Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ATHEROSCLEROSIS / RESEARCH PAPER
Deep Learning-Based Multimodal Risk Stratification for Atherosclerosis Management
1
Yongkang First People's Hospital Affiliated to Hangzhou Medical College, China
Submission date: 2025-06-05
Final revision date: 2025-07-09
Acceptance date: 2025-07-14
Online publication date: 2025-08-23
Corresponding author
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Atherosclerosis is a leading cause of cardiovascular events, requiring accurate risk stratification. Traditional methods rely on subjective imaging and clinical scores, limiting precision.
Material and methods:
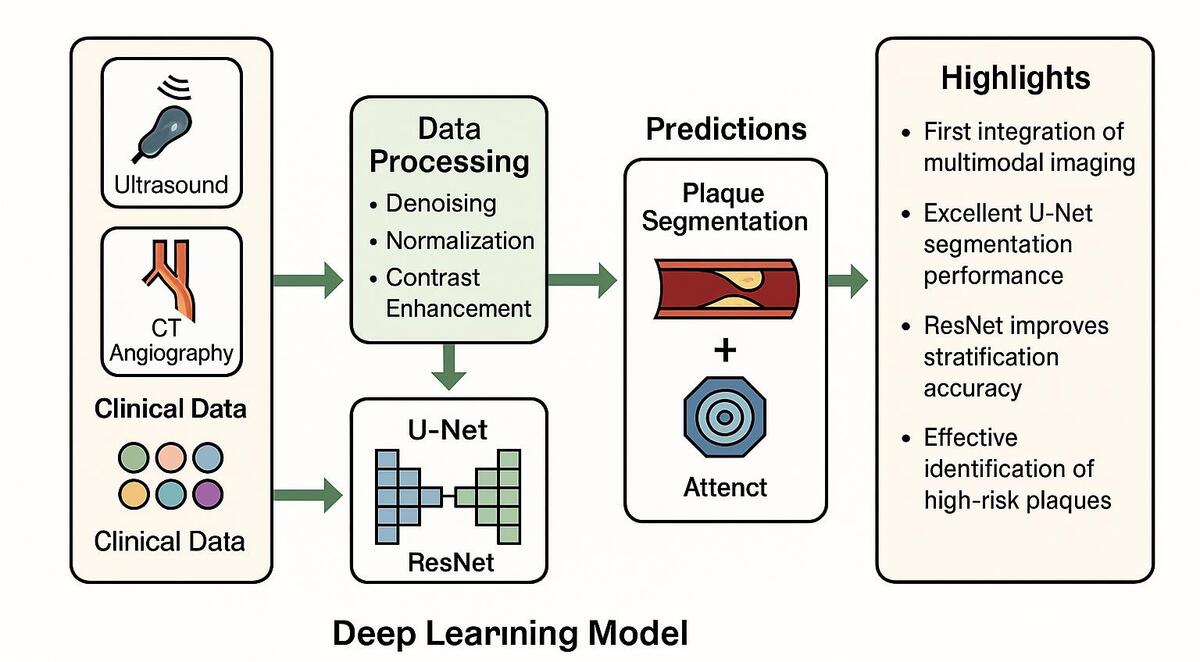
We developed a deep learning (DL) model combining U-Net for lesion segmentation, ResNet for classification, and an attention mechanism to enhance detection of high-risk plaques. Multimodal data—including ultrasound, CTA, and clinical variables—underwent standard preprocessing. The dataset was split (8:1:1) and evaluated using 5-fold cross-validation.
Results:
The U-Net achieved a Dice coefficient of 0.88. The ResNet, integrated with clinical features, reached 92% classification accuracy and an AUC of 0.97. The attention mechanism improved vulnerable plaque detection by 10%. Grad-CAM visualizations showed 85% agreement with expert annotations. Processing time was reduced by 70% compared to traditional assessment methods. Multicenter validation confirmed strong generalizability.
Conclusions:
This study constructed a multimodal DL model that significantly enhances the clinical value of atherosclerosis risk stratification, the prediction accuracy increased to 92% with an AUC of 0.97, and the average processing time per case was reduced from 6.3 ± 1.4 minutes to 1.9 ± 0.4 minutes (a reduction of approximately 70%). The model demonstrated higher precision in both lesion segmentation and high-risk plaque identification, providing clinicians with a rapid and reliable decision-support tool that is expected to further optimize individualized intervention strategies and improve patient prognosis.
