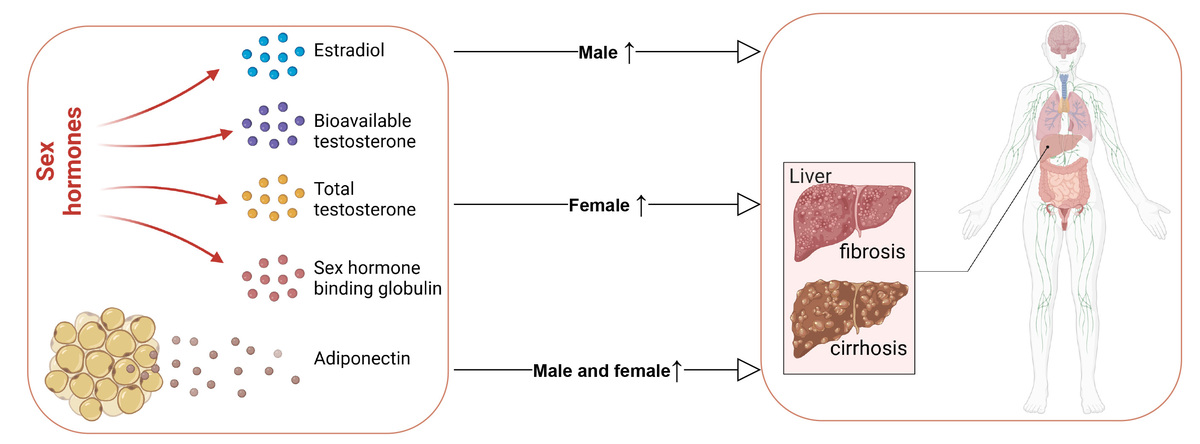
Introduction
Liver fibrosis is a reversible wound-healing response to acute or chronic liver injury, leading to excess deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) components [1]. The progression of liver fibrosis significantly impacts hepatic function and serves as a significant risk factor for the onset of hepatocellular carcinoma [2]. Liver cirrhosis is the advanced stage of liver fibrosis, and the prevalence of cirrhosis was reported to be 0.87% [3]. Liver cirrhosis is presently one of the leading causes of mortality globally, with approximately one million individuals succumbing to the disease annually [4]. In light of the high incidence and mortality rates of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, the identification of relevant biomarkers has the potential to enhance comprehension of disease development and offer therapeutic approaches for patients and healthcare professionals [5].
As diseases significantly related to metabolism, liver fibrosis and cirrhosis may be influenced by a variety of metabolism-related circulating hormones [6]. A review indicated that sex hormones play a crucial role in modulating both hepatic biochemistry and the immune system [7]. Low total testosterone (< 8.3 nmol/l) was significantly associated with the development of major infection in male patients with cirrhosis [8]. However, high sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and low bioactive testosterone [9], and high total testosterone [10] have also been observed to be associated with the progression of liver fibrosis in the male population. Furthermore, the liver functions as a critical target tissue for estrogen signaling, and it is widely recognized that estrogen exerts significant protective effects on hepatocytes [11]. Multiple animal studies have indicated that estrogen was crucial in improving liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, but further clinical research evidence is still lacking. In addition to sex hormones, adipocytokines secreted by adipocytes were deemed to significantly affect liver function [12]. Adipocytokines have been regarded as a potential biomarker for cirrhosis due to their ability to effectively reflect the complex interplay between adipose tissue dysfunction, inflammation, and metabolic disturbances [13]. A previous epidemiological study reported that high levels of adiponectin, one of the most important adipocytokines, was associated with poorer liver function and worse prognosis [14], and adiponectin was also found to be a promising therapeutic candidate for the treatment of liver fibrosis [15]. A systematic review and meta-analysis revealed that levels of adiponectin were elevated in patients with liver cirrhosis, particularly in advanced stages, suggesting its potential utility as a biomarker for advanced cirrhosis [13].
