Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
GASTROENTEROLOGY / CLINICAL RESEARCH
The causal effects of 1400 genetically determined human blood metabolites and metabolite ratios on the risk of gastrointestinal tumors: a Mendelian randomization study
1
Qinghai University Affiliated Hospital (The Clinical Medical School), Qinghai University, Xining, China
2
Gansu Corps Hospital of CAPF, Lanzhou, China
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2025-02-21
Final revision date: 2025-04-29
Acceptance date: 2025-05-04
Online publication date: 2025-06-22
Corresponding author
Ji Di
Qinghai University, Affiliated Hospital (The Clinical Medical School), Qinghai University, Xining, China
Qinghai University, Affiliated Hospital (The Clinical Medical School), Qinghai University, Xining, China
Article (PDF)
Supplementary files
References (64)
The causal effects - Supplementary Table SI.XLSX
The causal effects - Supplementary Table SII.XLSX
The causal effects - Supplementary Table SIII.DOCX
The causal effects - Supplementary Table SIV.XLSX
The causal effects - Supplementary Table SV.DOCX
The causal effects - Supplementary Table SVI.XLSX
The causal effects - Supplementary Table SVII.DOCX
The causal effects - Supplementary Table SVIII.XLSX
The causal effects - Supplementary Table SIX.DOCX
The causal effects - Supplementary Figure S1, S2.doc
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
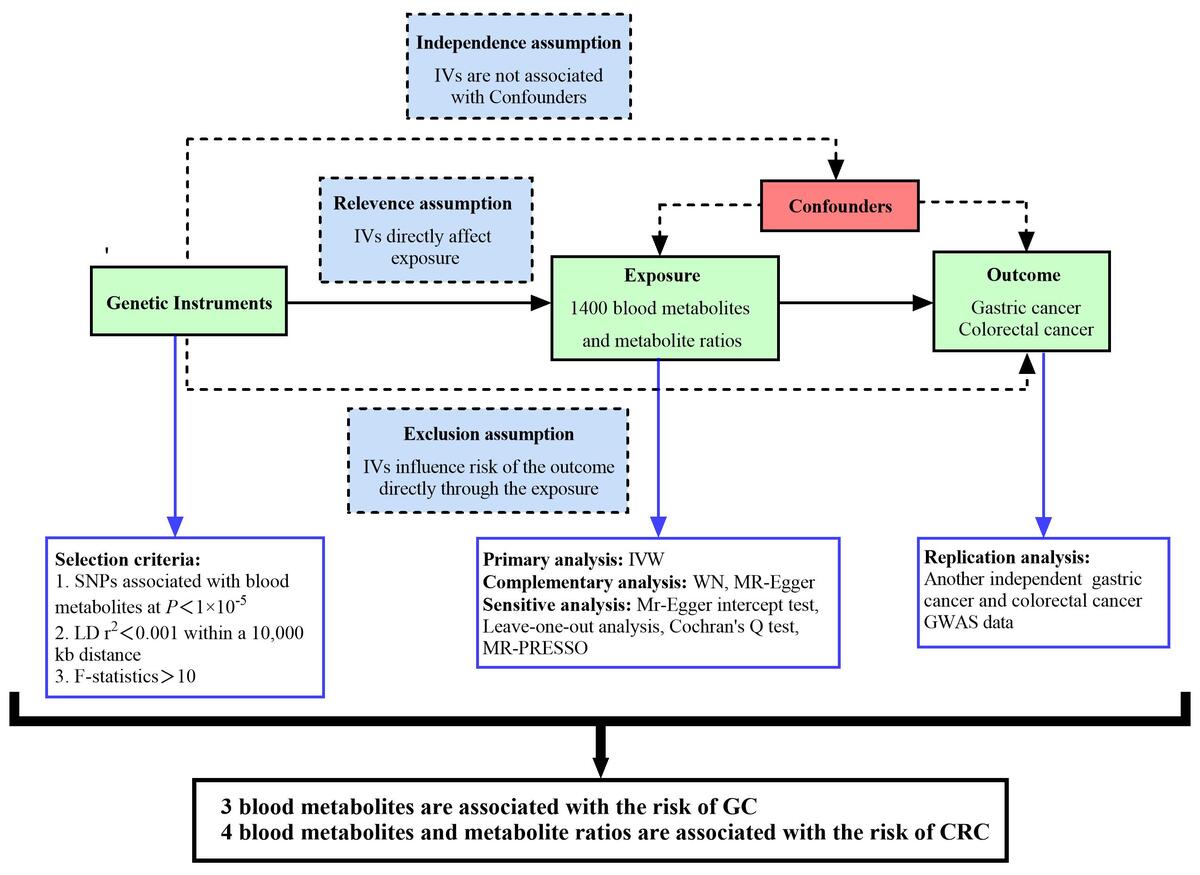
Introduction:
Recently, studies investigating the association between blood metabolites and gastrointestinal tumors have gained increased attention. A Mendelian randomization (MR) study is considered the second most persuasive research method to explore the causal relationship between exposure and outcome after RCT.
