Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
LIPID DISORDERS / CLINICAL RESEARCH
Facts and myths about the use and effects of statins in patients with dyslipidaemia: a survey of physicians
1
AD-Med Medical Center, Wroclaw, Poland
2
Department of Family Medicine, Wroclaw Medical University, Wroclaw, Poland
3
MEDFIT Karolina Kloda, Szczecin, Poland
Submission date: 2024-05-30
Final revision date: 2024-11-03
Acceptance date: 2024-12-03
Online publication date: 2025-02-22
Corresponding author
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
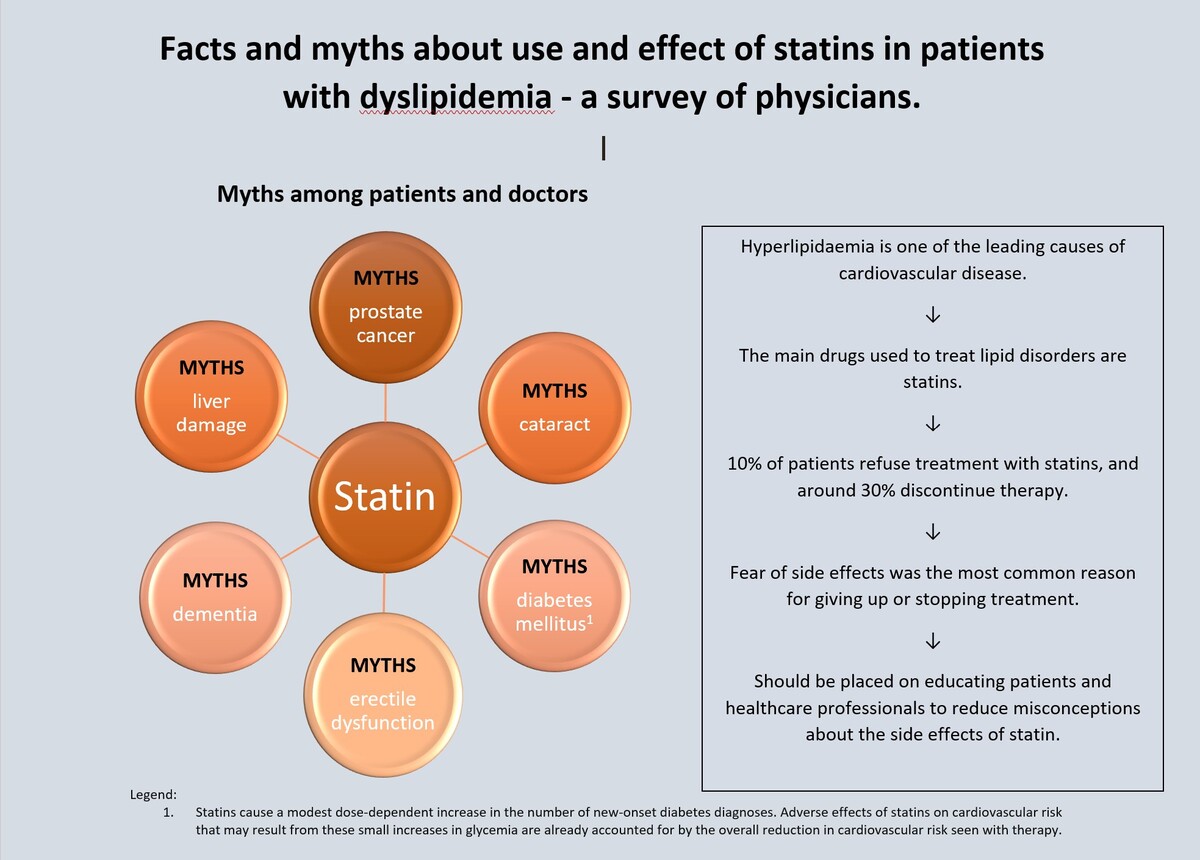
Statins are the primary medications used to treat lipid disorders. However, numerous myths surrounding statin therapy lead to patient non-adherence and therapy discontinuation. The aim of this study was to assess the most common patient concerns regarding statin use.
Material and methods:
A survey was conducted targeting doctors using an online questionnaire The first section included questions regarding socio-economic status, while the second focused on patient experiences related to refusing statin treatment due to fears of specific side effects, encounters with side effects during therapy, and estimates of the percentage of patients who discontinue treatment. The concluding section addressed the most common reasons for treatment termination from the perspective of practitioners, along with efforts to educate their patients.