Previous observational studies may have been influenced by unavoidable confounding factors and limited sample size, making it difficult to establish causation [16]. Therefore, the causal association between sex hormones, adiponectin and the risk of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis remains uncertain and requires additional investigation. Mendelian randomization (MR) is an epidemiological method widely used in various clinical research, utilizing single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) as instrumental variables (IVs) to establish the causal relationship between exposure and outcome [16]. In the present study, we investigated the potential causal effects of sex hormones and adiponectin on the risk of fibrosis, cirrhosis, and primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC: a subtype of cirrhosis) by gender, aiming to provide a relevant research basis for elucidating the mechanism of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis and identifying new therapeutic targets [11, 17].
Material and methods
Data design
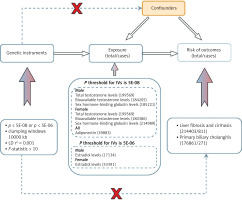
We conducted a two-sample MR study using publicly available data from large-scale genome-wide association studies (GWAS) to investigate the potential causal links between sex hormones (including estradiol, bioavailable testosterone, total testosterone, and SHBG) and adiponectin and the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis. An overview of the study design is depicted in Figure 1. An MR study needs to meet the following three assumptions: (1) the chosen IVs should exhibit a significant association with exposure; (2) the chosen IVs should not be associated with confounding factors between exposure and outcome; (3) the impact of the chosen IVs on the outcome should solely occur through the direct influence on exposure, rather than via alternative pathways [18].
Figure 1
Study design overview. Firstly, the chosen instrumental variables (IVs) should exhibit a significant association with exposure. Secondly, the chosen IVs should not be associated with confounding factors between exposure and outcome. Lastly, the impact of the chosen IVs on the outcome should solely occur through direct influence on exposure, rather than via alternative pathways
GWAS data for liver fibrosis and cirrhosis and primary biliary cirrhosis
As shown in Supplementary Table SI, the GWAS summary data regarding liver fibrosis and cirrhosis were acquired from the FinnGen database in 214,403 European individuals (811 liver fibrosis and cirrhosis cases) https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk/datasets/finn-b-K11_FIBROCHIRLIV/. Similarly, the summary-level data for PBC were available from GWAS of 176,861 individuals (271 PBC cases) https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk/datasets/finn-b-CHIRBIL_PRIM/. All individuals included in the study were of European ancestry.
GWAS data for sex hormones and adiponectin
As shown in Supplementary Table SI, we obtained summary statistics of estradiol levels (n = 171,34), bioavailable testosterone levels (n = 184,205), total testosterone levels (n = 199,569), and SHBG levels (n = 185,221) in males from GWAS using genotype and phenotype data obtained from the UK Biobank. Summary statistics of estradiol levels (n = 53,391), bioavailable testosterone levels (n = 180,386), total testosterone levels (n = 199,569), and SHBG levels (n = 214,989) in females were obtained from GWAS based on individuals of European ancestry. Additionally, the genetic data of adiponectin were derived from one meta-analysis with 39,883 participants. Our study was a secondary analysis of publicly available data, so the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Fourth People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University waived the requirement for ethical approval of this study.
Selection of instrumental variables
Firstly, we detected SNPs exhibiting a significant association with the exposure variable (p < 5 × 10–8). In cases where no appropriate SNPs were identified, we adjusted the threshold for p value to 5 × 10–6 [19]. Then, SNPs exhibiting linkage disequilibrium (LD) (clump: r2 = 0.001, kb = 10000) and palindromic intermediate allele frequencies were excluded [20]. Lastly, the strength of instrumental variables was evaluated using F-statistics. SNPs with F-statistics < 10 were considered as weak instruments and thus removed [21].
Statistical analysis
In this MR study, we used various statistical approaches to evaluate the potential causal associations of sex hormones and adiponectin with the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis. These methods included inverse variance weighted (IVW), MR-Egger, weighted median, simple mode, and weighted mode [16]. IVW was used as the main statistical approach in our MR analysis, out of all the methods employed. We employed the MR-Egger regression and MR-Pleiotropy Residual Sum and Outlier (MR-PRESSO) global test methods to evaluate the potential presence of horizontal pleiotropy in IVs, considering a significance level below p < 0.05 as indicative of its presence [22]. Causal estimates were given as the odds ratio (OR) along with the 95% confidence interval (CI). To assess heterogeneity, we used Cochran’s Q test, considering a significance level of p < 0.05 as indicative of the existence of heterogeneity. Sensitivity analysis was conducted using the leave-one-out method. A significance level of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant [23, 24]. All analyses were performed using the R software with the package “TwoSampleMR” (version 0.6.5), MRInstruments (version 0.3.2), and MR-PRESSO (version 1.0) [25].