Material and methods:
This analysis utilized the inverse variance weighted (IVW) method, the weighted median (WM) method, and MR-Egger regression. Initially, we analyzed GWAS data from the FinnGen database to identify various metabolites and their ratios. Subsequently, we repeatedly analyzed GWAS data from the Open GWAS database to filter out duplicate results.
Results:
5-methyluridine (FinnGen : odds ratio (OR) = 1.16, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.02–1.31, p = 0.03, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 1.08, 95% CI = 1.01–1.17, p = 0.03, FDR-P = 0.04) and 1-dihomo-linolenylglycerol (FinnGen: OR = 1.30, 95% CI = 1.02–1.65, p = 0.03, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 1.16, 95% CI = 1.02–1.31, p = 0.03, FDR-P = 0.04) were positively associated with the risk of gastric cancer (GC). Sphingomyelin (FinnGen: OR = 0.73, 95% CI = 0.54–0.98, p = 0.04, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 0.81, 95% CI = 0.67–0.97, p = 0.02, FDR-P = 0.04) was negatively correlated with GC risk. Carnitine to propionylcarnitine (C3) ratio (FinnGen: OR = 1.11, 95% CI = 1.01–1.22, p = 0.03, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 1.07, 95% CI = 1.01–1.14, p = 0.04, FDR-P = 0.04), arachidonate to linoleate ratio (FinnGen: OR = 1.10, 95% CI = 1.02–1.19, p = 0.02, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 1.12, 95% CI = 1.06–1.18, p = 4.44 × 10–5, FDR-P = 3.55 × 10–4), and androsterone sulfate (FinnGen: OR = 1.07, 95% CI = 1.01–1.14, p = 0.03, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 1.05, 95% CI = 1.01–1.10, p = 0.04, FDR-P = 0.04) were positively associated with the risk of colorectal cancer (CRC). 1-oleoyl-2-docosahexaenoyl-GPC (FinnGen: OR = 0.89, 95% CI = 0.81–0.98, p = 0.02, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 0.93, 95% CI = 0.87–0.99, p = 0.02, FDR-P = 0.04) was negatively correlated with CRC risk.
Conclusions:
Three blood metabolites were found to be associated with the risk of GC; 4 blood metabolites and metabolite ratios were associated with the risk of CRC. These findings may provide valuable guidance for the early clinical diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal tumors.
Recently, studies investigating the association between blood metabolites and gastrointestinal tumors have gained increased attention. A Mendelian randomization (MR) study is considered the second most persuasive research method to explore the causal relationship between exposure and outcome after RCT.
Material and methods:
This analysis utilized the inverse variance weighted (IVW) method, the weighted median (WM) method, and MR-Egger regression. Initially, we analyzed GWAS data from the FinnGen database to identify various metabolites and their ratios. Subsequently, we repeatedly analyzed GWAS data from the Open GWAS database to filter out duplicate results.
