Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
PANCREATOLOGY / CLINICAL RESEARCH
Increased blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio is associated with poor prognosis in patients with acute pancreatitis: a retrospective cohort study
1
Department of International Medical Center, The First People’s Hospital of Foshan, Foshan, Guangdong, China
2
Department of Nursing, The First People’s Hospital of Foshan, Foshan, Guangdong, China
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2025-03-17
Final revision date: 2025-04-19
Acceptance date: 2025-04-25
Online publication date: 2025-05-22
Corresponding author
Xia Xiang
Department of Nursing The First People’s Hospital of Foshan No. 81 Lingnan North Road 528000 Foshan Guangdong, China
Department of Nursing The First People’s Hospital of Foshan No. 81 Lingnan North Road 528000 Foshan Guangdong, China
KEYWORDS
blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratioacute pancreatitisMIMIC-IV databasemortalityretrospective cohort study
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
The blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio (BAR) may serve as a prognostic marker. This study evaluated its association with clinical outcomes in patients with acute pancreatitis (AP).
Material and methods:
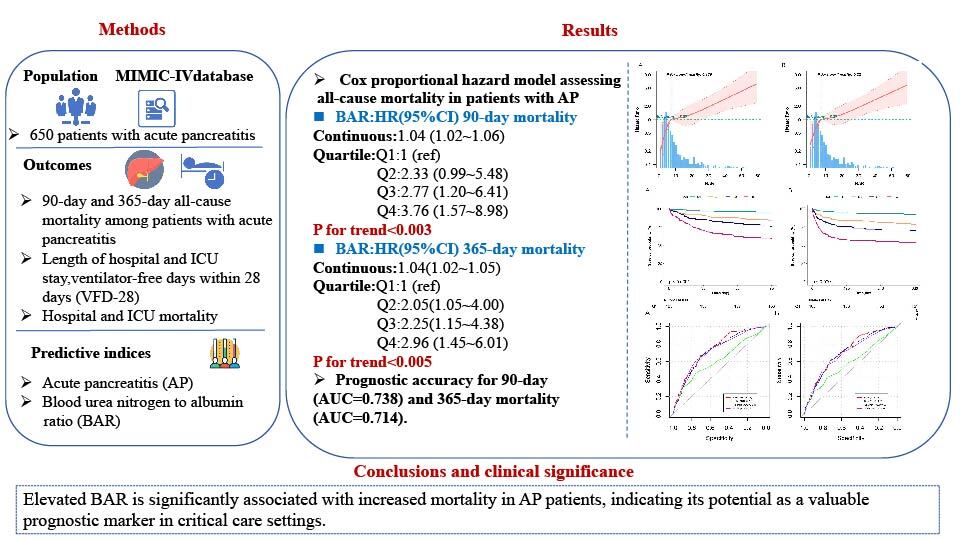
We performed a retrospective cohort analysis using data from the MIMIC-IV 2.2 database, including 650 patients diagnosed with AP. The primary outcomes were 90-day and 365-day mortality. Cox proportional hazards models assessed the relationship between BAR and mortality. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis examined the non-linear relationship.
Results:
Among the 650 patients, the mortality rates at 90 days and 365 days were 21.2% and 26.2%, respectively. Higher BAR levels correlated with increased 90-day and 365-day mortality (p < 0.001). BAR had hazard ratios (HR) of 1.04 (95% CI: 1.02–1.06) for 90-day and 1.04 (95% CI: 1.02–1.05) for 365-day mortality. ROC analysis revealed that BAR’s AUC was 0.738 for 90-day and 0.714 for 365-day mortality. Subgroup and sensitivity analyses indicated stable results across various conditions.
Conclusions:
Elevated BAR is significantly associated with increased mortality in AP patients, indicating its potential as a valuable prognostic marker in critical care settings.
The blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio (BAR) may serve as a prognostic marker. This study evaluated its association with clinical outcomes in patients with acute pancreatitis (AP).
Material and methods:
We performed a retrospective cohort analysis using data from the MIMIC-IV 2.2 database, including 650 patients diagnosed with AP. The primary outcomes were 90-day and 365-day mortality. Cox proportional hazards models assessed the relationship between BAR and mortality. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis examined the non-linear relationship.
Results:
Among the 650 patients, the mortality rates at 90 days and 365 days were 21.2% and 26.2%, respectively. Higher BAR levels correlated with increased 90-day and 365-day mortality (p < 0.001). BAR had hazard ratios (HR) of 1.04 (95% CI: 1.02–1.06) for 90-day and 1.04 (95% CI: 1.02–1.05) for 365-day mortality. ROC analysis revealed that BAR’s AUC was 0.738 for 90-day and 0.714 for 365-day mortality. Subgroup and sensitivity analyses indicated stable results across various conditions.
Conclusions:
Elevated BAR is significantly associated with increased mortality in AP patients, indicating its potential as a valuable prognostic marker in critical care settings.
REFERENCES (29)
1.
Mederos MA, Reber HA, Girgis MD. Acute pancreatitis: a review. JAMA 2021; 325: 382-90.