Results
Selection of instrumental variables
Following application of the aforementioned inclusion and exclusion criteria, we have identified eligible SNPs for this MR analysis. As presented in Table I, when the outcome was liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, we extracted 11 SNPs associated with estradiol, 148 SNPs with total testosterone, 72 SNPs with bioavailable testosterone, and 186 SNPs with SHBG in males; 16 SNPs with estradiol, 101 SNPs with total testosterone, 118 SNPs with bioavailable testosterone, and 179 SNPs with SHBG in females; and 14 SNPs with adiponectin across all populations. Similarly, when the outcome was PBC, the corresponding SNPs were presented in Table I. In addition, the F-statistic values for these identified SNPs exceed the threshold of 10, indicating the absence of weak IV bias.
Table I
Results of heterogeneity and horizontal pleiotropy tests
Causal effects of sex hormones and adiponectin on fibrosis and cirrhosis and primary biliary cirrhosis
The causal effect estimates of sex hormones and adiponectin on the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis and PBC are displayed in Table II. The IVW analysis revealed a significant relationship between genetically predicted total testosterone levels and the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis (OR = 1.537, 95% CI: 1.082–2.182, p = 0.016) in females. Similar risk estimates were obtained using MR-Egger, weighted median, simple mode, and weighted mode, although the associations did not reach statistical significance (Supplementary Table SII). Based on the results of the MR analysis, there was a significant association between genetically predicted estradiol levels and an increased risk of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis (OR = 2.287, 95% CI: 1.403–3.727, p = 0.001) and PBC (OR = 3.075, 95% CI: 1.306–7.240, p = 0.010) in males (Table II). Other methods exhibited consistent trends (Supplementary Table SII). In addition, we found that genetically predicted adiponectin was causally associated with an increased risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis (OR = 1.608, 95% CI: 1.063–2.430, p = 0.024) and PBC (OR = 2.631, 95% CI: 1.211–5.715, p = 0.015) (Table II). MR-Egger, weighted median, simple mode, and weighted mode consistently yielded similar results (Supplementary Table SII). The IVs did not exhibit heterogeneity according to Cochrane’s Q test (Table I), and there was no significant directional pleiotropy as indicated by the MR-Egger regression intercept and MR-PRESSO global test (Table I).
Table II
Causal effects of genetically predicted sex hormones, adiponectin and the risk of liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and PBC evaluated by the IVW method
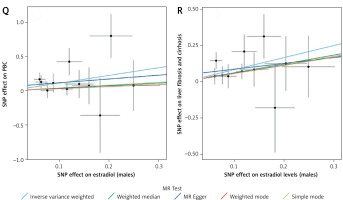
Figure 2 presents scatter plots of the MR analysis regarding the potential causal effect of sex hormones and adiponectin on the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis and PBC, respectively. Supplementary Figures S1–S3 demonstrate that none of the IVW estimates were significantly influenced by individual outlier SNPs based on leave-one-out plots.
Figure 2
Forest plots of the causal relationship between (A) adiponectin and primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC); (B) adiponectin and liver fibrosis and cirrhosis; (C) total testosterone and PBC in females; (D) total testosterone and liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in females; (E) total testosterone and PBC in males; (F) total testosterone and liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in males; (G) bioavailable testosterone and PBC in males; (H) bioavailable testosterone and liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in males; (I) bioavailable testosterone and PBC in females; (J) bioavailable testosterone and liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in females; (K) sex hormone-binding globulin and PBC in females; (L) sex hormone-binding globulin and liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in females; (M) sex hormone-binding globulin and PBC in males; (N) sex hormone-binding globulin and liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in males; (O) estradiol and PBC in females; (P) estradiol and liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in females; (Q) estradiol and PBC in males; (R) estradiol and liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in males
Discussion
This was an MR study using genetic variation to investigate the causality between sex hormones and adiponectin and the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis and PBC. The findings showed a positive causal relationship between total testosterone levels and fibrosis and cirrhosis in females, estradiol levels and liver fibrosis and cirrhosis and PBC in males, as well as adiponectin and fibrosis and cirrhosis and PBC. The consistent findings obtained from various MR methods ensured the reliability of the research outcomes. Our study may help elucidate the role played by sex hormones and adiponectin in susceptibility to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, carrying significant clinical implications for both clinicians and researchers in this field [26, 27].
