Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
NUTRITION / RESEARCH PAPER
Ketogenic diet alleviates neuronal ferroptosis in epilepsy via HDAC4/TFRC signalling
1
, China
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2024-08-26
Final revision date: 2025-06-29
Acceptance date: 2025-06-29
Online publication date: 2025-07-02
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Ketogenic diets (KD) recapitulate certain metabolic aspects of dietary restriction such as reliance on fatty acid metabolism and production of ketone bodies. This study aimed to investigate whether a KD might, like dietary restriction, affect brain functions in epilepsy.
Material and methods:
Kainic acid (KA) injection was used to establish epilepsy model in vivo. Histone deacetylation 4 (HDAC4) mRNA expression was determined using RT-qPCR. Protein expression was detected using western blot. Gene expression was determined using immunofluorescence. The release of malondialdehyde (MDA), ferrous iron, and glutathione (GSH) was detected using corresponding commercial kits. The interaction between HDAC4 and transferrin receptor (TFRC) was verified using co-immunoprecipitation assay. Neuronal viability was detected using cell counting kit 8 (CCK-8) assay. Neuronal death was detected using propidium iodide (PI) staining.
Results:
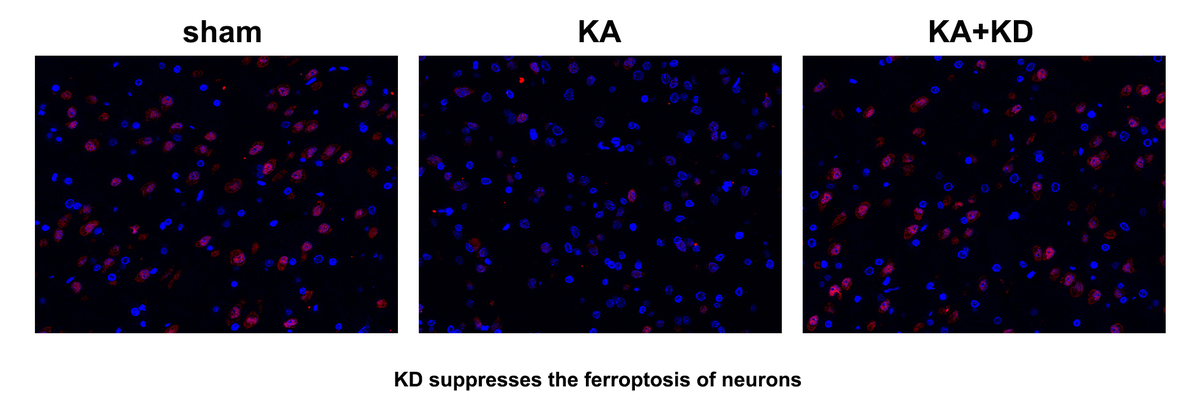
Epilepsy mediated iron accumulation- and lipid peroxidation-induced neuronal ferroptosis. Interestingly, KD treatment alleviated epilepsy as well as the accumulation of ferrous iron and lipid peroxidation, resulting in the inhibition of neuronal ferroptosis in epileptic models in vivo and in vitro. Mechanically, KD promoted the upregulation of HDAC4, which inhibited the acetylation of TFRC and suppressed its protein expression. However, downregulation of HDAC4 by its specific inhibitor LMK235 promoted the ferroptosis of neurons.
Conclusions:
Collectively, KD protect against the ferroptosis of neurons in epilepsy via promoting HDAC4-mediated deacetylation and downregulation of TFRC. Therefore, KD may be a promising strategy for epilepsy.
Ketogenic diets (KD) recapitulate certain metabolic aspects of dietary restriction such as reliance on fatty acid metabolism and production of ketone bodies. This study aimed to investigate whether a KD might, like dietary restriction, affect brain functions in epilepsy.
Material and methods:
Kainic acid (KA) injection was used to establish epilepsy model in vivo. Histone deacetylation 4 (HDAC4) mRNA expression was determined using RT-qPCR. Protein expression was detected using western blot. Gene expression was determined using immunofluorescence. The release of malondialdehyde (MDA), ferrous iron, and glutathione (GSH) was detected using corresponding commercial kits. The interaction between HDAC4 and transferrin receptor (TFRC) was verified using co-immunoprecipitation assay. Neuronal viability was detected using cell counting kit 8 (CCK-8) assay. Neuronal death was detected using propidium iodide (PI) staining.
Results:
Epilepsy mediated iron accumulation- and lipid peroxidation-induced neuronal ferroptosis. Interestingly, KD treatment alleviated epilepsy as well as the accumulation of ferrous iron and lipid peroxidation, resulting in the inhibition of neuronal ferroptosis in epileptic models in vivo and in vitro. Mechanically, KD promoted the upregulation of HDAC4, which inhibited the acetylation of TFRC and suppressed its protein expression. However, downregulation of HDAC4 by its specific inhibitor LMK235 promoted the ferroptosis of neurons.
Conclusions:
Collectively, KD protect against the ferroptosis of neurons in epilepsy via promoting HDAC4-mediated deacetylation and downregulation of TFRC. Therefore, KD may be a promising strategy for epilepsy.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.