Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
NEPHROLOGY / CLINICAL RESEARCH
M1 macrophage exosomes induce ferroptosis via MiR-582-5p-mediated ZBTB10 suppression in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury
1
Department of Emergency, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
Submission date: 2024-11-29
Final revision date: 2025-03-21
Acceptance date: 2025-05-08
Online publication date: 2025-06-22
Corresponding author
Ying Deng
Department of Emergency the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University 246 Xuefu Road Nangang District Harbin 150086, China
Department of Emergency the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University 246 Xuefu Road Nangang District Harbin 150086, China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury (S-AKI) poses a significant clinical challenge, necessitating effective therapeutic strategies. This study investigated the influence of M1-polarized macrophage-derived exosomes on the proliferation and ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells (HK2).
Material and methods:
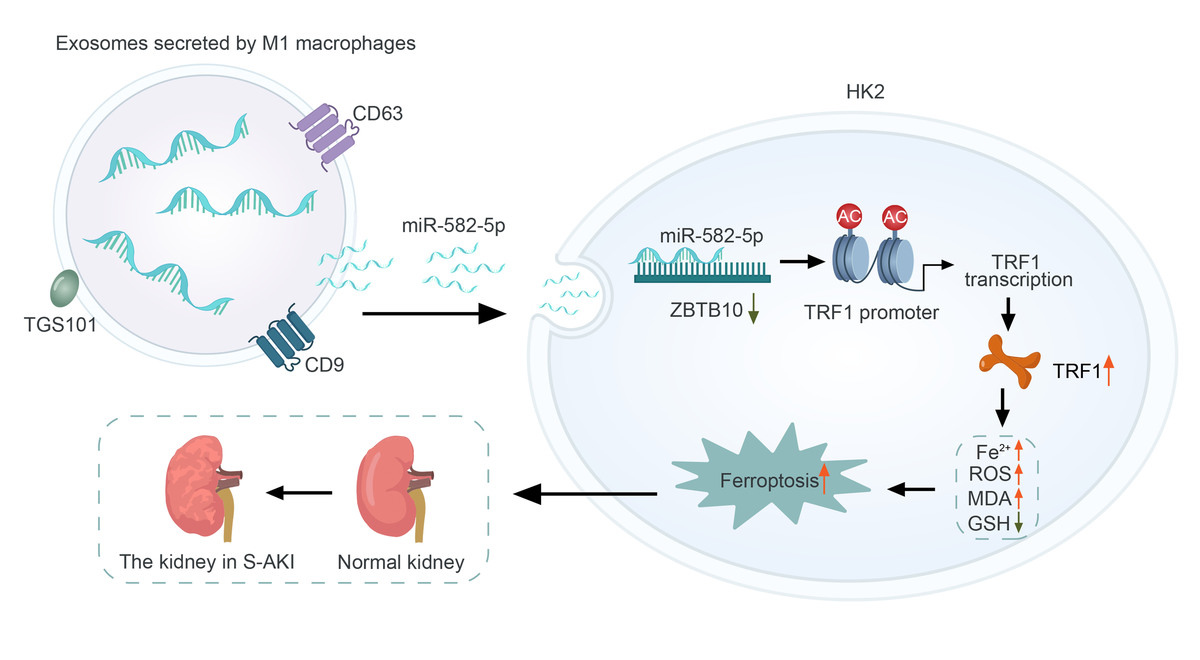
We polarized THP-1 and RAW264.7 cells to the M1 phenotype and validated their polarization through reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Exosomes isolated from these macrophages were applied to treat HK2 cells, resulting in a significant reduction in cell proliferation, as demonstrated by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and 5-ethynyl-2deoxyuridine (EdU) assays. Furthermore, increased malondialdehyde (MDA) and Fe2+ levels, decreased glutathione (GSH) levels, and altered mitochondrial morphology indicated enhanced ferroptosis. RT-qPCR and Western blot analyses showed upregulation of the ferroptosis-promoting gene TFR1, while other related genes remained unaffected.
Results:
We identified miR-582-5p as a key exosomal miRNA significantly upregulated in HK2 cells following treatment with M1-polarized macrophage exosomes. Overexpression of miR-582-5p in HK2 cells mirrored the exosomal effects, inhibiting proliferation and promoting ferroptosis. Mechanistic studies revealed that miR-582-5p binds to the 3 untranslated region (UTR) of ZBTB10, suppressing its expression. This suppression led to increased H3K27ac modification of the TFR1 promoter, enhancing TFR1 transcription and ferroptosis.
Conclusions:
These findings uncover a novel pathway by which M1 macrophage exosomes deliver miR-582-5p to induce ferroptosis in HK2 cells, highlighting potential therapeutic targets for S-AKI.
Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury (S-AKI) poses a significant clinical challenge, necessitating effective therapeutic strategies. This study investigated the influence of M1-polarized macrophage-derived exosomes on the proliferation and ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells (HK2).
Material and methods:
We polarized THP-1 and RAW264.7 cells to the M1 phenotype and validated their polarization through reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Exosomes isolated from these macrophages were applied to treat HK2 cells, resulting in a significant reduction in cell proliferation, as demonstrated by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and 5-ethynyl-2deoxyuridine (EdU) assays. Furthermore, increased malondialdehyde (MDA) and Fe2+ levels, decreased glutathione (GSH) levels, and altered mitochondrial morphology indicated enhanced ferroptosis. RT-qPCR and Western blot analyses showed upregulation of the ferroptosis-promoting gene TFR1, while other related genes remained unaffected.
