Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
OTOLARYNGOLOGY / STATE OF THE ART PAPER
Obstructive Sleep Apnea and selected comorbidities- literature review of cohort studies
1
Department of Otolaryngology, Doctoral School of the Medical University of Bialystok, Medical University of Bialystok, Poland
2
Department of Cardiology and Internal Medicine with Cardiac Intensive Care Unit, Doctoral School of the Medical University of Bialystok, Medical University of Bialystok, Poland
3
Department of Otolaryngology, Medical University of Bialystok, Poland
4
Department of Otolaryngology, Sleep Apnea Surgery Center, Medical University of Bialystok, Poland
Submission date: 2025-06-04
Final revision date: 2025-11-06
Acceptance date: 2025-12-02
Online publication date: 2026-02-15
Corresponding author
Urszula Karaszewska
Department of Otolaryngology, Doctoral School of the Medical University of Bialystok, Medical University of Bialystok, 15-089, Bialystok, Poland
Department of Otolaryngology, Doctoral School of the Medical University of Bialystok, Medical University of Bialystok, 15-089, Bialystok, Poland
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
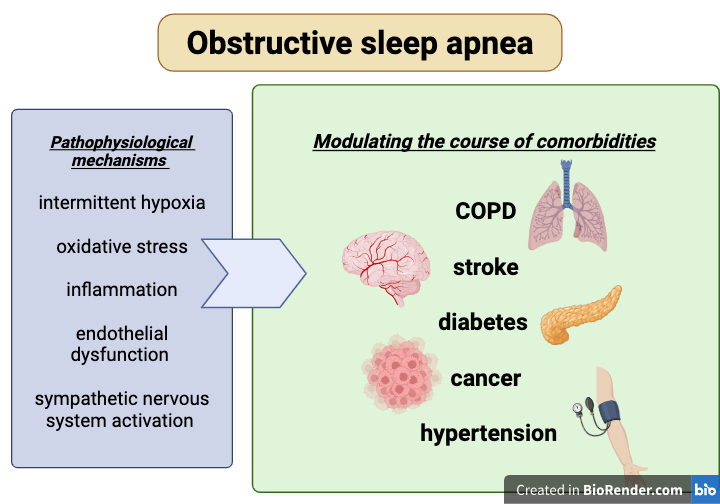
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common type of sleep-related breathing disorder, characterized by repeated episodes of upper airway collapse and resulting hypoxia during sleep. Intermittent hypoxemia may exert a multisystemic impact and modulate the course of comorbidities. Pathophysiological mechanisms such as oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction contribute to adverse health outcomes, including cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular complications, metabolic disorders, cancer, neurodegenerative conditions, or behavioral abnormalities. Treatment of OSA may mitigate the progression of comorbidities and reduce the associated social and economic burden. This literature review aims to explore the relationships between OSA and selected co-morbid diseases, including COPD , stroke, diabetes, cancer and hypertension, utilizing the cohort studies in the literature.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.