Results:
260 questionnaires were collected. Notably, 84% and 81% of doctors reported encountering refusals of statin treatment due to patients’ fears of liver and muscle damage, respectively. The majority of respondents indicated that 10–20% of patients discontinue treatment on their own, despite significant side effects occurring in less than 10% of cases. Muscular symptoms were cited as the reason for discontinuing therapy in 75% of cases, while misinformation regarding statin side effects contributed to 53% of discontinuations. Additionally, 96.5% of doctors reported making efforts to educate their patients about statins.
Conclusions:
Many harmful beliefs about the side effects of statins persist among patients, resulting in non-adherence to treatment. The most prevalent concerns involve fears related to muscle and liver damage. These issues can be mitigated through targeted education for both patients and healthcare professionals.
Statins are the primary medications used to treat lipid disorders. However, numerous myths surrounding statin therapy lead to patient non-adherence and therapy discontinuation. The aim of this study was to assess the most common patient concerns regarding statin use.
Material and methods:
A survey was conducted targeting doctors using an online questionnaire The first section included questions regarding socio-economic status, while the second focused on patient experiences related to refusing statin treatment due to fears of specific side effects, encounters with side effects during therapy, and estimates of the percentage of patients who discontinue treatment. The concluding section addressed the most common reasons for treatment termination from the perspective of practitioners, along with efforts to educate their patients.
Results:
260 questionnaires were collected. Notably, 84% and 81% of doctors reported encountering refusals of statin treatment due to patients’ fears of liver and muscle damage, respectively. The majority of respondents indicated that 10–20% of patients discontinue treatment on their own, despite significant side effects occurring in less than 10% of cases. Muscular symptoms were cited as the reason for discontinuing therapy in 75% of cases, while misinformation regarding statin side effects contributed to 53% of discontinuations. Additionally, 96.5% of doctors reported making efforts to educate their patients about statins.
Conclusions:
Many harmful beliefs about the side effects of statins persist among patients, resulting in non-adherence to treatment. The most prevalent concerns involve fears related to muscle and liver damage. These issues can be mitigated through targeted education for both patients and healthcare professionals.
REFERENCES (58)
1.
Borghi CF, Fogacci D, Agnoletti A, Cicero FG. Hypertension and dyslipidemia combined therapeutic approaches. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 2022; 29: 221-30.
2.
Strandberg TE. Role of statin therapy in primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in elderly patients. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2019; 21: 28.
3.
Solnica B, Sygitowicz G, Sitkiewicz D, et al. 2024 Guidelines of the Polish Society of Laboratory Diagnostics and the Polish Lipid Association on laboratory diagnostics of lipid metabolism disorders. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 357-74.
4.
Endo A, Tsujita Y, Kuroda M, Tanzawa K. Inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in vitro and in vivo by ML-236A and ML-236B, competitive inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutarylcoenzyme A reductase. Eur J Biochem 1977; 77: 31-6.
5.
Endo A. A historical perspective on the discovery of statins. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 2010; 86: 484-93.
6.
Grundy S. Consensus statement: role of therapy with “statins” in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. Am J Cardiol 1998; 81: 1B–6B.
7.
Liao JK. Clinical implications for statin pleiotropy. Curr Opin Lipidol 2005; 16: 624-9.
8.
Sosnowska B, Stepinska J, Mitkowski P, et al. Recommendations of the Experts of the Polish Cardiac Society (PCS) and the Polish Lipid Association (PoLA) on the diagnosis and management of elevated lipoprotein(a) levels. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 8-27.
9.
Fu Q, Liao H, Li Z, Chen X, Zhang X, Di J. Preventive effects of 13 different drugs on colorectal cancer: a network meta-analysis. Arch Med Sci 2023; 19: 1428-45.
10.
Vahedian-Azimi A, Beni FH, Fras Z, et al. Effects of statins on the incidence and outcomes of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Med Sci 2023; 19: 952-64.
11.
Shepherd J. Who should receive a statin these days? Lessons from recent clinical trials. J Intern Med 2006; 260: 305-19.
12.
Banach M, Surma S, Kapłon-Cieślicka A, et al. Position paper of the Polish Expert Group on the use of pitavastatin in the treatment of lipid disorders in Poland endorsed by the Polish Lipid Association. Arch Med Sci 2023; 20: 28-42.