Testosterone, an endogenous hormone, is primarily synthesized by the testis in males and acts as a precursor to estrogen production in females [28]. A recent MR analysis found that genetically predicted bioavailable testosterone and SHBG in female were linked to PBC [29]. However, our study did not reveal any significant causal associations of female bioavailable testosterone or SHBG with the risk of PBC. The discrepancy may be attributed to the diverse origins of GWAS summary data for PBC. Further exploration was still warranted about the causality between sex hormones and the risk of PBC in females. Previous evidence also pointed to a significant difference in testosterone levels between men and women [30]. In our MR study, we noted that genetically predicted total testosterone levels were associated with increased risk of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in females; however, no significant association was found of male total testosterone levels with liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. A meta-analysis including 10 observational studies found that testosterone may serve as a potential risk factor for pulmonary fibrosis [31]. Wang et al. reported significant differences in total testosterone between women with and without non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), establishing a significant association between total testosterone levels and the extent of hepatic steatosis [32]. Activation of the NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in the liver was found to be increased by testosterone in a mouse model study, thereby inducing an inflammatory response and influencing liver injury [33]. Estradiol is a form of estrogen that exhibits pro-fibrotic effects [34]. This MR analysis indicated that genetically predicted estradiol in male was positively associated with increased risk of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis and PBC. Regarding potential mechanisms, Vaishnav et al. noted that the estradiol level was high in patients with liver cirrhosis [35], which may be involved in alterations in the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis among patients with chronic liver diseases.
In the current study, we found that genetically predicted adiponectin was causally related to the risk of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis and PBC. Previous studies have reported that adiponectin possesses insulin-sensitizing, anti-atherogenic, and anti-inflammatory properties [36, 37]. However, the phenomenon known as the “adiponectin paradox” has also highlighted that adiponectin exhibits pro-inflammatory effects, which have been found to be associated with an elevated risk of heart failure, atrial fibrillation, aortic valve stenosis, and myocardial infarction [38]. A comparative analysis conducted on patients with liver cirrhosis and a control group revealed that the levels of adiponectin were notably elevated in the former, showing a positive correlation with the progression of liver cirrhosis severity [39]. The study conducted by Vachliotis et al. implicated adiponectin in the pathogenesis of NAFLD and its potential involvement in the progression to advanced stages, including NAFLD-associated hepatocellular carcinoma [40]. Our MR analysis aligns with these findings.
This study explores the potential causal association between sex hormones, adiponectin and the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis, as well as PBC, using the two-sample MR method, which helps avoid confounding factors and substantially minimizes reverse causality. The use of different MR statistical methods, such as IVW, MR-Egger, weighted median, simple mode, and weighted mode, makes our results more objective and accurate. However, several limitations need to be considered when interpreting our results. Firstly, the genetic data used in this MR analysis were derived from individuals with European ancestry, and additional investigations are needed to determine the applicability of our findings in various populations and geographical areas. Additionally, we used a relatively lenient SNP screening threshold of p < 5 × 10–6 to select the SNPs when estradiol levels were considered as the exposure, potentially increasing the risk of violating the first assumption of the MR design. However, it should be noted that the F-statistic of each SNP was higher than 10, indicating that weak IVs were not included in the estimation process. Future studies are warranted to better understand the causal relationship between sex hormones, adiponectin and the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis and explore the underlying mechanisms.
In our study, total testosterone levels showed a positive causal association with fibrosis and cirrhosis among females. Moreover, positive causal relationships of estradiol levels with liver fibrosis and cirrhosis and with PBC in males were also observed. Genetically determined adiponectin was positively related to increased risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis and PBC. These findings offer new perspectives and guidelines on the management and prevention strategies for patients with liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.