conditions requires a comprehensive understanding of their shared pathophysiology, and the implementation of preventive and interventional strategies using evidence-based therapies for HF, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, lipid disorders, and obesity. There is often a significant overlap in treatment approaches for HF and atherosclerosis, while effective management of atherosclerosis and its complications may aid in controlling HF progression and symptom amelioration, ultimately leading to morbidity and mortality reductions. Although the translation of guideline-directed therapies into clinical practice may be challenged by a number of factors, such as therapeutic inertia, adherence, cost of drugs and their availability, the emergence of novel pharmacological approaches offers new insights into the treatment of HF and atherosclerosis and the prevention of atherosclerosis-mediated HF. This, together with the integrated care of patients with heart failure, may help to fight against the HF epidemic that can be observed in most countries.