13.
Banach M, Shekoohi N, Mikhailidis DP, Lip GYH, Hernandez AV, Mazidi M. Relationship between low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, lipid-lowering agents and risk of stroke: a meta-analysis of observational studies (n = 355,591) and randomized controlled trials (n = 165,988). Arch Med Sci 2022; 18: 912-29.
14.
Bogdański P, Musialik-Pupek D. Statyny – standard terapii XXI wieku. Jak wybrać optymalną dawkę? Forum Zaburzen Metab 2010; 1: 131-140.
15.
Banach M, Penson PE. Adherence to statin therapy: it seems we know everything, yet we do nothing. Eur Heart J Open 2022; 2: oeac071.
16.
Bradley CK, Wang TY, Li S, et al. Patient-reported reasons for declining or discontinuing statin therapy: insights from the PALM Registry. J Am Heart Assoc 2019; 8: e011765.
17.
Ofori-Asenso R, Zoungas S, Liew D. Reinitiation of statin therapy after discontinuation: a meta-analysis. Mayo Clin Proc 2018; 93: 666-8. Erratum in: Mayo Clin Proc 2018; 93: 960.
18.
De Vera MA, Bhole V, Burns LC, Lacaille D. Impact of statin adherence on cardiovascular disease and mortality outcomes: a systematic review. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2014; 78: 684-98.
19.
Cybulska B, Kłosowicz-Latoszek L. Statin intolerance. Is it class effect or individual drugs? Choroby Serca i Naczyń 2014; 11: 257-64.
20.
Bytyçi I, Penson PE, Mikhailidis DP, et al. Prevalence of statin intolerance: a meta-analysis. Eur Heart J 2022; 43: 3213-23.
22.
Aragon G, Younossi Z. When and how to evaluate mildly elevated liver enzymes in apparently healthy patients. Clev Clin J Med 2010; 71: 195-204.
23.
Calderon R, Cubeddu L, Goldberg R, Schiff E. Satins and the treatment of dyslipidaemia in the presence of elevated liver aminotransferase levels: a therapeutic dilemma. Mayo Clin Proc 2010; 85: 349-56.
24.
Law M, Rudnicka AR. Statin safety: a systematic review. Am J Cardiol 2006; 97(8A): 52C-60C.
25.
Smith CC, Bernstein LI, Davis RB, Rind DM, Shmerling RH. Screening for statin-related toxicity: the yield of transaminase and creatine kinase measurements in a primary care setting. Arch Intern Med 2003; 163: 688-92.
26.
Charles E, Olson K, Sandhoff B. Evaluation of cases of severe statin-related transaminitis within a large health maintenance organization. Am J Med 2005; 118: 618-24.
27.
de Denus S, Spinler SA, Miller K, Peterson AM. Statins and liver toxicity: a meta-analysis. Pharmacotherapy 2004; 24: 584-91.
28.
Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL., et al. Wytyczne ESC/EAS dotyczące postępowania w dyslipidemiach: jak dzięki leczeniu zaburzeń lipidowych obniżyć ryzyko sercowo-naczyniowe. Zeszyty Edukacyjne Kardiol Pol 2020; 1-103.
29.
Stroes E, Thompson P, Corsini A. European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Statin-associated muscle symptoms: impact on statin therapy-European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel Statement on Assessment, Aetiology and Management. Eur Heart J 2015; 36: 1012-22.
30.
Joy TR, Hegele RA. Narrative review: statin-related myopathy. Ann Intern Med 2009; 150: 858-68.
31.
Fernandez G, Spatz E, Phillips P, Statin myopathy: a common dilemma not reflected in clinical trials. Clevel Clin J Med 2011; 78: 393-403.
32.
Parker BA, Capizzi JA, Grimaldi AS, et al. Effect of statins on skeletal muscle function. Circulation 2013; 127: 96-103.
33.
Collaborative Group Heart Protection Study. MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin in 20,536 high-risk individuals: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2002; 360: 7-22.
34.
Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, et al. Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 2195-207.
35.
Kashani A, Phillips CO, Foody JM, et al. Risks associated with statin therapy: a systematic overview of randomized clinical trials. Circulation 2006; 114: 2788-97.
36.
Armitage J. The safety of statins in clinical practice. Lancet 2007; 370: 1781-90.
37.
