Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
CLINICAL RESEARCH
The association of liver and pancreatic fat accumulation patterns with diabetes and prediabetes in young and middle-aged Chinese adults
1
Department of Endocrinology, Gongli Hospital of Shanghai Pudong New Area, Shanghai, China
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2025-10-09
Final revision date: 2025-11-04
Acceptance date: 2025-11-16
Online publication date: 2025-12-30
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
The combined role of fatty liver disease (FLD) and pancreatic fat accumulation (PFA) in diabetes is unknown. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the relationship between the phenotype of FLD and PFA and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) or prediabetes in young and middle-aged adults.
Material and methods:
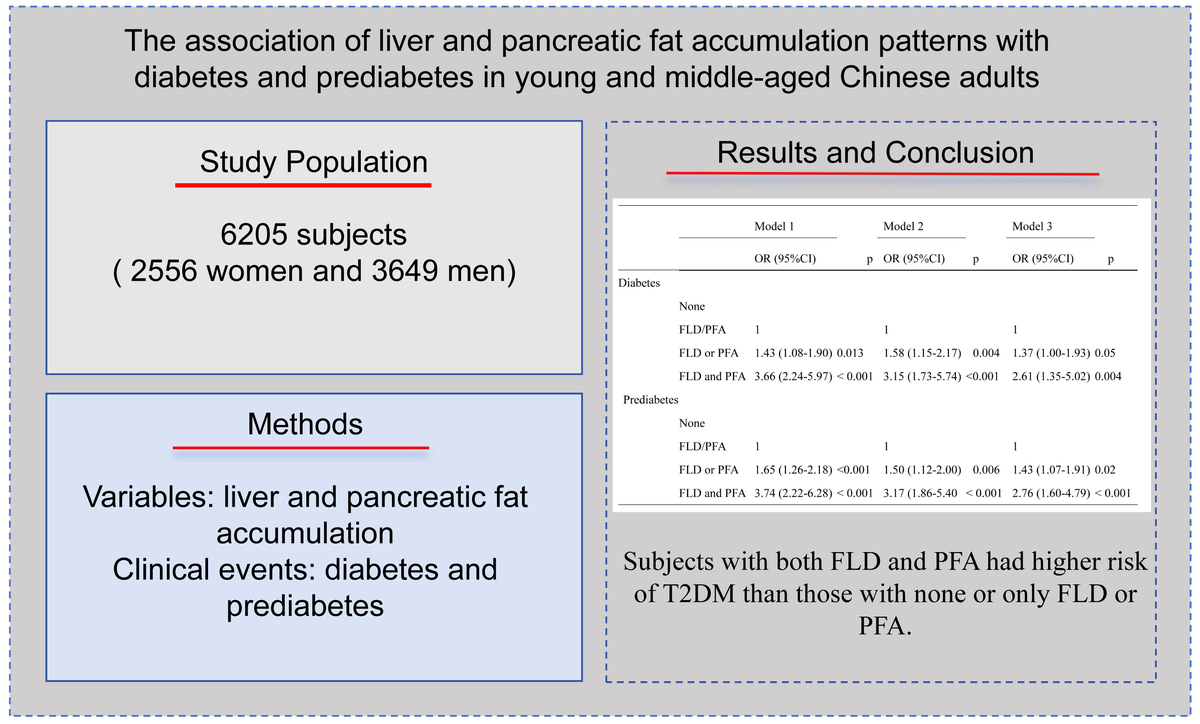
6205 adults aged 25–60 years who underwent computed tomography (CT) chest examinations were included in this study. Fatty liver disease was defined based on the ratio of liver CT attenuation and spleen CT attenuation (ratio < 0.8). PFA was defined based on the ratio of pancreatic CT attenuation and spleen CT attenuation (ratio < 0.9). The phenotype of FLD and PFA was divided into three groups: neither FLD nor PFA; either FLD or PFA; both FLD and PFA.
Results:
There were 236 patients with T2DM and 242 subjects with prediabetes. 1861 subjects had FLD or PFA, and 190 subjects had both FLD and PFA. Subjects with both FLD and PFA or subjects with either FLD or PFA had higher risk of T2DM or prediabetes than those with neither FLD nor PFA (odds ratio (OR) = 2.61, 95% CI:1.35–5.02; OR = 1.37, 95% CI: 1.00–1.93; OR = 2.76, 95% CI: 1.60–4.790; OR = 1.43, 95% CI: 1.07–1.91). Subjects with both FLD and PFA also had a higher risk of prediabetes and prediabetes + diabetes than those with FLD or PFA alone (OR = 1.66, 95% CI: 1.00–2.88; OR = 1.64, 95% CI: 1.02–2.63).