Results:
We identified miR-582-5p as a key exosomal miRNA significantly upregulated in HK2 cells following treatment with M1-polarized macrophage exosomes. Overexpression of miR-582-5p in HK2 cells mirrored the exosomal effects, inhibiting proliferation and promoting ferroptosis. Mechanistic studies revealed that miR-582-5p binds to the 3 untranslated region (UTR) of ZBTB10, suppressing its expression. This suppression led to increased H3K27ac modification of the TFR1 promoter, enhancing TFR1 transcription and ferroptosis.
Conclusions:
These findings uncover a novel pathway by which M1 macrophage exosomes deliver miR-582-5p to induce ferroptosis in HK2 cells, highlighting potential therapeutic targets for S-AKI.
REFERENCES (26)
1.
Lin YH, Platt MP, Fu H, et al. Global proteome and phosphoproteome characterization of sepsis-induced kidney injury. Mol Cell Proteomics 2020; 19: 2030-47.
2.
Wang Y, Xi W, Zhang X, et al. CTSB promotes sepsis-induced acute kidney injury through activating mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Front Immunol 2022; 13: 1053754.
3.
Poudel N, Zheng S, Schinderle CM, et al. Peritubular capillary oxygen consumption in sepsis-induced AKI: multi-parametric photoacoustic microscopy. Nephron 2020; 144: 621-5.
4.
He FF, Wang YM, Chen YY, et al. Sepsis-induced AKI: from pathogenesis to therapeutic approaches. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 981578.
5.
Zan H, Liu J, Yang M, et al. Melittin alleviates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by promoting GPX4 expression to inhibit ferroptosis. Redox Rep 2024; 29: 2290864.
6.
Zhang L, Rao J, Liu X, et al. Attenuation of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by exogenous H(2)S via inhibition of ferroptosis. Molecules 2023; 28: 4770.
7.
Ross EA, Devitt A, Johnson JR. Macrophages: the good, the bad, and the gluttony. Front Immunol 2021; 12: 708186.
8.
Krylova SV, Feng D. The machinery of exosomes: biogenesis, release, and uptake. Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24: 1337.
9.
Isaac R, Reis FCG, Ying W, et al. Exosomes as mediators of intercellular crosstalk in metabolism. Cell Metabolism 2021; 33: 1744-62.
10.
Wang C, Li Z, Liu Y, et al. Exosomes in atherosclerosis: performers, bystanders, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets. Theranostics 2021; 11: 3996-4010.
11.
Zhao G, Lyu J, Huang X, et al. The role and underlying mechanism of dental pulp stem cell-derived exosomal miR-31 in the treatment of osteoarthritis by targeting mTOR to enhance chondrocyte autophagy levels. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 1680-94.
12.
Ilieva M, Panella R, Uchida S. MicroRNAs in cancer and cardiovascular disease. Cells 2022; 11: 3551.
13.
Li M, Li J, Ye C, et al. miR-200a-3p predicts prognosis and inhibits bladder cancer cell proliferation by targeting STAT4. Arch Med Sci 2023; 19: 724-35.
14.
Rojas-Pirela M, Andrade-Alviárez D, Medina L, et al. MicroRNAs: master regulators in host-parasitic protist interactions. Open Biol 2022; 12: 210395.
15.
Jiang S, Yan J, Chen X, et al. Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits thyroid cancer cell migration and proliferation via activation of miR-524-5p. Arch Med Sci 2022; 18: 164-70.
16.
Fuhrmann DC, Brüne B. A graphical journey through iron metabolism, microRNAs, and hypoxia in ferroptosis. Redox Biol 2022; 54: 102365.
17.
Tian Y, Guan Y, Su Y, et al. MiR-582-5p inhibits bladder cancer-genesis by suppressing TTK expression. Cancer Manag Res 2020; 12: 11933-44.
18.
Mei J, Zhang Y, Lu S, et al. Long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 regulates proliferation, apoptosis, inflammation and airway remodeling of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease via targeting miR-582-5p/FBXO11 axis. Biomed Pharmacother 2020; 129: 110326.
19.
Fang X, Ardehali H, Min J, et al. The molecular and metabolic landscape of iron and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 2023; 20: 7-23.
20.
Li L, Huang L, Huang C, et al. The multiomics landscape of serum exosomes during the development of sepsis J Adv Res 2022; 39: 203-23.
21.
Wen YC, Chen WY, Tram VTN, et al. Pyruvate kinase L/R links metabolism dysfunction to neuroendocrine differentiation of prostate cancer by ZBTB10 deficiency. Cell Death Dis 2022; 13: 252.
22.
Tang Y, Yang LJ, Liu H, et al. Exosomal miR-27b-3p secreted by visceral adipocytes contributes to endothelial inflammation and atherogenesis. Cell Rep 2023; 42: 111948.
23.
Gao M, Yu T, Liu D, et al. Sepsis plasma-derived exosomal miR-1-3p induces endothelial cell dysfunction by targeting SERP1. Clin Sci 2021; 135: 347-65.
24.
Yin X, Wang X, Wang S, et al. Screening for regulatory network of miRNA-inflammation, oxidative stress and prognosis-related mRNA in acute myocardial infarction: an in silico and validation study. Int J General Med 2022; 15: 1715-31.
25.
Akhter N, Kochumon S, Hasan A, et al. IFN- and LPS induce synergistic expression of CCL2 in monocytic cells via H3K27 acetylation. J Inflam Res 2022; 15: 4291-302.
26.
Fang Y, Tang Y, Zhang Y, et al. The H3K36me2 methyltransferase NSD1 modulates H3K27ac at active enhancers to safeguard gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 2021; 49: 6281-95.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.