Atherosclerosis is a leading cause of cardiovascular events, requiring accurate risk stratification. Traditional methods rely on subjective imaging and clinical scores, limiting precision.
Material and methods:
We developed a deep learning (DL) model combining U-Net for lesion segmentation, ResNet for classification, and an attention mechanism to enhance detection of high-risk plaques. Multimodal data—including ultrasound, CTA, and clinical variables—underwent standard preprocessing. The dataset was split (8:1:1) and evaluated using 5-fold cross-validation.
Results:
The U-Net achieved a Dice coefficient of 0.88. The ResNet, integrated with clinical features, reached 92% classification accuracy and an AUC of 0.97. The attention mechanism improved vulnerable plaque detection by 10%. Grad-CAM visualizations showed 85% agreement with expert annotations. Processing time was reduced by 70% compared to traditional assessment methods. Multicenter validation confirmed strong generalizability.
Conclusions:
This study constructed a multimodal DL model that significantly enhances the clinical value of atherosclerosis risk stratification, the prediction accuracy increased to 92% with an AUC of 0.97, and the average processing time per case was reduced from 6.3 ± 1.4 minutes to 1.9 ± 0.4 minutes (a reduction of approximately 70%). The model demonstrated higher precision in both lesion segmentation and high-risk plaque identification, providing clinicians with a rapid and reliable decision-support tool that is expected to further optimize individualized intervention strategies and improve patient prognosis.
REFERENCES (28)
1.
Savo MT, De Amicis M, Cozac DA, et al. Comparative Prognostic Value of Coronary Calcium Score and Perivascular Fat Attenuation Index in Coronary Artery Disease. JCM. 2024;13(17):5205. doi:10.3390/jcm13175205.
2.
Monlezun DJ, MacKay K. Artificial Intelligence and Health Inequities in Dietary Interventions on Atherosclerosis: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2024;16(16):2601. doi:10.3390/nu16162601.
3.
Koloi A, Loukas VS, Hourican C, et al. Predicting early-stage coronary artery disease using machine learning and routine clinical biomarkers improved by augmented virtual data. European Heart Journal - Digital Health. 2024;5(5):542-550. doi:10.1093/ehjdh/ztae049.
4.
Singh M, Kumar A, Khanna NN, et al. Artificial intelligence for cardiovascular disease risk assessment in personalised framework: a scoping review. eClinicalMedicine. 2024;73:102660. doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102660.
5.
Oikonomou EK, Khera R. Machine learning in precision diabetes care and cardiovascular risk prediction. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023;22(1). doi:10.1186/s12933-023-01985-3.
6.
Saba L, Maindarkar M, Khanna NN, et al. A Pharmaceutical Paradigm for Cardiovascular Composite Risk Assessment Using Novel Radiogenomics Risk Predictors in Precision Explainable Artificial Intelligence Framework: Clinical Trial Tool. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023;28(10). doi:10.31083/j.fbl2810248.
7.
Banchhor SK, Londhe ND, Araki T, et al. Calcium detection, its quantification, and grayscale morphology-based risk stratification using machine learning in multimodality big data coronary and carotid scans: A review. Computers in Biology and Medicine. 2018;101:184-198. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.08.017.
8.
He K, Zhang R, Liang M, et al. The application of deep learning in early enamel demineralization detection. PeerJ. 2025;13:e18593. doi:10.7717/peerj.18593.
9.
Lakshmi K, Amaran S, Subbulakshmi G, Padmini S, Joshi GP, Cho W. Explainable artificial intelligence with UNet based segmentation and Bayesian machine learning for classification of brain tumors using MRI images. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1). doi:10.1038/s41598-024-84692-7.
10.
Chen H, Lai H, Chi H, et al. Multi-modal transcriptomics: integrating machine learning and convolutional neural networks to identify immune biomarkers in atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024;11. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2024.1397407.
11.
Jain PK, Dubey A, Saba L, et al. Attention-Based UNet Deep Learning Model for Plaque Segmentation in Carotid Ultrasound for Stroke Risk Stratification: An Artificial Intelligence Paradigm. JCDD. 2022;9(10):326. doi:10.3390/jcdd9100326.