Conclusions:
Subjects with both FLD and PFA had higher risk of T2DM than those with neither condition or either FLD or PFA.
The combined role of fatty liver disease (FLD) and pancreatic fat accumulation (PFA) in diabetes is unknown. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the relationship between the phenotype of FLD and PFA and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) or prediabetes in young and middle-aged adults.
Material and methods:
6205 adults aged 25–60 years who underwent computed tomography (CT) chest examinations were included in this study. Fatty liver disease was defined based on the ratio of liver CT attenuation and spleen CT attenuation (ratio < 0.8). PFA was defined based on the ratio of pancreatic CT attenuation and spleen CT attenuation (ratio < 0.9). The phenotype of FLD and PFA was divided into three groups: neither FLD nor PFA; either FLD or PFA; both FLD and PFA.
Results:
There were 236 patients with T2DM and 242 subjects with prediabetes. 1861 subjects had FLD or PFA, and 190 subjects had both FLD and PFA. Subjects with both FLD and PFA or subjects with either FLD or PFA had higher risk of T2DM or prediabetes than those with neither FLD nor PFA (odds ratio (OR) = 2.61, 95% CI:1.35–5.02; OR = 1.37, 95% CI: 1.00–1.93; OR = 2.76, 95% CI: 1.60–4.790; OR = 1.43, 95% CI: 1.07–1.91). Subjects with both FLD and PFA also had a higher risk of prediabetes and prediabetes + diabetes than those with FLD or PFA alone (OR = 1.66, 95% CI: 1.00–2.88; OR = 1.64, 95% CI: 1.02–2.63).
Conclusions:
Subjects with both FLD and PFA had higher risk of T2DM than those with neither condition or either FLD or PFA.
REFERENCES (32)
1.
Ismail A, Mousa NMA, Elgendy SKM, et al. Effect of lifestyle changes on liver enzymes, triglycerides, sex hormones, and daytime sleepiness in polycystic ovarian syndrome women with obstructive sleep apnea and fatty liver–a randomized controlled trial. Prz Menopauzalny 2025; 24: 94-101.
2.
El-Hadidy H, Ismail AA, El Sayed SG, Ahmed A, Elgohary O. Additive effect of free walking exercise on liver enzymes, fatigue severity, triglycerides, and sleeping quality in obstructive sleep apnea patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver: randomized controlled trial. Adv Rehab 2025; 39: 16-27.
3.
Ismail AMA, Saad AE, Draz RS. Effect of low-calorie diet on psoriasis severity index, triglycerides, liver enzymes, and quality of life in psoriatic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Reumatologia 2023; 61: 116-22..
4.
Yamazaki H, Tauchi S, Machann J, et al. Fat distribution patterns and future type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2022; 71: 1937-45.
5.
Stefan N, Häring HU, Cusi K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: causes, diagnosis, cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2019; 7: 313-24.
6.
Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018; 15: 11-20.
7.
Byrne CD, Targher G. Ectopic fat, insulin resistance, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: implications for cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2014; 34: 1155-61.
8.
London A, Lundsgaard AM, Kiens B, Bojsen-Møller KN. The role of hepatic fat accumulation in glucose and insulin homeostasis-dysregulation by the liver. J Clin Med 2021; 10: 390.
9.
Wagner R, Heni M, Kantartzis K, et al. Lower hepatic fat is associated with improved insulin secretion in a high-risk prediabetes subphenotype during lifestyle intervention. Diabetes 2023; 72: 362-6.
10.
Chan TT, Tse YK, Lui RN, et al. Fatty pancreas is independently associated with subsequent diabetes mellitus development: a 10-year prospective cohort study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022; 20: 2014-22.
11.
Chin SO, Hwang YC, Cho IJ, Jeong IK, Ahn KJ, Chung HY. Pancreatic fat accumulation is associated with decreased -cell function and deterioration in glucose tolerance in Korean adults. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2021; 37: e3425.
12.