Penson PE, Bruckert E, Marais D, et al. Step-by-step diagnosis and management of the nocebo/drucebo effect in statin-associated muscle symptoms patients: a position paper from the International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP). J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022; 13: 1596-622.
38.
Wood F, Howard J, Finegold J, et al. N of 1 trial of a statin, placebo, or no treatment to assess side effects. N Engl J Med 2020; 383: 2182-4.
39.
Nalewajska M, Marchelek-Myśliwiec M, Wojczyński Ł, Kacperczyk P, Dziedziejko V. New applications of statin in therapy. Terapia Leki 2018; 74: 12.
40.
Olmastroni E, Molari G, De Beni N, et al. Statin use and risk of dementia or Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2022; 29: 804-14.
41.
Chu CS, Tseng PT, Stubbs B, et al. Use of statins and the risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 2018; 8: 5804.
42.
Geifman N, Brinton RD, Kennedy RE, Schneider LS, Butte AJ. Evidence for benefit of statins to modify cognitive decline and risk in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 2017; 9: 10.
43.
Wu C, Yang Y, Lin T, et al. Statin use reduces the risk of dementia in elderly patients: a nationwide data survey and propensity analysis. J Intern Med 2015; 277: 343-52.
44.
Tsunekawa T, Hayashi T, Kano H, et al. Cerivastatin, a hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitor, improves endothelial function in elderly diabetic patients within 3 days. Circulation 2001; 104: 376-9.
45.
Masumoto A, Hirooka Y, Hironaga K, et al. Effect of pravastatin on endothelial function in patients with coronary artery disease (cholesterol-independent effect of pravastatin). Am J Cardiol 2001; 88: 1291-4.
46.
Cai X, Tian Y, Wu T, Cao CX, Bu SY, Wang KJ. The role of statins in erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian J Androl 2014; 16: 461-6.
47.
Joseph P, Lonn E, Bosch J, et al. Long-term effects of statins, blood pressure-lowering, and both on erectile function in persons at intermediate risk for cardiovascular disease: a substudy of the Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation-3 (HOPE-3) Randomized Controlled Trial [correction Can J Cardiol 2018; 34: 811. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2018.02.013]. Can J Cardiol 2018; 34: 38-44.
48.
Corona G, Boddi V, Balercia G, et al. The effect of statin therapy on testosterone levels in subjects consulting for erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 2010; 7: 1547-56.
49.
Schooling CM, Au Yeung SL, Freeman G, Cowling BJ. The effect of statins on testosterone in men and women, a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Med 2013; 11: 57.
50.
Yu S, Chu Y, Li G, Ren L, Zhang Q, Wu L. Statin use and the risk of cataracts: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc 2017; 6: e004180.
51.
Craig EL, Stopsack KH, Evergren E, et al. Statins and prostate cancer-hype or hope? The epidemiological perspective. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2022; 25: 641-9.
52.
Kim H, Kim JK. Evidence on statins, omega-3, and prostate cancer: a narrative review. World J Mens Health 2022; 40: 412-24.
53.
Ridker PM, Pradhan A, MacFadyen JG, Libby P, Glynn RJ. Cardiovascular benefits and diabetes risks of statin therapy in primary prevention: an analysis from the JUPITER trial. Lancet 2012; 380: 565-71.
54.
Waters DD, Ho JE, DeMicco DA, et al. Predictors of new-onset diabetes in patients treated with atorvastatin: results from 3 large randomized clinical trials. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011; 57: 1535-45.
55.
Mansi I, Chansard M, Lingvay I, Zhang S, Halm E, Alvarez C. Association of statin therapy initiation with diabetes progression: a retrospective matched-cohort study. JAMA Intern Med 2021; 181: 1562-74.
56.
Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaboration. Electronic address: ctt@ndph.ox.ac.uk, & Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaboration (2024). Effects of statin therapy on diagnoses of new-onset diabetes and worsening glycaemia in large-scale randomised blinded statin trials: an individual participant data meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2024; 12: 306-19.
57.
Sattar N, Preiss D, Murray HM, et al. Statins and risk of incident diabetes: a collaborative meta-analysis of randomised statin trials. Lancet 2010; 375: 735-42.
58.
Banach M, López-Sendon JL, Averna M, et al. Treatment adherence and effect of concurrent statin intensity on the efficacy and safety of alirocumab in a real-life setting: results from ODYSSEY APPRISE. Arch Med Sci 2021; 18: 285-92.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.