Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
HEMATOLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
UBC9 silencing-mediated PPARα desumoylation induces inhibition of cell proliferation by ferroptosis in acute myeloid leukemia
1
Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital, Affiliated People’s Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, China
Submission date: 2024-02-04
Final revision date: 2024-06-26
Acceptance date: 2025-04-22
Online publication date: 2025-06-08
Corresponding author
Jianping Lan
Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital, Affiliated People’s Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, China
Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital, Affiliated People’s Hospital, Hangzhou Medical College, China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
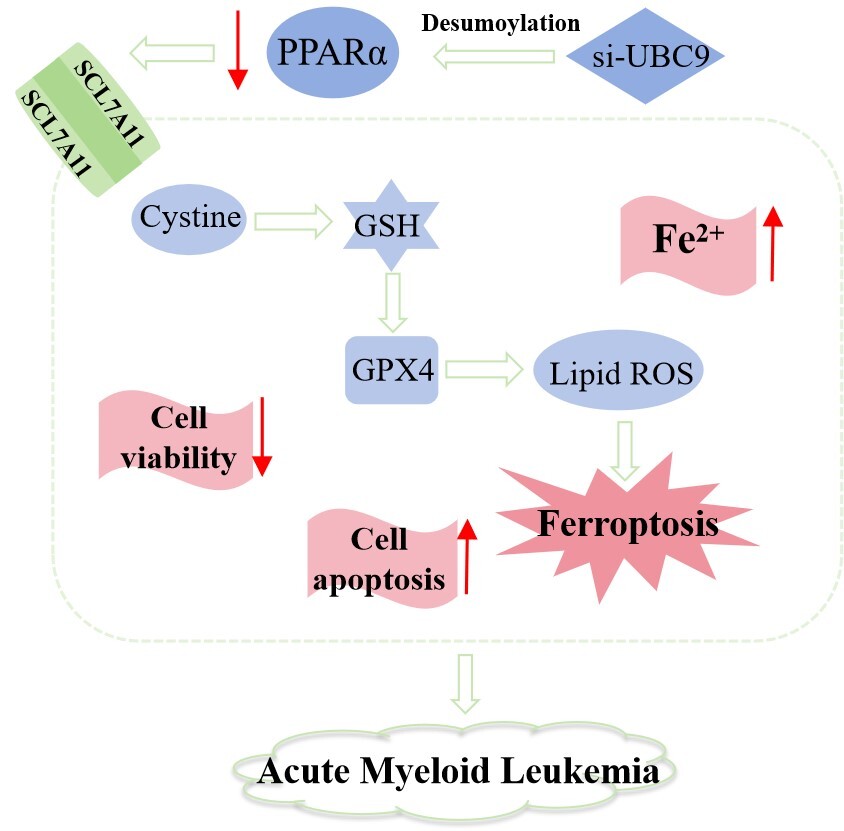
Inhibited acute myeloid leukemia (AML) proliferation is accompanied by downregulated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), which however can be stabilized via sumoylation. This study investigated how PPARα sumoylation impacts on AML cell growth.
Material and methods:
Human AML HL-60 and tohoku hospital pediatrics-1 (THP-1) cells were treated with the PPARα inhibitor, GW6471 (10 µM), for 24 and 48 h. THP-1 cells were exposed to the PPARα agonist, pirinixic acid (10 µM), after the expression of the small ubiquitin-like modifier proteins (SUMO)-conjugating enzyme UBC9 was manipulated. The interaction between PPARα and SUMO1 was detected by immunoprecipitation assay. HL-60 and THP-1 cell viability, apoptosis and ferroptosis were measured via cell counting kit-8 assay, flow cytometry, BODIPY-C11 staining and/or colorimetric assay. UBC9, glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), recombinant solute carrier family 7, member 11(SLC7A11) and PPARα expressions were analyzed by qRT-PCR or Western blot.
Results:
GW6471 treatment for 24 and 48 h suppressed viability, promoted apoptosis and lipid peroxidation, increased the level of Fe2+, and decreased the expressions of GPX4, SLC7A11 and PPARα in HL-60/THP-1 cells. PPARα antibody induced enrichment of PPARα and SUMO1 in THP-1 cells, which was attenuated after UBC9 silencing. UBC9 silencing resulted in viability decrease, apoptosis and lipid peroxidation promotion, Fe2+ upregulation, and GPX4, SLC7A11 and PPARα downregulation in THP-1 cells, which were all counteracted by pirinixic acid.
Conclusions:
UBC9 silencing-induced PPARα desumoylation induces suppression of AML cell growth by ferroptosis.
Inhibited acute myeloid leukemia (AML) proliferation is accompanied by downregulated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), which however can be stabilized via sumoylation. This study investigated how PPARα sumoylation impacts on AML cell growth.
Material and methods:
Human AML HL-60 and tohoku hospital pediatrics-1 (THP-1) cells were treated with the PPARα inhibitor, GW6471 (10 µM), for 24 and 48 h. THP-1 cells were exposed to the PPARα agonist, pirinixic acid (10 µM), after the expression of the small ubiquitin-like modifier proteins (SUMO)-conjugating enzyme UBC9 was manipulated. The interaction between PPARα and SUMO1 was detected by immunoprecipitation assay. HL-60 and THP-1 cell viability, apoptosis and ferroptosis were measured via cell counting kit-8 assay, flow cytometry, BODIPY-C11 staining and/or colorimetric assay. UBC9, glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), recombinant solute carrier family 7, member 11(SLC7A11) and PPARα expressions were analyzed by qRT-PCR or Western blot.
Results:
GW6471 treatment for 24 and 48 h suppressed viability, promoted apoptosis and lipid peroxidation, increased the level of Fe2+, and decreased the expressions of GPX4, SLC7A11 and PPARα in HL-60/THP-1 cells. PPARα antibody induced enrichment of PPARα and SUMO1 in THP-1 cells, which was attenuated after UBC9 silencing. UBC9 silencing resulted in viability decrease, apoptosis and lipid peroxidation promotion, Fe2+ upregulation, and GPX4, SLC7A11 and PPARα downregulation in THP-1 cells, which were all counteracted by pirinixic acid.
Conclusions:
UBC9 silencing-induced PPARα desumoylation induces suppression of AML cell growth by ferroptosis.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.