Results:
5-methyluridine (FinnGen : odds ratio (OR) = 1.16, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.02–1.31, p = 0.03, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 1.08, 95% CI = 1.01–1.17, p = 0.03, FDR-P = 0.04) and 1-dihomo-linolenylglycerol (FinnGen: OR = 1.30, 95% CI = 1.02–1.65, p = 0.03, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 1.16, 95% CI = 1.02–1.31, p = 0.03, FDR-P = 0.04) were positively associated with the risk of gastric cancer (GC). Sphingomyelin (FinnGen: OR = 0.73, 95% CI = 0.54–0.98, p = 0.04, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 0.81, 95% CI = 0.67–0.97, p = 0.02, FDR-P = 0.04) was negatively correlated with GC risk. Carnitine to propionylcarnitine (C3) ratio (FinnGen: OR = 1.11, 95% CI = 1.01–1.22, p = 0.03, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 1.07, 95% CI = 1.01–1.14, p = 0.04, FDR-P = 0.04), arachidonate to linoleate ratio (FinnGen: OR = 1.10, 95% CI = 1.02–1.19, p = 0.02, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 1.12, 95% CI = 1.06–1.18, p = 4.44 × 10–5, FDR-P = 3.55 × 10–4), and androsterone sulfate (FinnGen: OR = 1.07, 95% CI = 1.01–1.14, p = 0.03, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 1.05, 95% CI = 1.01–1.10, p = 0.04, FDR-P = 0.04) were positively associated with the risk of colorectal cancer (CRC). 1-oleoyl-2-docosahexaenoyl-GPC (FinnGen: OR = 0.89, 95% CI = 0.81–0.98, p = 0.02, FDR-P = 0.04; Open GWAS: OR = 0.93, 95% CI = 0.87–0.99, p = 0.02, FDR-P = 0.04) was negatively correlated with CRC risk.
Conclusions:
Three blood metabolites were found to be associated with the risk of GC; 4 blood metabolites and metabolite ratios were associated with the risk of CRC. These findings may provide valuable guidance for the early clinical diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal tumors.
REFERENCES (64)
1.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, et al. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 2023; 73: 17-48.
2.
Ilic M, Ilic I. Epidemiology of stomach cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28: 1187-203.
3.
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021; 71: 209-49.
5.
Murphy N, Moreno V, Hughes DJ, et al. Lifestyle and dietary environmental factors in colorectal cancer susceptibility. Mol Aspects Med 2019; 69: 2-9.
6.
Hughes LAE, Simons CCJM, van den Brandt PA, et al. Lifestyle, diet, and colorectal cancer risk according to (Epi)genetic instability: current evidence and future directions of molecular pathological epidemiology. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep 2017; 13: 455-69.
7.
Johnson CH, Ivanisevic J, Siuzdak G. Metabolomics: beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2016; 17: 451-9.
8.
Wishart DS. Metabolomics for investigating physiological and pathophysiological processes. Physiol Rev 2019; 99: 1819-75.
9.
Kala P, Hnat T, Padrova K, et al. Eicosanoids in human heart failure: pilot study of plasma epoxyeicosatrienoic and dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid levels. Arch Med Sci 2023; 19: 513-7.
10.
Antonowicz S, Kumar S, Wiggins T, et al. Diagnostic metabolomic blood tests for endoluminal gastrointestinal cancer--a systematic review and assessment of quality. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2016; 25: 6-15.
11.
Song G, Wang L, Tang J, et al. Circulating metabolites as potential biomarkers for the early detection and prognosis surveillance of gastrointestinal cancers. Metabolomics 2023; 19: 36.
12.
Qu R, Zhang Y, Ma Y, et al. Role of the gut microbiota and its metabolites in tumorigenesis or development of colorectal cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2023; 10: e2205563.
13.
Dai D, Yang Y, Yu J, et al. Interactions between gastric microbiota and metabolites in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis 2021; 12: 1104.
14.
Coker OO, Liu C, Wu WKK, et al. Altered gut metabolites and microbiota interactions are implicated in colorectal carcinogenesis and can be non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers. Microbiome 2022; 10: 35.