Wen Y, Chen C, Kong X, et al. Pancreatic fat infiltration, beta-cell function and insulin resistance: a study of the young patients with obesity. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2022; 187: 109860.
13.
Petrov MS, Taylor R. Intra-pancreatic fat deposition: bringing hidden fat to the fore. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022; 19: 153-68.
14.
Wagner R, Eckstein SS, Yamazaki H, et al. Metabolic implications of pancreatic fat accumulation. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2022; 18: 43-54.
15.
Stefan N, Cusi K. A global view of the interplay between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2022; 10: 284-96.
16.
Yamazaki H, Wang J, Tauchi S, et al. Inverse association between fatty liver at baseline ultrasonography and remission of type 2 diabetes over a 2-year follow-up period. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021; 19: 556-64.
17.
Miljkovic I, Kuipers AL, Cvejkus RK, et al. Hepatic and skeletal muscle adiposity are associated with diabetes independent of visceral adiposity in nonobese African-Caribbean Men. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 2020; 18: 275-83.
18.
Sung KC, Jeong WS, Wild SH, Byrne CD. Combined influence of insulin resistance, overweight/obesity, and fatty liver as risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016; 35: 717-22.
19.
Martin S, Sorokin EP, Thomas EL, et al. Estimating the effect of liver and pancreas volume and fat content on risk of diabetes: a mendelian randomization study. Diabetes Care 2022; 45: 460-8.
20.
Bacha F, Hannon TS, Tosur M, et al. Pathophysiology and treatment of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in youth. Diabetes Care 2024; 47: 2038-49.
21.
Meex RCR, Watt MJ. Hepatokines: linking nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2017; 13: 509-20.
22.
Wagner R, Jaghutriz BA, Gerst F, et al. Pancreatic steatosis associates with impaired insulin secretion in genetically predisposed individuals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2020; 105: 3518-25.
23.
Zheng ZG, Xu YY, Liu WP, et al. Discovery of a potent allosteric activator of DGKQ that ameliorates obesity-induced insulin resistance via the sn-1,2-DAG-PKCepsilon signaling axis. Cell Metab 2023; 35: 101-17.e11.
24.
Moraes-Vieira PM, Yore MM, Dwyer PM, Syed I, Aryal P, Kahn BB. RBP4 activates antigen-presenting cells, leading to adipose tissue inflammation and systemic insulin resistance. Cell Metab 2014; 19: 512-26.
25.
Gerst F, Wagner R, Oquendo MB, et al. What role do fat cells play in pancreatic tissue? Mol Metab 2019; 25: 1-10.
26.
Romero-Gómez M, Zelber-Sagi S, Trenell M. Treatment of NAFLD with diet, physical activity and exercise. J Hepatol 2017; 67: 829-46.
27.
Ismail AMA, Tolba AMN. Effectiveness of lifestyle-modification approach (a randomized-controlled program of diet restriction and treadmill walking exercise) on elderly’s metabolic syndrome-associated subjective tinnitus. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2025; 282: 4307-15.
28.
Ciftel E, Klisic A, Ciftel S, et al. Assessing the impact of a wheat flour and baker’s yeast restricted diet vs. calorie restriction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Arch Med Sci 2024; 21: 719-28.
29.
Ismail A, El Gressy NSSA, Hegazy MD, Elfahl AMAH, Ahmed OSM. Randomized controlled effect of treadmill walking exercise on liver enzymes, psychological burden, and erectile dysfunction in men with hepatitis C. Gastroenterology Rev 2024; 19: 263-70.
30.
Ismail AMA, El-Moatasem AM, El-Moatasem AM. Effect of baduanjin exercise on salivary inflammatory and oxidative markers in the elderly with metabolic syndrome and periodontal disease: a randomized trial. J Bodyw Mov Ther 2025; 45: 536-44.
31.
Ismail AMA, Morsy MM. Effect of Baduanjin exercise on lipid profile, blood pressure, and thyroid-stimulating hormone in elderly with subclinical hypothyroidism and mild cognitive impairment: a randomized-controlled trial in women. Geriatr Nurs 2025; 64: 103434.
32.
Wang J, Wei Z, Wang Y, et al. Pancreatic fat infiltration is associated with risk of vertebral fracture in older patients with type 2 diabetes: a longitudinal multicenter study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2024; 217: 111904.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.