2.
Lee PJ, Papachristou GI. New insights into acute pancreatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019; 16: 479-96.
3.
Silva-Vaz P, Abrantes AM, Castelo-Branco M, et al. Multifactorial scores and biomarkers of prognosis of acute pancreatitis: applications to research and practice. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 338.
5.
Tao H, Xu J, Li N, et al. Early identification of high-risk patients with recurrent acute pancreatitis progression to chronic pancreatitis. Arch Med Sci 2022; 18: 535-9.
6.
Tarján D, Szalai E, Lipp M, et al. Persistently high procalcitonin and c-reactive protein are good predictors of infection in acute necrotizing pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci 2024; 25: 1273.
7.
Simsek O, Kocael A, Kocael P, et al. Inflammatory mediators in the diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis: pentraxin-3, procalcitonin and myeloperoxidase. Arch Med Sci 2018; 14: 288-96.
8.
Arihan O, Wernly B, Lichtenauer M, et al. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) is independently associated with mortality in critically ill patients admitted to ICU. PLoS One 2018; 13: e0191697.
9.
Checchio LM, Como AJ. Electrolytes, BUN, creatinine: who’s at risk? Ann Emerg Med 1986; 15: 363-6.
10.
Yamamoto M, Adachi H, Enomoto M, et al. Lower albumin levels are associated with frailty measures, trace elements, and an inflammation marker in a cross-sectional study in Tanushimaru. Environ Health Prev Med 2021; 26: 25.
11.
Kaysen GA, Dubin JA, Müller HG, et al. Relationships among inflammation nutrition and physiologic mechanisms establishing albumin levels in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 2002; 61: 2240-9.
12.
Cai S, Wang Q, Chen C, et al. Association between blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio and in-hospital mortality of patients with sepsis in intensive care: a retrospective analysis of the fourth-generation Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care database. Front Nutr 2022; 9: 967332.
13.
Chen H, Wang Y, Ji R, et al. Association between blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio and in-hospital mortality in critical patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: a retrospective analysis of the eICU database. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2024; 15: 1411891.
14.
Shi Y, Duan H, Liu J, et al. Blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio is associated with all-cause mortality in patients with AKI: a cohort study. Front Nutr 2024; 11: 1353956.
15.
Efgan MG. Comparison of the BUN/albumin ratio and BISAP score in predicting severity of acute pancreatitis. Cukurova Med J 2023; 48: 1096-05.
16.
Biyik Z, Biyik M, Yavuz YC, et al. The role of the BUN/albumin ratio in predicting poor clinical outcomes in patients with acute pancreatitis. Niger J Clin Pract 2025; 28: 360-6.
17.
Johnson AEW, Bulgarelli L, Shen L, et al. MIMIC-IV, a freely accessible electronic health record dataset. Sci Data 2023; 10: 1.
18.
Dai M, Fan Y, Pan P, et al. Blood urea nitrogen as a prognostic marker in severe acute pancreatitis. Dis Markers 2022; 2022: 7785497.
19.
Wu BU, Bakker OJ, Papachristou GI, et al. Blood urea nitrogen in the early assessment of acute pancreatitis: an international validation study. Arch Intern Med 2011; 171: 669-76.
20.
Pando E, Alberti P, Mata R, et al. Early changes in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) can predict mortality in acute pancreatitis: comparative study between BISAP Score, APACHE-II, and other laboratory markers-a prospective observational study. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021; 2021: 6643595.
21.
Allison SP, Lobo DN. The clinical significance of hypoalbuminaemia. Clin Nutr 2024; 43: 909-14.
22.
Hong W, Lin S, Zippi M, et al. Serum albumin is independently associated with persistent organ failure in acute pancreatitis. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017; 2017: 5297143.
23.
Wu BU, Hwang JQ, Gardner TH, et al. Lactated Ringer’s solution reduces systemic inflammation compared with saline in patients with acute pancreatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 9: 710-7.
24.
Hang T, Huang J, He G, et al. Blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio as a new prognostic indicator in critically ill patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: a retrospective cohort study. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2024; 132: 249-59.
25.
Alirezaei T, Hooshmand S, Irilouzadian R, et al. The role of blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio in the prediction of severity and 30-day mortality in patients with COVID-19. Health Sci Rep 2022; 5: e606.
26.
Nguyen KN, Chuang TI, Wong LT, et al. Association between early blood urea nitrogen-to-albumin ratio and one-year post-hospital mortality in critically ill surgical patients: a propensity score-matched study. BMC Anesthesiol 2023; 23: 247.
27.
Wang Y, Gao S, Hong L, et al. Prognostic impact of blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio on patients with sepsis: a retrospective cohort study. Sci Rep 2023; 13: 10013.
28.
Fang J, Xu B. Blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio independently predicts mortality in critically ill patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2021; 27: 10760296211010241.
29.
Zhang L, Xing M, Yu Q, et al. Blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio: a novel mortality indicator in intensive care unit patients with coronary heart disease. Sci Rep 2024; 14: 7466.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.