15.
Zuccolo L, Holmes MV. Commentary: Mendelian randomization-inspired causal inference in the absence of genetic data. Int J Epidemiol 2017; 46: 962-5.
16.
Liang G, Miao D, Du C. Causal associations between blood metabolites and breast cancer. Arch Med Sci 2024; 21: 206-14.
18.
Zheng J, Baird D, Borges MC, et al. Recent developments in mendelian randomization studies. Curr Epidemiol Rep 2017; 4: 330-45.
19.
Thomas DC, Conti DV. Commentary: the concept of ‘Mendelian Randomization’. Int J Epidemiol 2004; 33: 21-5.
20.
Chen Y, Lu T, Pettersson-Kymmer U, et al. Genomic atlas of the plasma metabolome prioritizes metabolites implicated in human diseases. Nat Genet 2023; 55: 44-53.
21.
Sakaue S, Kanai M, Tanigawa Y, et al. A cross-population atlas of genetic associations for 220 human phenotypes. Nat Genet 2021; 53: 1415-24.
22.
Cai J, Li X, Wu S, et al. Assessing the causal association between human blood metabolites and the risk of epilepsy. J Transl Med 2022; 20: 437.
23.
Xiao G, He Q, Liu L, et al. Causality of genetically determined metabolites on anxiety disorders: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. J Transl Med 2022; 20: 475.
24.
Lawlor DA, Harbord RM, Sterne JA, et al. Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat Med 2008; 27: 1133-63.
25.
Hemani G, Zheng J, Elsworth B, et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife 2018; 7: e34408.
26.
Burgess S, Bowden J, Fall T, et al. Sensitivity analyses for robust causal inference from mendelian randomization analyses with multiple genetic variants. Epidemiology 2017; 28: 30-42.
27.
Burgess S, Butterworth A, Thompson SG. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet Epidemiol 2013; 37: 658-65.
28.
Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol 2015; 44: 512-25.
29.
Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Haycock PC, et al. Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol 2016; 40: 304-14.
30.
Gronau QF, Wagenmakers EJ. Limitations of Bayesian leave-one-out cross-validation for model selection. Comput Brain Behav 2019; 2: 1-11.
31.
Yuan S, Kim JH, Xu P, et al. Causal association between celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease: a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol 2023; 13: 1057253.
32.
Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet 2018; 50: 693-8.
33.
Sánchez-López JY, Díaz-Herrera LC, Rizo-de la Torre LDC. Pepsinogen I, pepsinogen II, gastrin-17, and Helicobacter pylori serological biomarkers in the diagnosis of precursor lesions of gastric cancer. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 1016-21.
34.
Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, et al. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2019; 394: 1467-80.
35.
Xing C, Zhihao L, Ji D. Diagnostic value of fecal Fusobacterium nucleatum in colorectal cancer. Arch Med Sci 2023; 19: 1929-33.
36.
Guan WL, He Y, Xu RH. Gastric cancer treatment: recent progress and future perspectives. J Hematol Oncol 2023; 16: 57.
37.
Lu J, Feng Y, Guo K, et al. Association between human blood metabolome and the risk of gastrointestinal tumors. PLoS One 2024; 19: e0304574.
38.
Yun Z, Guo Z, Li X, et al. Genetically predicted 486 blood metabolites in relation to risk of colorectal cancer: a Mendelian randomization study. Cancer Med 2023; 12: 13784-99.
39.
Desrosiers R, Friderici K, Rottman F. Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1974; 71: 3971-5.
40.
Shaon MSH, Karim T, Ali MM, et al. A robust deep learning approach for identification of RNA 5-methyluridine sites. Sci Rep 2024; 14: 25688.
41.
Jonkhout N, Tran J, Smith MA, et al. The RNA modification landscape in human disease. RNA 2017; 23: 1754-69.
42.
Witzenberger M, Burczyk S, Settele D, et al. Human TRMT2A methylates tRNA and contributes to translation fidelity. Nucleic Acids Res 2023; 51: 8691-710.
