Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
CLINICAL RESEARCH
J-shaped relationship between relative fat mass and osteoarthritis: a US population-based study
1
Xiangyang No. 1 People’s Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Hubei, China
2
The Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China
3
Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital, School of Clinical Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2025-06-16
Final revision date: 2025-10-13
Acceptance date: 2025-11-16
Online publication date: 2025-12-30
KEYWORDS
relative fat massosteoarthritisJ-shaped relationshipNational Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common chronic joint disease that severely affects patients’ quality of life and causes a significant socioeconomic burden. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between relative fat mass (RFM) and OA and to assess the diagnostic efficacy of RFM in predicting OA risk.
Material and methods:
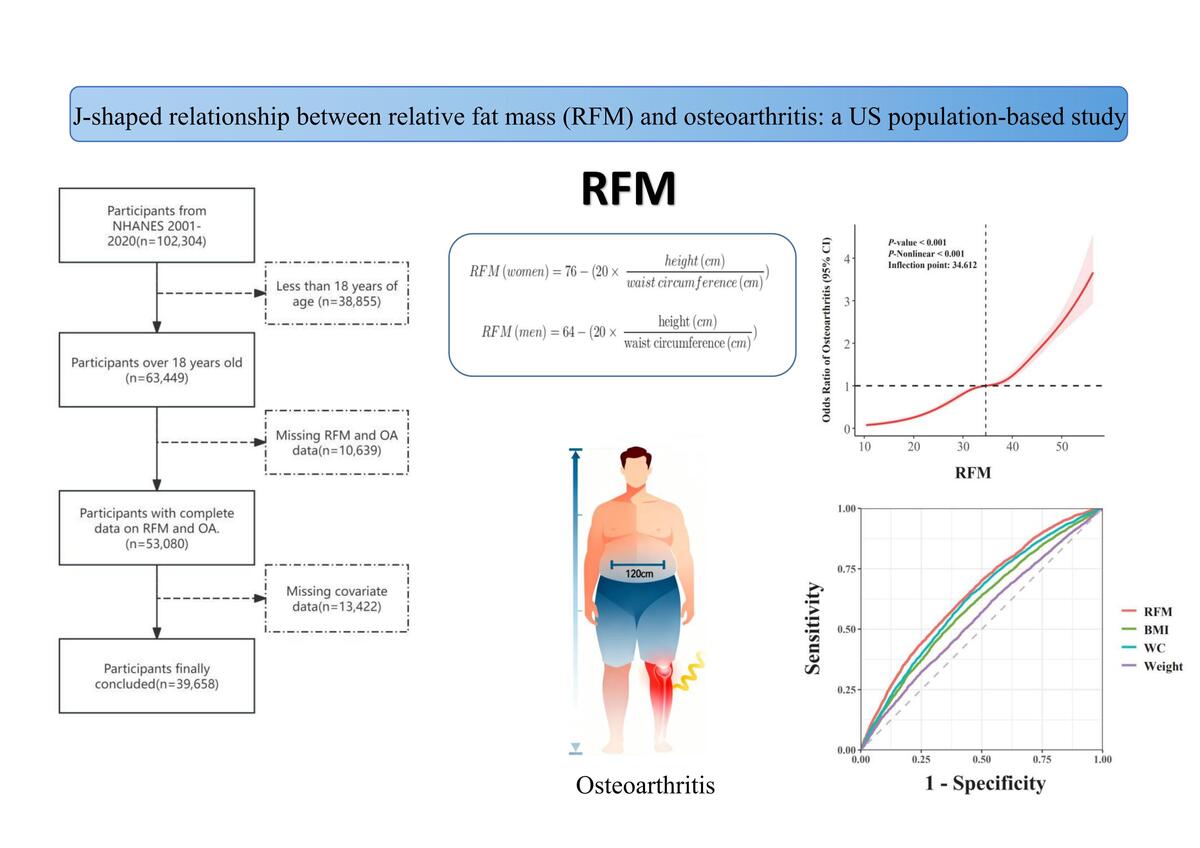
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2001 to 2020. Thirty-nine thousand six hundred and fifty-eight study participants were included in the study, which used multifactorial logistic regression analyses, stratified analyses, restricted cubic spline curves (RCS), and ROC curves to explore the association between RFM and OA.