12.
Lee YC, Cha J, Shim I, et al. Multimodal deep learning of fundus abnormalities and traditional risk factors for cardiovascular risk prediction. npj Digit Med. 2023;6(1). doi:10.1038/s41746-023-00748-4.
13.
Barriada RG, Masip D. An Overview of Deep-Learning-Based Methods for Cardiovascular Risk Assessment with Retinal Images. Diagnostics. 2022;13(1):68. doi:10.3390/diagnostics13010068.
14.
Tokodi M, Shah R, Jamthikar A, et al. Deep Learning Model of Diastolic Dysfunction Risk Stratifies the Progression of Early-Stage Aortic Stenosis. JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging. 2025;18(2):150-165. doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2024.07.017.
15.
Huang Z, Lam S, Lin Z, et al. Predicting major adverse cardiac events using radiomics nomogram of pericoronary adipose tissue based on CCTA: A multi‐center study. Medical Physics. 2024;51(11):8348-8361. doi:10.1002/mp.17324.
16.
Omarov M, Zhang L, Doroodgar Jorshery S, et al. Deep Learning-Based Detection of Carotid Plaques Informs Cardiovascular Risk Prediction and Reveals Genetic Drivers of Atherosclerosis. Published online October 18, 2024. doi:10.1101/2024.10.17.24315675.
17.
Jaltotage B, Lu J, Dwivedi G. Use of Artificial Intelligence Including Multimodal Systems to Improve the Management of Cardiovascular Disease. Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 2024;40(10):1804-1812. doi:10.1016/j.cjca.2024.07.014.
18.
Kampaktsis PN, Emfietzoglou M, Al Shehhi A, et al. Artificial intelligence in atherosclerotic disease: Applications and trends. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023;9. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2022.949454.
19.
van Assen M, Tariq A, Razavi AC, Yang C, Banerjee I, De Cecco CN. Fusion Modeling: Combining Clinical and Imaging Data to Advance Cardiac Care. Circ: Cardiovascular Imaging. 2023;16(12). doi:10.1161/circimaging.122.014533.
20.
Gallone G, Bellettini M, Gatti M, et al. Coronary Plaque Characteristics Associated With Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Atherosclerotic Patients and Lesions. JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging. 2023;16(12):1584-1604. doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2023.08.006.
21.
Sarraju A, Nissen SE. Atherosclerotic plaque stabilization and regression: a review of clinical evidence. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024;21(7):487-497. doi:10.1038/s41569-023-00979-8.
22.
Lin A, Kolossváry M, Motwani M, et al. Artificial Intelligence in Cardiovascular Imaging for Risk Stratification in Coronary Artery Disease. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging. 2021;3(1):e200512. doi:10.1148/ryct.2021200512.
23.
Bhagawati M, Paul S, Mantella L, et al. Cardiovascular Disease Risk Stratification Using Hybrid Deep Learning Paradigm: First of Its Kind on Canadian Trial Data. Diagnostics. 2024;14(17):1894. doi:10.3390/diagnostics14171894.
24.
Amal S, Safarnejad L, Omiye JA, Ghanzouri I, Cabot JH, Ross EG. Use of Multi-Modal Data and Machine Learning to Improve Cardiovascular Disease Care. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2022.840262.
25.
Prajapati NK, Patel A, Mewada H. Automated diagnosis of atherosclerosis using multi-layer ensemble models and bio-inspired optimization in intravascular ultrasound imaging. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2024;63(1):213-227. doi:10.1007/s11517-024-03190-0.
26.
Quan X, Ou X, Gao L, Yin W, Hou G, Zhang H. SCINet: A Segmentation and Classification Interaction CNN Method for Arteriosclerotic Retinopathy Grading. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci. 2024;16(4):926-935. doi:10.1007/s12539-024-00650-x.
27.
Lewandowski Ł, Czapla M, Uchmanowicz I, et al. Machine Learning and Clinical Predictors of Mortality in Cardiac Arrest Patients: A Comprehensive Analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2024;30. doi:10.12659/msm.944408.
28.
Nazir S, Dickson DM, Akram MU. Survey of explainable artificial intelligence techniques for biomedical imaging with deep neural networks. Computers in Biology and Medicine. 2023;156:106668. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106668.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.