43.
Cardano M, Tribioli C, Prosperi E. Targeting proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) as an effective strategy to inhibit tumor cell proliferation. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2020; 20: 240-52.
44.
Steeg PS. Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med 2006; 12: 895-904.
45.
Shakor ABA, Taniguchi M, Kitatani K, et al. Sphingomyelin synthase 1-generated sphingomyelin plays an important role in transferrin trafficking and cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 36053-62.
46.
Fhaner CJ, Liu S, Ji H, et al. Comprehensive lipidome profiling of isogenic primary and metastatic colon adenocarcinoma cell lines. Anal Chem 2012; 84: 8917-26.
47.
Wang S, Chen X, Luan H, et al. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging of cell cultures for the lipidomic analysis of potential lipid markers in human breast cancer invasion. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2016; 30: 533-42.
48.
Marien E, Meister M, Muley T, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer is characterized by dramatic changes in phospholipid profiles. Int J Cancer 2015; 137: 1539-48.
49.
Merchant TE, de Graaf PW, Minsky BD, et al. Esophageal cancer phospholipid characterization by 31P NMR. NMR Biomed 1993; 6: 187-93.
50.
Brandán YR, Guaytima EDV, Favale NO, et al. The inhibition of sphingomyelin synthase 1 activity induces collecting duct cells to lose their epithelial phenotype. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2018; 1865: 309-22.
51.
Barceló-Coblijn G, Martin ML, de Almeida RF, et al. Sphingomyelin and sphingomyelin synthase (SMS) in the malignant transformation of glioma cells and in 2-hydroxyoleic acid therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 19569-74.
52.
Van der Luit AH, Budde M, Zerp S, et al. Resistance to alkyl-lysophospholipid-induced apoptosis due to downregulated sphingomyelin synthase 1 expression with consequent sphingomyelin- and cholesterol-deficiency in lipid rafts. Biochem J 2007; 401: 541-9.
53.
Gnoni A, Longo S, Gnoni GV, et al. Carnitine in human muscle bioenergetics: can carnitine supplementation improve physical exercise? Molecules 2020; 25: 182.
54.
Chang B, Nishikawa M, Nishiguchi S, et al. L-carnitine inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis via protection of mitochondria. Int J Cancer 2005; 113: 719-29.
55.
Wang J, Zhou Y, Zhang D, et al. CRIP1 suppresses BBOX1-mediated carnitine metabolism to promote stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma. EMBO J 2022; 41: e110218.
56.
Lee YH, Park S. Genetic and lifestyle-related factors influencing serum hyper-propionylcarnitine concentrations and their association with metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease risk. Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24: 15810.
58.
Wang D, Buchanan FG, Wang H, et al. Prostaglandin E2 enhances intestinal adenoma growth via activation of the Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 1822-9.
59.
Castellone MD, Teramoto H, Williams BO, et al. Prostaglandin E2 promotes colon cancer cell growth through a Gs-axin-beta-catenin signaling axis. Science 2005; 310: 1504-10.
60.
Daniel CR, McCullough ML, Patel RC, et al. Dietary intake of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids and risk of colorectal cancer in a prospective cohort of U.S. men and women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2009; 18: 516-25.
61.
Pot GK, Geelen A, van Heijningen EM, et al. Opposing associations of serum n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids with colorectal adenoma risk: an endoscopy-based case-control study. Int J Cancer 2008; 123: 1974-7.
62.
Karpisheh V, Nikkhoo A, Hojjat-Farsangi M, et al. Prostaglandin E2 as a potent therapeutic target for treatment of colon cancer. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 2019; 144: 106338.
63.
Yu B, Heiss G, Alexander D, et al. Associations between the serum metabolome and all-cause mortality among African Americans in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Am J Epidemiol 2016; 183: 650-6.
64.
Tong X, Cui Y. Mendelian randomization analysis of the causal relationship between serum metabolites and thoracic aortic aneurysm. Medicine (Baltimore) 2024; 103: e39686.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.