Results:
RFM was significantly and positively associated with OA, which remained statistically significant after correction for confounders (OR = 1.062, 95% CI: 1.056–1.069, p < 0.0001). Restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis showed a J-shaped relationship between RFM and OA (p = 0.024 for non-linear test). Stratified analyses further confirmed that the association between RFM and OA was positive in all subgroups, and the strength of this association varied by age and ethnicity (p < 0.05 for interaction). ROC curve analyses showed that RFM was significantly more diagnostic of OA than body weight, waist circumference (WC) and body mass index (BMI), with areas under the curve (AUC) of 0.646, 0.550, 0.621 and 0.550, respectively.
Conclusions:
RFM may be an important risk factor for OA and has a diagnostic efficacy superior to traditional anthropometric indices in predicting OA risk. Future studies should further explore the mechanisms linking RFM and OA and validate its clinical applicability, with a view to providing new insights and methods for the prevention and diagnosis of OA.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common chronic joint disease that severely affects patients’ quality of life and causes a significant socioeconomic burden. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between relative fat mass (RFM) and OA and to assess the diagnostic efficacy of RFM in predicting OA risk.
Material and methods:
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2001 to 2020. Thirty-nine thousand six hundred and fifty-eight study participants were included in the study, which used multifactorial logistic regression analyses, stratified analyses, restricted cubic spline curves (RCS), and ROC curves to explore the association between RFM and OA.
Results:
RFM was significantly and positively associated with OA, which remained statistically significant after correction for confounders (OR = 1.062, 95% CI: 1.056–1.069, p < 0.0001). Restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis showed a J-shaped relationship between RFM and OA (p = 0.024 for non-linear test). Stratified analyses further confirmed that the association between RFM and OA was positive in all subgroups, and the strength of this association varied by age and ethnicity (p < 0.05 for interaction). ROC curve analyses showed that RFM was significantly more diagnostic of OA than body weight, waist circumference (WC) and body mass index (BMI), with areas under the curve (AUC) of 0.646, 0.550, 0.621 and 0.550, respectively.
Conclusions:
RFM may be an important risk factor for OA and has a diagnostic efficacy superior to traditional anthropometric indices in predicting OA risk. Future studies should further explore the mechanisms linking RFM and OA and validate its clinical applicability, with a view to providing new insights and methods for the prevention and diagnosis of OA.
REFERENCES (30)
2.
Network, G. C. Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 (GBD 2019) Results (Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation Seattle, 2020).
3.
Safaei M, Sundararajan EA, Driss M, Boulila W, Shapi’i A. A systematic literature review on obesity: understanding the causes and consequences of obesity and reviewing various machine learning approaches used to predict obesity. Comput Biol Med 2021; 136: 104754.
4.
Woolcott OO, Bergman RN. Relative fat mass (RFM) as a new estimator of whole-body fat percentage – a cross-sectional study in American adult individuals. Sci Rep 2018; 8: 10980.
5.
Kobo O, Leiba R, Avizohar O, Karban A. Relative fat mass (RFM) as abdominal obesity criterion for metabolic syndrome. Eur J Intern Med 2019; 63: e9-11.
6.
Woolcott OO, Samarasundera E, Heath AK. Association of relative fat mass (RFM) index with diabetes-related mortality and heart disease mortality. Sci Rep 2024; 14: 30823.
7.
Al-Shahrani AM, Alqahtani SM, Alghamdi MA, et al. Awareness of obesity and weight loss management among adults in the Asir Region, Saudi Arabia. Cureus 2024; 16: e75066.
8.
Yang S, Zhou L, Gong W, Guo B, Wang L. Global burden of osteoarthritis from 1990 to 2019 attributable to high body mass index. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 1841-53.
9.
Zhang H, Mei J. The association between relative fat mass (RFM) and lumbar bone density in US adults: Insight from 2011-2018 NHANES. PLoS One 2025; 20: e0323243.
10.
Zhang C, Dong X, Chen J, Liu F. Association between lipid accumulation product and psoriasis among adults: a nationally representative cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Dis 2024; 23: 143.
11.
Ma W, Yan Z, Wu W, Li D, Zheng S, Lyu J. Dose-response association of waist-to-height ratio plus BMI and risk of depression: evidence from the NHANES 05-16. Int J Gen Med 2021; 14: 1283-91.
12.
March LM, Schwarz JM, Carfrae BH, Bagge E. Clinical validation of self-reported osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 1998; 6: 87-93.
13.
Chen S, Sun X, Zhou G, Jin J, Li Z. Association between sensitivity to thyroid hormone indices and the risk of osteoarthritis: an NHANES study. Eur J Med Res 2022; 27: 114.
14.
Henriques J, Berenbaum F, Mobasheri A. Obesity-induced fibrosis in osteoarthritis: pathogenesis, consequences and novel therapeutic opportunities. Osteoarthr Cartil Open 2024; 6: 100511.
15.
Wen S, Huang Z, Zhang B, Huang Y. The effect of cheese intake on osteoarthritis: a Mendelian randomization study. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 1943-56.
16.
Qu Q, Jiang R, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Zhu W. Whole-body water mass and osteoarthritis: a Mendelian randomization study. Arch Med Sci 2025; 21: 1916-24.
17.
Timofte DV, Tudor RC, Mocanu V, Labusca L. Obesity, osteoarthritis, and myokines: balancing weight management strategies, myokine regulation, and muscle health. Nutrients 2024; 16: 4231.
18.
Salis Z, Gallagher R, Lawler L, Sainsbury A. Loss of body weight is dose-dependently associated with reductions in symptoms of hip osteoarthritis. Int J Obes 2025; 49: 147-53.
19.
Wiltink J, Michal M, Wild PS. et al. Associations between depression and different measures of obesity (BMI, WC, WHtR, WHR). BMC Psychiatry 2013; 13: 223.
20.
Rawdha T, Aicha BT, Leila R, et al. Correlation between abdominal obesity and pain in knee osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev 2023; 19: 174-9.
21.
Kim JE, Huh Y, Lee JH, et al. Association of body mass index and waist circumference with osteoarthritis among Korean adults: a Nationwide Study. Korean J Fam Med 2024; 45: 157-63.
22.
Humphreys S. The unethical use of BMI in contemporary general practice. Br J Gen Pract 2010; 60: 696-7.
23.
Park D, Park YM, Ko SH, et al. Association of general and central obesity, and their changes with risk of knee osteoarthritis: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Sci Rep 2023; 13: 3796.
24.
Freedland ES. Role of a critical visceral adipose tissue threshold (CVATT) in metabolic syndrome: implications for controlling dietary carbohydrates: a review. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2004; 1: 12.
25.
Wu M, Wang Z. Relative fat mass (RFM) is linked to testosterone deficiency in adult males. Steroids 2025; 214: 109544.
26.
Freystaetter G, Fischer K, Orav EJ, et al. Total serum testosterone and Western Ontario and McMaster universities osteoarthritis Index Pain and function among older men and women with severe knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res 2020; 72: 1511-8.
27.
Pang H, Chen S, Klyne DM, et al. Low back pain and osteoarthritis pain: a perspective of estrogen. Bone Res 2023; 11: 42.
28.
Ko SH, Jung Y. Energy metabolism changes and dysregulated lipid metabolism in postmenopausal women. Nutrients 2021; 13: 4556
29.
Chu X, Niu H, Wang N, et al. Triglyceride-glucose-based anthropometric indices for predicting incident cardiovascular disease: relative fat mass (RFM) as a robust indicator. Nutrients 2025; 17: 2212.
30.
Zheng Y, Huang C, Jin J, Zhao Y, Cui H, Wei C. Association between stroke and relative fat mass: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES. Lipids Health Dis 2024; 23: 354.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.